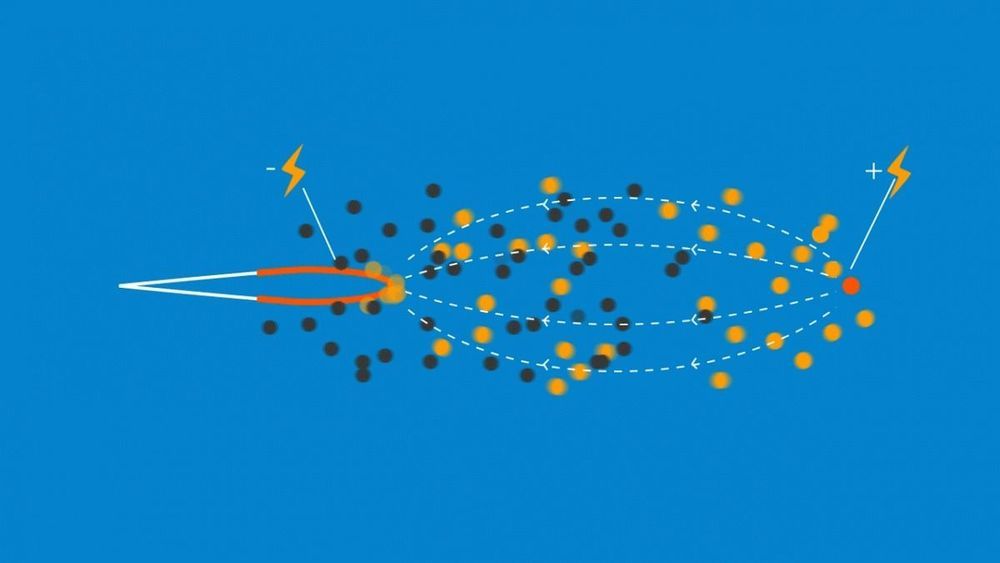
The turbineless design uses electroaerodynamic propulsion to fly and could herald the arrival of quieter, lower-emission aircraft.


It’s a fascinating competition that paints an incredibly detailed picture of what the future of Moon or even Mars exploration could look like one day — and we’ve never been closer to that future.
READ MORE: Top Three Teams Share $100,000 Prize in Complete Virtual Construction Level of 3D-Printed Habitat Challenge [NASA]
More on the Challenge: Here Are The Finalists For NASA’s Mars Habitat Design Competition.

The city of the future is a symbol of progress. The sci-fi vision of the future city with sleek skyscrapers and flying cars, however, has given way to a more plausible, human, practical, and green vision of tomorrow’s smart city. Whilst smart city visions differ, at their heart is the notion that in the coming decades, the planet’s most heavily concentrated populations will occupy city environments where a digital blanket of sensors, devices and cloud connected data is being weaved together to build and enhance the city living experience for all. In this context, smart architecture must encompass all the key elements of what enable city ecosystems to function effectively. This encompasses everything from the design of infrastructure, workspaces, leisure, retail, and domestic homes to traffic control, environmental protection, and the management of energy, sanitation, healthcare, security, and a building’s eco-footprint.
The world’s premier cities and architects are competing to design and build highly interconnected smart environments where people, government and business operate in symbiosis with spectacular exponentially improving technologies such as big data, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, hyperconnectivity, artificial intelligence (AI), robots, drones, autonomous green vehicles, 3D/4D printing, smart materials, and renewable energy. The architectural promise of future smart cities is to harmonize the benefits of these key disruptive technologies for society and provide a high quality of life by design. Some have already implemented smart city architecture and, as the concepts, experiences and success stories spread, the pursuit of smart will become a key driver in the evolving future of cities as communities and economic centres. Here we explore some of the critical trends, visions, ideas, and disruptions shaping the rise of smart cities and smart architecture.
Smart Cities – Purpose, Engagement and Vision

Livingston is sitting comfortably in his office in Portland, Oregon, when he appears on the screens inside the car and announces he’ll be our teleoperator this afternoon. A moment later, the MKZ pulls into traffic, responding not to the man in the driver’s seat, but to Livingston, who’s sitting in front of a bank of screens displaying feeds from the four cameras on the car’s roof, working the kind of steering wheel and pedals serious players use for games like Forza Motorsport. Livingston is a software engineer for Designated Driver, a new company that’s getting into teleoperations, the official name for remotely controlling self- driving vehicles.
Designated Driver is just the latest competitor to enter the market for the teleoperation tech that will make robo-cars work.

