Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
What If We Sent Our Trash Into the Sun?
Is this the solution to stop humans from trashing the planet?
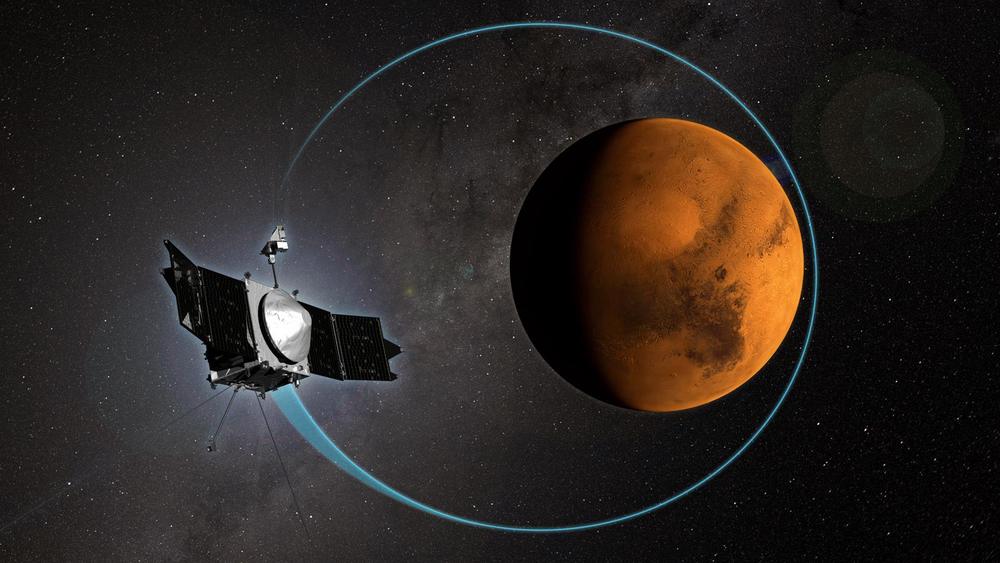

MAVEN has been in orbit at Mars for 5 years
After a 10-month journey from Earth, the MAVEN spacecraft entered Mars orbit on September 21, 2014. The mission originally planned to gather data for one-Earth-year continues to provide unique insight into the history of #Mars ’ atmosphere and climate, liquid water, and planetary habitability.
It is a tremendous credit to the entire MAVEN team that the instruments and spacecraft continue to operate well and that the science continues to provide exciting results related to the #Martian upper atmosphere, ionosphere, and interactions with the Sun and solar wind.


Bullying And The Shaping of The Adolescent Brain
There has been a continuously increasing volume of data which has demonstrated that victimization, the clinical term for bullying, affects hundreds of millions of children and adolescents which can sometimes last for years and even decades. This is seen as a global health challenge by the World Health Organization and the United Nations. However, researchers maintain there is still a limited understanding of how this act can affect the developing brain physically.
Most of the research into the neurobiological processes that might contribute to these negative health outcomes has occurred in the past decade, much of it focused on bullying’s impact on the body’s stress response system. A paper published last December in the journal Molecular Psychiatry sheds some light on a different area: brain architecture. The trauma stemming from chronic bullying can affect the structure of the brain, according to longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data collected by an international team based at King’s College London. The findings echo previous research, which has demonstrated similar changes in children and adults who experienced what’s known as “child maltreatment” — neglect or abuse by adult caregivers.
Long-term changes to the brain’s structure and chemistry are an indicator “of how sinister bullying is” says Tracy Vaillancourt, a developmental psychologist at the University of Ottawa. Along with others in the field, she is hopeful that studies like the one from King’s College will be a catalyst for further research which could ultimately be used to inform policy decisions and support anti-bullying interventions.
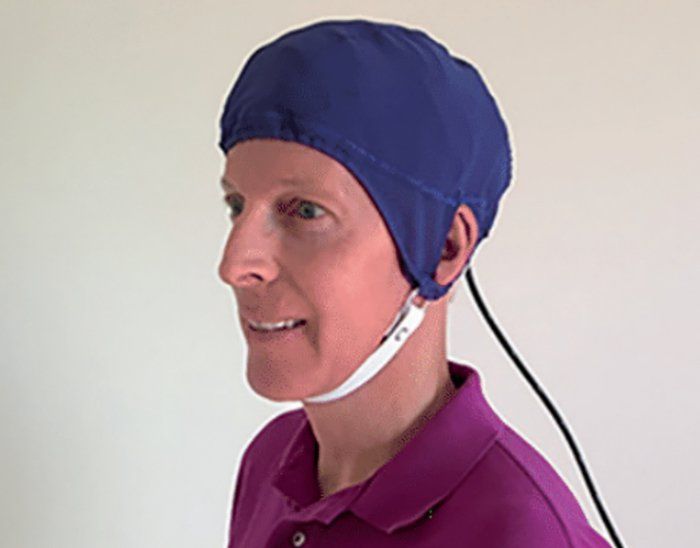
Small Trial Reverses a Year of Alzheimer’s Cognitive Decline in Just Two Months
In the ongoing efforts to control and treat Alzheimer’s, one of the more promising avenues of research is using electromagnetic waves to reverse memory loss – and a small study using this approach has reported some encouraging results.
Scientists get closer to a cure for the common cold
Despite the common cold being so — well — common, researchers have never succeeded in the long dream of curing or immunizing against the array of rhinoviruses that generally cause it. Though the common cold generally does not kill those who are not infirm or immunocompromised, it costs billions in lost time and energy. Now, new research hints that science might be closing in on the cold.
In a study to be published in Nature Microbiology, researchers at Stanford University and University of California, San Francisco say that the cure to the common cold could be the result of disabling one single host protein.
Advertisement:

