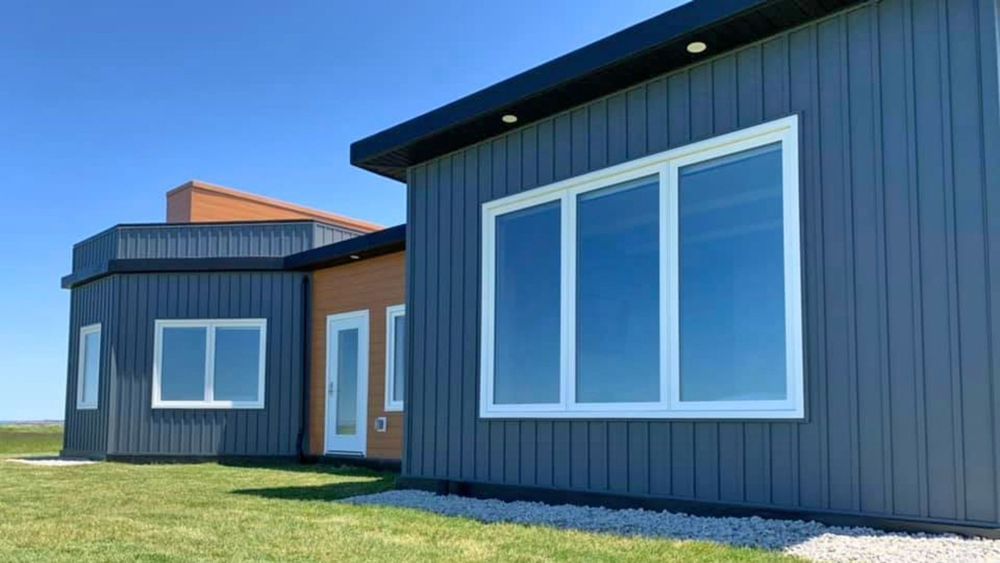
If you’re looking to build a new home on coastal waters where hurricanes are known to roam, you might want to skip the two-by-fours and cement and instead start drinking bottled soda. A Canadian company has recently completed construction of a home with exterior walls made from recycled plastic, and it’s claimed to be able to withstand winds gusting at over 300 miles per hour.
Built by JD Composites, the three bedroom home is situated near the Meteghan River in Nova Scotia. Aside from a distinct lack of trees, gardens, and neighbors, the house looks like any other dwelling with a clean modern design and a minimalist facade. Inside it’s fully furnished and finished with drywall covered lumber walls, but the exterior is what makes the house appealing as a new, and seemingly much improved, approach to construction.

 Last year, Pentagon mad science arm DARPA was working on one of its wildest projects yet: a microchip-sized nuclear reactor. The program is now officially done, the agency says. But these sorts of far-out projects have a habit of being reemerging under new managers and new names.
Last year, Pentagon mad science arm DARPA was working on one of its wildest projects yet: a microchip-sized nuclear reactor. The program is now officially done, the agency says. But these sorts of far-out projects have a habit of being reemerging under new managers and new names.