Dr. Been Kim wants to rip open the black box of deep learning.
A senior researcher at Google Brain, Kim specializes in a sort of AI psychology. Like cognitive psychologists before her, she develops various ways to probe the alien minds of artificial neural networks (ANNs), digging into their gory details to better understand the models and their responses to inputs.
The more interpretable ANNs are, the reasoning goes, the easier it is to reveal potential flaws in their reasoning. And if we understand when or why our systems choke, we’ll know when not to use them—a foundation for building responsible AI.
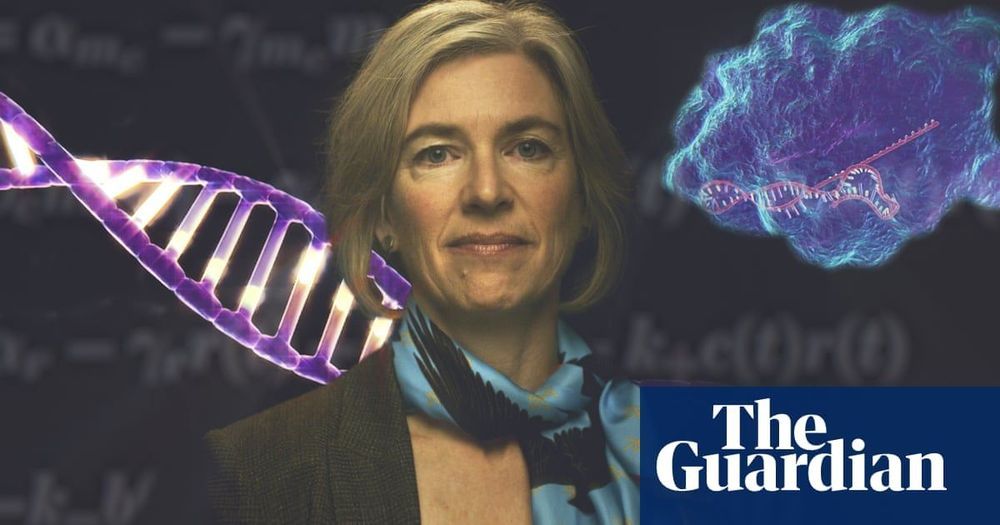

Prof Jennifer Doudna, one the pioneers of Crispr-Cas9 gene editing, explains how this revolutionary discovery enables precise changes to our DNA, which can be used to correct mutations that cause genetic diseases and eradicate them from a germ line. Doudna raises the key issues of debate around gene editing and suggests what will have the most immediate impact.
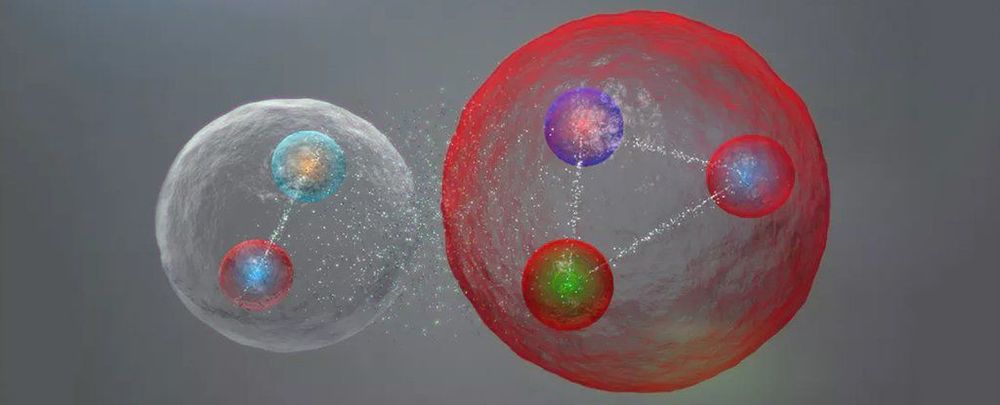
Everything you see around you is made up of elementary particles called quarks and leptons, which can combine to form bigger particles such as protons or atoms.
But that doesn’t make them boring – these subatomic particles can also combine in exotic ways we’ve never spotted.
Now CERN’s LHCb collaboration has announced the discovery of a clutch of new particles dubbed “pentaquarks”. The results can help unveil many mysteries of the theory of quarks, a key part of the standard model of particle physics.

You might think we’re not in Texas anymore but in some strange episode of Black Mirror, the Netflix series, says Nikos Acuna who is moderating this SXSW panel on transhumanism.
In fact you’d be forgiven if you did as there is talk about cryo-preserving the body after being declared dead, in the hopes you can be resurrected when the science is here to safely defrost your body and cure you of your ailments. There is also talk on mind uploading, and replacing parts of our brains with neural prosthetics. This all sounds like science-fiction but these days the stuff of science fiction has become fact.
Transhumanist technologies are about overcoming the limitations of human biology and Dr Max More and Dr Randal Koene are at the forefront of these technologies.
The Singularity is Near.
The first 500 people to click this link get 2 months of Skillshare for free: http://skl.sh/justwrite5
Support the channel here: https://www.patreon.com/justwrite
For fifteen years, I’ve assumed that the Matrix Sequels were irredeemable failures. But looking back on them with fresh eyes reveals a pair of films that are exhilarating, interesting, and sometimes hilarious. In this video I try to make sense of these two movies, and what they have to say about free will and the systems that control society.
Join the community!
Website ▶ https://www.justwritemedia.com
Twitter ▶ https://www.twitter.com/SageHyden
Facebook ▶ http://ow.ly/6u9Z30iyp8J
Works Cited: