Scientists and religious leaders joined forces to create programs on neuroscience, cosmology—and even some evolutionary science.
LOL Photo 2
Posted in futurism
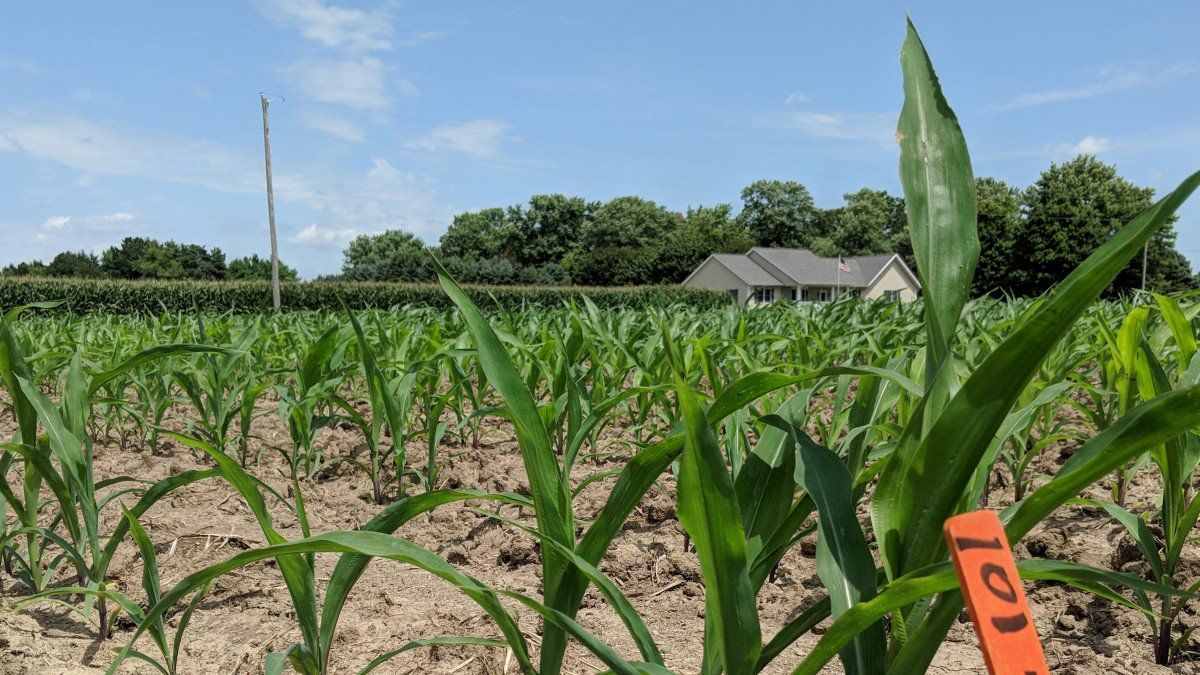
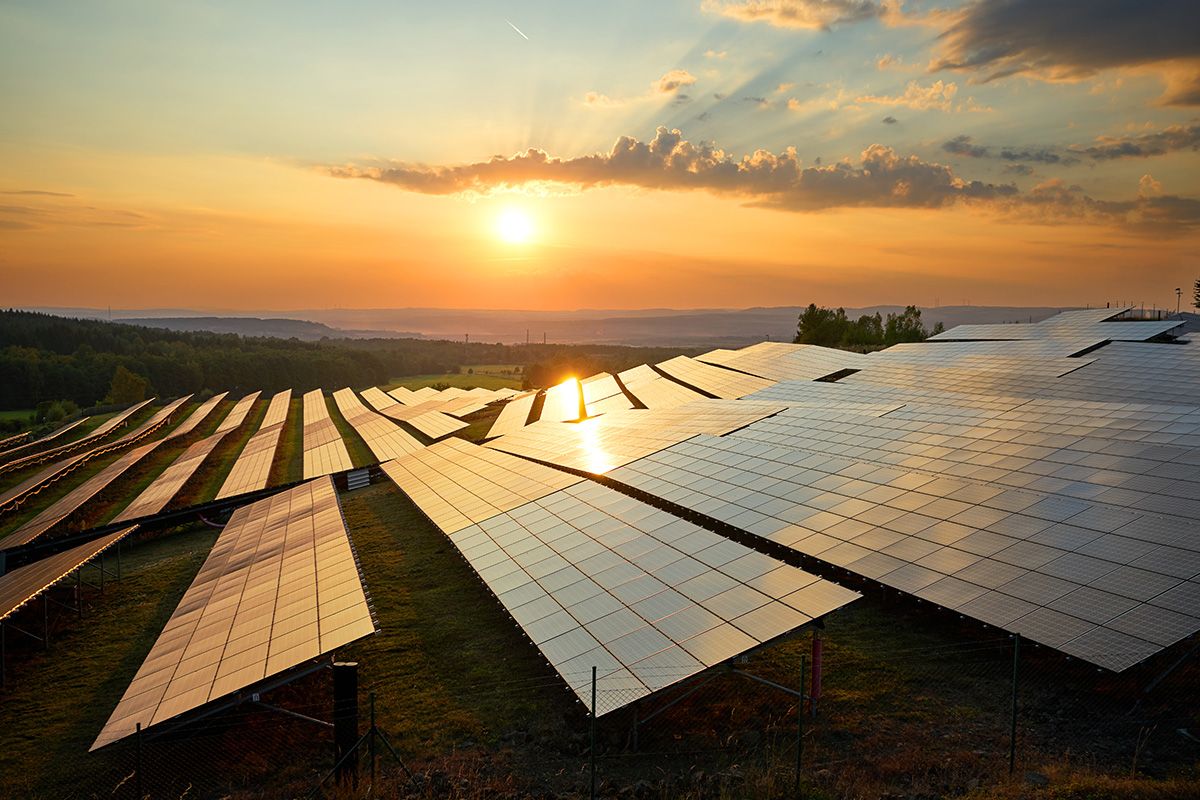
Pivot Bio just got a $70 million infusion from Bill Gates’s energy fund and other investors to launch its commercial product next year.
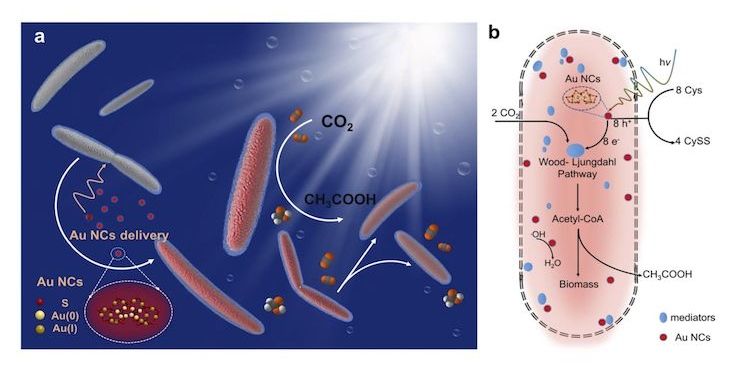
The science: The biotechnology company, based in Berkeley, California, is creating probiotics for plants. The firm’s researchers have identified microbes with a dormant ability to produce nitrogen, a crucial nutrient in synthetic fertilizer, and engineered them to reawaken and enhance it. For its initial product, Pivot Bio has created a liquid treatment for corn crops that can be applied when the seeds are planted.
The sell: In early field tests, patches treated with the microbes produce comparable yields to those relying on synthetic fertilizers. Pivot Bio’s pitch to farmers is that the product reduces work and complexity, because a single application takes less time than spraying multiple rounds of fertilizer.
A new discovery might make immunotherapy applicable to more patients.
