Scientists discover that dental pulp stem cells from wisdom teeth could regenerate neurons and bones and offer treatments for many diseases.

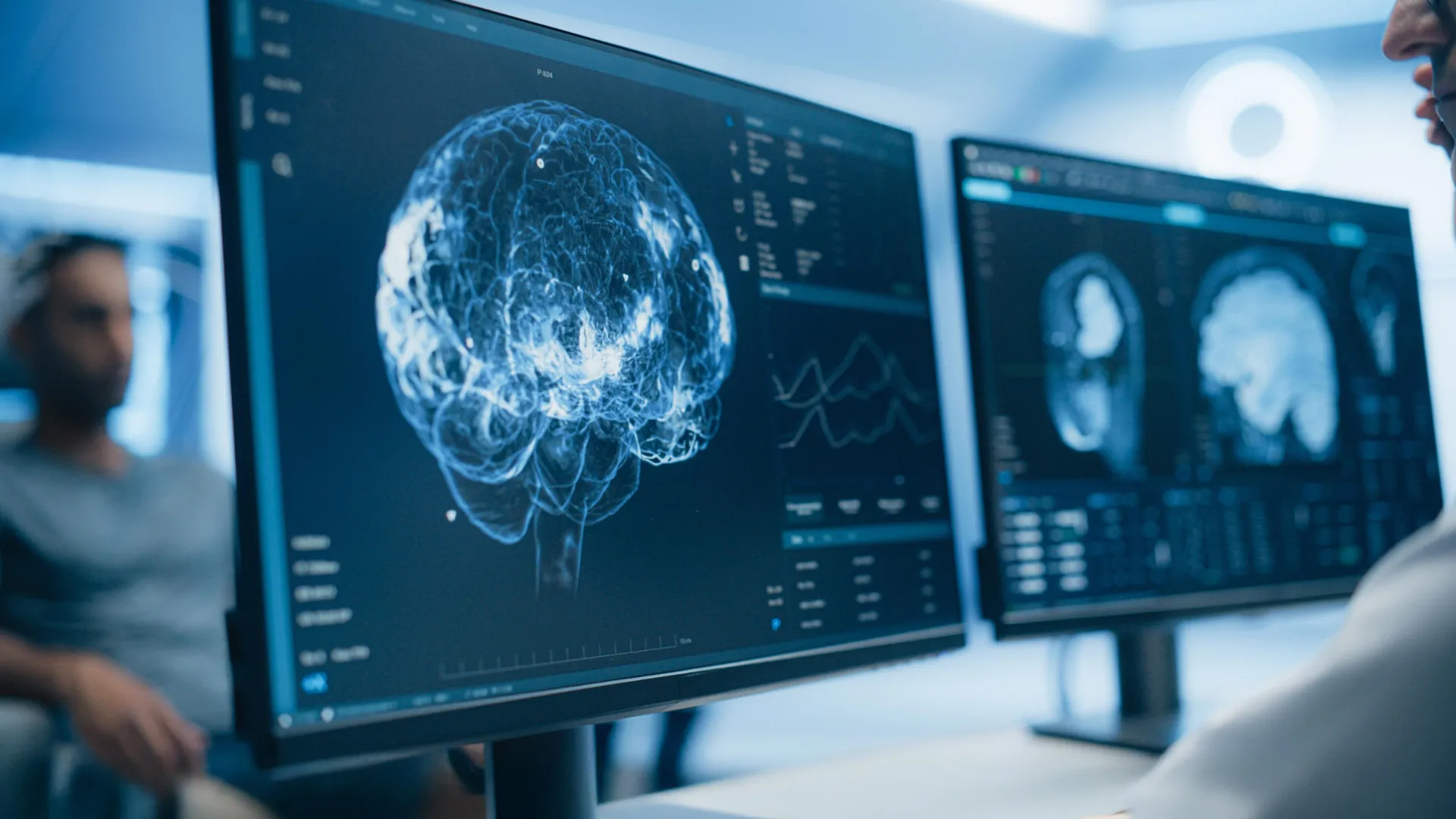
Illinois engineers fused ultrafast imaging with smart algorithms to peek at living brain chemistry, turning routine MRIs into metabolic microscopes. The system distinguishes healthy regions, grades tumors, and forecasts MS flare-ups long before structural MRI can. Precision-medicine neurology just moved closer to reality.


