North Korea’s impressive cyber capabilities, explained.
Merging Humans with Machines
Posted in transhumanism
I just received the video of the Eureka! comedy show I was on, which focuses on science. The 90-minute show was on #transhumanism (and a bit on my Governor run). This may be the first (or one of the first) live comedy shows that focused entirely on transhumanism. Check it out!
Interested in becoming post-Human? What if it promised you eternal six-packs? Still on the fence?
Check out Eureka! featuring transhumanist Zoltan Istvan (http://www.zoltanistvan.com/) alongside guest comedians Chris Conatser (Learn from Me Comedy) and Allison Page (Killing My Lobster) and your hosts Allen Saakyan & Kevin Whittinghill.
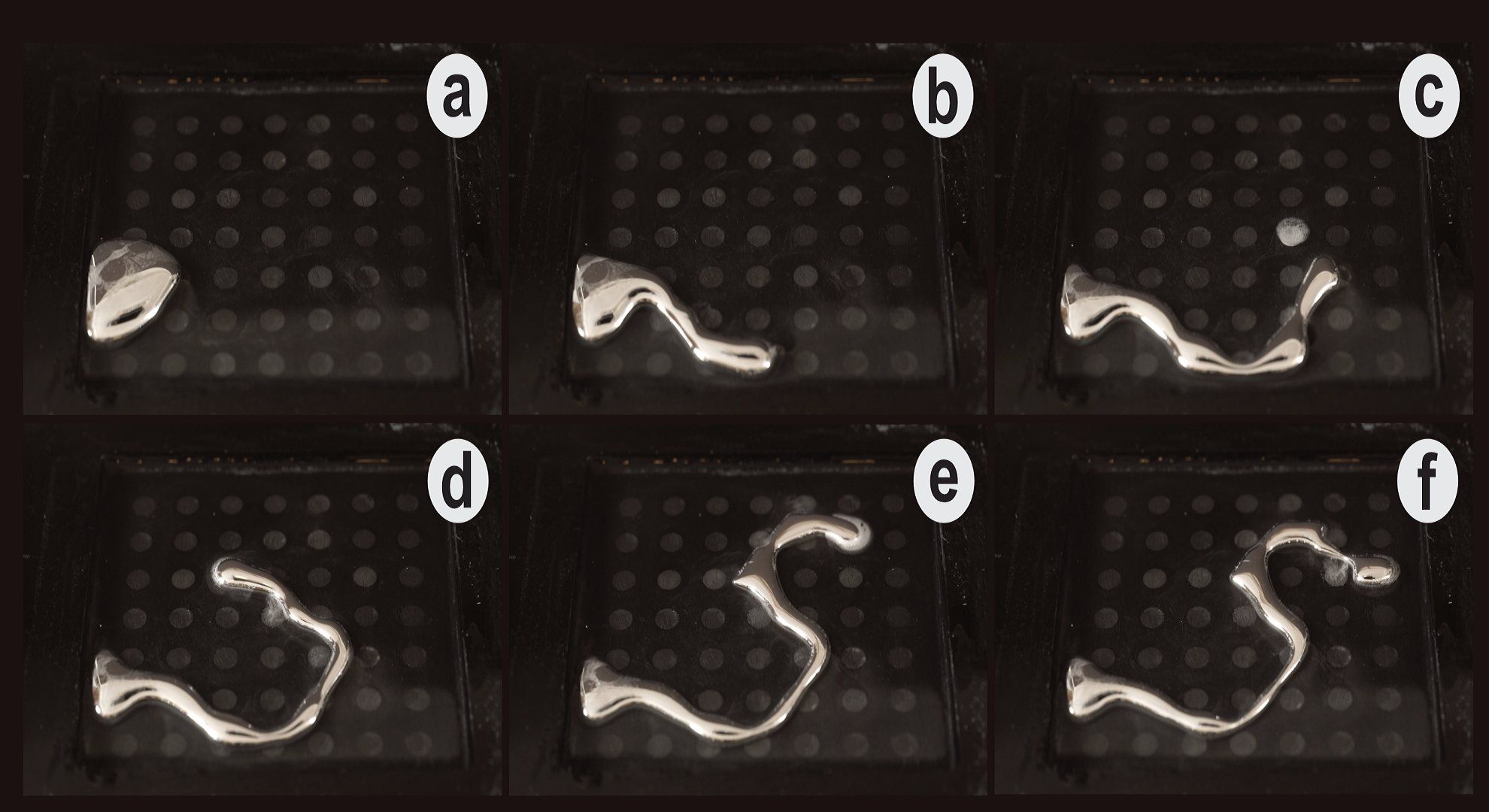
Scientists have invented a way to morph liquid metal into physical shapes.