Led by Dr. Alicja Copik, scientists at the University of Central Florida College of Medicine have discovered that it might be possible to make cancer immunotherapy work for a larger portion of patients by employing PM21-activated natural killer (PM21-NK) cells [1].
Study abstract
Anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 therapies have shown success in cancer treatment but responses are limited to ~ 15% of patients with lymphocyte infiltrated, PD-L1 positive tumors. Hence, strategies that increase PD-L1 expression and tumor infiltration should make more patients eligible for PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy, thus improving overall outcomes. PD-L1 expression on tumors is induced by IFNγ, a cytokine secreted by NK cells. Therefore, we tested if PM21-particle expanded NK cells (PM21-NK cells) induced expression of PD-L1 on tumors and if anti-PD-L1 treatment enhanced NK cell anti-tumor efficacy in an ovarian cancer model. Studies here showed that PM21-NK cells secrete high amounts of IFNγ and that adoptively transferred PM21-NK cells induce PD-L1 expression on SKOV-3 cells in vivo. The induction of PD-L1 expression on SKOV-3 cells coincided with the presence of regulatory T cells (Tregs) in the abdominal cavity and within tumors.
Today, we have another video from our Ending Age-Related Diseases 2018 conference, which was held earlier this year at the Cooper Union in New York City. The conference was designed to bring the worlds of research and investment together in one place and explore the progress and challenges that the industry faces in developing and funding therapies to end age-related disease.
This was the second panel during the conference and featured Dr. Aubrey de Grey of the SENS Research Foundation, Keith Comito of Lifespan.io, Dr. James Peyer of Apollo Ventures, Dr. Mark Hammond of Deep Science Ventures, Joe Betts Lacroix of Y Combinator and Vium, Dr. Oliver Medvedik of Lifespan.io and The Cooper Union, and Ramphis Castro of ScienceVest.
Previous research published earlier this year in Nature Medicine involving University of Minnesota Medical School faculty Paul D. Robbins and Laura J. Niedernhofer and Mayo Clinic investigators James L. Kirkland and Tamara Tchkonia, showed it was possible to reduce the burden of damaged cells, termed senescent cells, and extend lifespan and improve health, even when treatment was initiated late in life. They now have shown that treatment of aged mice with the natural product Fisetin, found in many fruits and vegetables, also has significant positive effects on health and lifespan.
As people age, they accumulate damaged cells. When the cells get to a certain level of damage they go through an aging process of their own, called cellular senescence. The cells also release inflammatory factors that tell the immune system to clear those damaged cells. A younger person’s immune system is healthy and is able to clear the damaged cells. But as people age, they aren’t cleared as effectively. Thus they begin to accumulate, cause low level inflammation and release enzymes that can degrade the tissue.
Robbins and fellow researchers found a natural product, called Fisetin, reduces the level of these damaged cells in the body. They found this by treating mice towards the end of life with this compound and see improvement in health and lifespan. The paper, “Fisetin is a senotherapeutic that extends health and lifespan,” was recently published in EBioMedicine.
