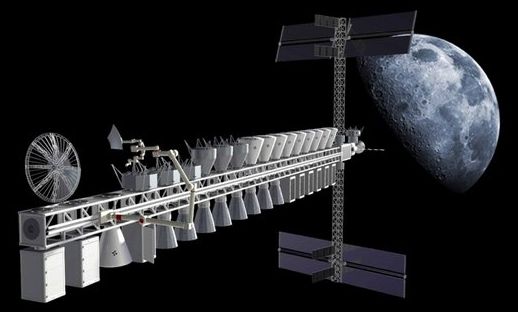
More than four years ago, I covered the issue of cislunar planning here (see “The cislunar gateway with no gate”, The Space Review, October 1, 2012). Now the same “gateless” base concept has returned, but this time, it is not the only concept on the table. Currently there seem to be a plethora of achievable cislunar and lunar concepts, but few people seem to understand what makes any of them practical and affordable. Multiple reusable launchers, in-space vehicles, and components are being developed or have recently been announced, including the New Glenn, the Blue Moon lunar lander, SpaceX’s gigantic Interplanetary Transport System with its still unnamed booster. In addition, there are various lunar orbit combination habitats and depots proposed by Bigelow and the previously announced vehicles and concepts such as the Falcon Heavy, the XEUS lander, and the Cryote depot concept.
Operational plans that only include cislunar bases are being proposed, as well as plans which call for only lunar surface bases to be supplied directly from the Earth, in addition to the more modern, cislunar resource-supported lunar base scenarios. These plans and designs are all like pieces of a very important jigsaw puzzle, but one that, due to the current circumstances, forces us to start with the individual pieces, instead of a whole original image. Our mission, if we can manage it (politically, fiscally and technically), is to try to create a functional whole—a cislunar transportation system —out of some or most of these pieces.
As the obvious and practical location for a gateway to the Moon, Mars, and the asteroids, a cislunar logistics base is the first component we need in place. I am not as concerned about which orbit any cislunar station is placed in compared to the base components, but it is still clear that the Earth Moon L1 point has an advantage since it is always in the same general area, and can be reached from any location on the moon in about 12 hours at any time without waiting for an orbital position to match. A station placed in the “near-rectilinear (lunar) halo orbit” (NRHO) proposed recently would actually be in a high, elliptical, lunar polar orbit (HELPO) that takes more propellant and time to reach from or to than most other options. The best orbits to support lunar operations have a short and relatively unchanging transit time from or to the lunar surface, a lower delta-V per trip, and which can be reached from most places on the surface at almost any time.