Researchers at the University of Sussex and Swansea University have applied electrical charges to manipulate liquid metal into 2D shapes such as letters and a heart.
The team says the findings represent an “extremely promising” new class of materials that can be programmed to seamlessly change shape. This open up new possibilities in ‘soft robotics’ and shape-changing displays, the researcher say.
One of the secrets to making tiny laser devices such as opthalmic surgery scalpels work even more efficiently is the use of tiny semiconductor particles, called quantum dots. In new research at Los Alamos National Laboratory’s Nanotech Team, the ~nanometer-sized dots are being doctored, or “doped,” with additional electrons, a treatment that nudges the dots ever closer to producing the desired laser light with less stimulation and energy loss.
“When we properly tailor the compositional profile within the particles during their fabrication, and then inject two or more electrons in each dot, they become more able to emit laser light. Importantly, they require considerably less power to initiate the lasing action,” said Victor Klimov, leader of the Nanotech team.
In order to force a material to emit laser light one has to work toward a “population inversion,” that is, making the number of electrons in a higher-energy electronic state exceed the number that are in a lower-energy state. To achieve this condition normally, one applies an external stimulus (optical or electrical) of a certain power, which should exceed a critical value termed the “optical-gain threshold.” In a recent paradigm-changing advance, Los Alamos researchers demonstrated that by adding extra electrons into their specially designed quantum dots, they can reduce this threshold to virtually zero.
How did you come to accept that aging was a problem?
#CrowdfundTheCure for #aging at www.lifespan.io
The topic of the gut microbiota is increasingly in the news of late, and its connection with chronic age-related inflammation, known as inflammaging, is becoming increasingly clear.
What is the microbiota?
The microbiota describes the community of symbiotic and pathogenic microorganisms that live in and on all multicellular organisms, and it includes bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses. In particular, the gut microbiota and its role in aging and disease have increasingly become of interest to researchers in recent years.
There’s a difference between editing genes in a person’s somatic cells and germline cells.
Editing somatic cells, which are differentiated (e.g., skin cells) and non-reproductive, impacts them alone. In contrast, editing germline DNA means changes are passed along to the next generation during reproduction. It’s no minor distinction.
Right now, the cautious consensus around gene editing in the US and parts of Europe is that it is okay to do therapeutic gene editing in a patient’s somatic DNA, meaning DNA that only exists in that individual and does not get passed on. But some believe the cautious consensus may be too cautious.
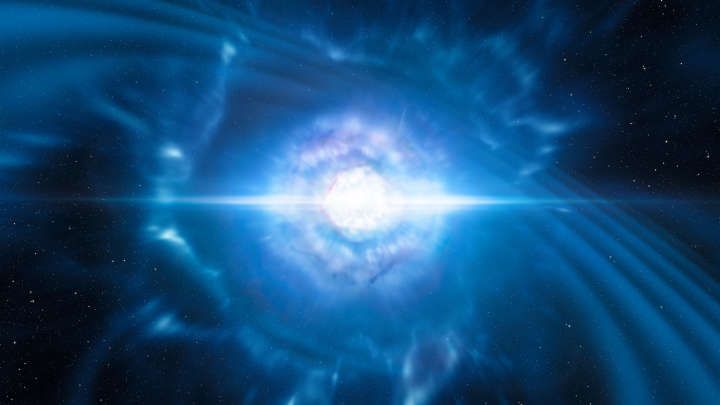
The fifth observation of gravitational waves (GW) marks the beginning of a new era in astronomy. On August 17, 2017, the LIGO and VIRGO collaborations detected neutron stars merging for the first time and immediately alerted observatories around the world. In a matter of minutes the event had been located, another first for GW astronomy, and telescopes around the world begun studying it almost immediately.
The event observed, called GW170817, was produced in galaxy NGC 4993, located 130 million light-years from Earth. The gravitational signal was the strongest ever observed, lasting over 100 seconds, and it emitted a gamma-ray burst (GRBs), providing the first piece of evidence that GRBs are produced by neutron star collisions. It also provided the strongest evidence yet that neutron star mergers are responsible for the creation of the heaviest elements in the universe, like gold and platinum.
The importance of this observation cannot be understated. We are witnessing Galileo pointing the telescope up, or Henrietta Swann Leavitt working out the relation that will be used to measure cosmic distances. This observation brings a completely new dimension to astronomy. The seven papers published in Nature, Nature Astronomy, and Astrophysical Journal Letter are also record-breakers. They have over 45,000 authors – around 35 percent of all active astronomers in the world – who worked at the over 70 observatories that helped to make this discovery.