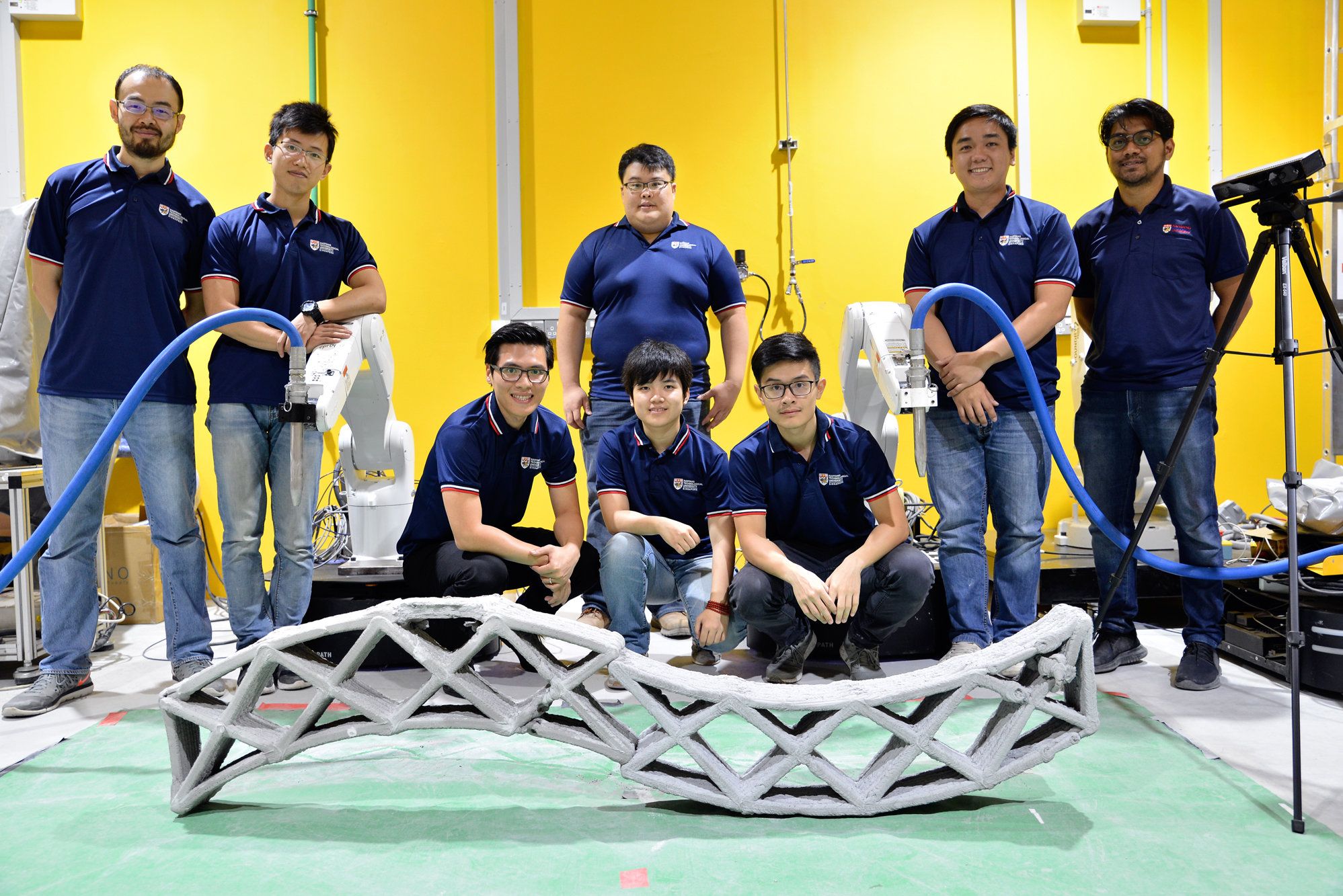
Scientists from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a technology whereby two robots can work in unison to 3D-print a concrete structure. This method of concurrent 3D printing, known as swarm printing, paves the way for a team of mobile robots to print even bigger structures in the future. Developed by Assistant Professor Pham Quang Cuong and his team at NTU’s Singapore Centre for 3D Printing, this new multi-robot technology is reported in Automation in Construction. The NTU scientist was also behind the Ikea Bot project earlier this year, in which two robots assembled an Ikea chair in about nine minutes.
Using a specially formulated cement mix suitable for 3D printing, this new development will allow for unique concrete designs currently impossible with conventional casting. Structures can also be produced on demand and in a much shorter period.
Currently, 3D-printing of large concrete structures requires huge printers that are larger in size than the printed objects, which is unfeasible since most construction sites have space constraints. Using multiple mobile robots that can 3D print in sync means large structures and specially designed facades can be printed anywhere, as long as there is enough space for the robots to move around the work site.