Ghost post! Google creates world’s most powerful computer, NASA ‘accidentally reveals’ …and then publication vanishes
Google’s new quantum computer reportedly spends mere minutes on the tasks the world’s top supercomputers would need several millennia to perform. The media found out about this after NASA “accidentally” shared the firm’s research.
The software engineers at Google have built the world’s most powerful computer, the Financial Times and Fortune magazine reported on Friday, citing the company’s now-removed research paper. The paper is said to have been posted on a website hosted by NASA, which partners with Google, but later quietly taken down, without explanation.
Google and NASA have refused to comment on the matter. A source within the IT giant, however, told Fortune that NASA had “accidentally” published the paper before its team could verify its findings.
Viewpoint: Cold Atoms Bear a Quantum Scar
Theorists attribute the unexpectedly slow thermalization of cold atoms seen in recent experiments to an effect called quantum many-body scarring.
×
Researchers still have some way to go before they can assemble enough quantum bits (qubits) to make a practical, large-scale quantum computer. But already the best prototypes, made up of several tens of qubits, are opening our eyes to new behavior in the quantum realm. Last year, a team from Harvard University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) unveiled a quantum “simulator” made up of a row of 51 interacting atoms [1]. Exciting the individual atoms in various patterns (Fig. 1), they discovered something unexpected: atoms in certain patterns took at least 10 times longer to relax towards thermal equilibrium than atoms in other patterns. Four groups of theorists have tried to make sense of this observation [2–6], in all cases attributing the slow thermalization to a never-before-seen effect called quantum many-body scarring.

Venus takes center stage in October 2020 observation campaign
Next October, Venus will be the focus of an international campaign of coordinated observations involving two space agencies, three missions and multiple ground-based telescopes and planetary scientists around the world. The collaboration aims to shed new light on the thick and complex atmosphere of Venus. Plans for the campaign and a call for astronomers to participate have been announced today by Dr. Yeon Joo Lee of TU Berlin and Dr. Valeria Mangano of INAF-IAPS at the EPSC-DPS Joint Meeting in Geneva.
On 15th October 2020, the ESA-JAXA BepiColombo spacecraft will pass close to Venus in the first of two flybys of the planet during the mission’s long journey to Mercury. The encounter will provide an unmissable opportunity to cross-check the accuracy of BepiColombo’s instrumentation with that of JAXA’s Venus orbiter, Akatsuki, and for the two missions to work together with Earth-based observers to study Venus’s atmosphere from multiple viewpoints and at different scales.
The BepiColombo mission was successfully launched on October 20th 2018, at 01:45 UTC. It consists of two scientific orbiters, ESA’s Mercury Planetary Orbiter (MPO) and JAXA’s Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter (MMO, renamed at launch Mio’), which are designed to explore Mercury and its environment. The mission will go into orbit around Mercury in December 2025. BepiColombo will use encounters with Venus in October 2020 and August 2021 to help it spiral onto an orbital path where it can catch up with fast-moving Mercury, which whizzes round the Sun every 88 days.