Making the exchange of a message invulnerable to eavesdropping doesn’t strictly require quantum resources. All you need to do is to encrypt the message using a one-use-only random key that is at least as long as the message itself. What quantum physics offers is a way to protect the sharing of such a key by revealing whether anyone other than sender and recipient has accessed it.
Imagine that a sender (Alice) wants to send a message to a recipient (Bob) in the presence of an eavesdropper (Eve). First, Alice creates a string of random bits. According to one of the most popular quantum communication protocols, known as BB84, Alice then encodes each bit in the polarization state of an individual photon. This encoding can be performed in either of two orientations, or “bases,” which are also chosen at random. Alice sends these photons one at a time to Bob, who measures their polarization states. If Bob chooses to measure a given photon in the basis in which Alice encoded its bit, Bob’s readout of the bit will match that of Alice’s. If he chooses the alternative basis, Bob will measure a random polarization state. Crucially, until Alice and Bob compare their sequence of measurement bases (but not their results) over a public channel, Bob doesn’t know which measurements reflect the bits encoded by Alice. Only after they have made this comparison—and excluded the measurements made in nonmatching bases—can Alice and Bob rule out that eavesdropping took place and agree on the sequence of bits that constitutes their key.
The efficiency and security of this process depend on Alice’s ability to generate single photons on demand. If that photon-generation method is not reliable—for example, if it sometimes fails to generate a photon when one is scheduled—the key will take longer to share. If, on the other hand, the method sometimes generates multiple photons simultaneously, Alice and Bob run the risk of having their privacy compromised, since Eve will occasionally be able to intercept one of those extra photons, which might reveal part of the key. Techniques for detecting such eavesdropping are available, but they involve the sending of additional photons in “decoy states” with randomly chosen intensities. Adding these decoy states, however, increases the complexity of the key-sharing process.

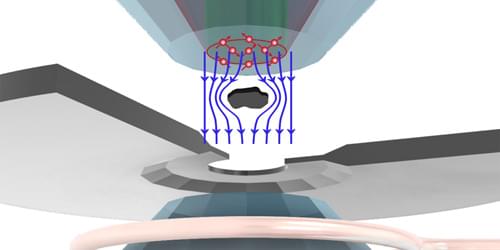
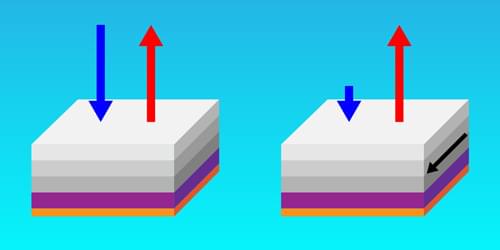
A newly designed structure exhibits the largest-recorded emissivity–absorptivity difference, a property that could prove useful in energy-harvesting and cloaking devices.
Hot objects glow. From the warmth of a stovetop to the invisible heat radiating from a building’s roof, thermal radiation flows outward. But it also flows inward in a reciprocal manner. This means that at thermal equilibrium, an object’s ability to thermally emit light in one direction, described as emissivity, is equal to its ability to absorb the same light coming in from the other direction, known as absorptivity. But what if this rule could be violated?
In a new study, Zhenong Zhang and colleagues from Pennsylvania State University demonstrate this exciting possibility [1]. The researchers apply an external magnetic field to a layered material, creating a system that breaks Lorentz reciprocity—a common symmetry that relates electromagnetic inputs and outputs. They then show that this nonreciprocal system exhibits much higher emissivity than absorptivity in the same direction. The observed difference between emissivity and absorptivity is twice that observed in previous experiments, thus setting a new benchmark in the field. These results pave the way for future technologies such as thermal diodes, radiative heat engines, and infrared camouflage.
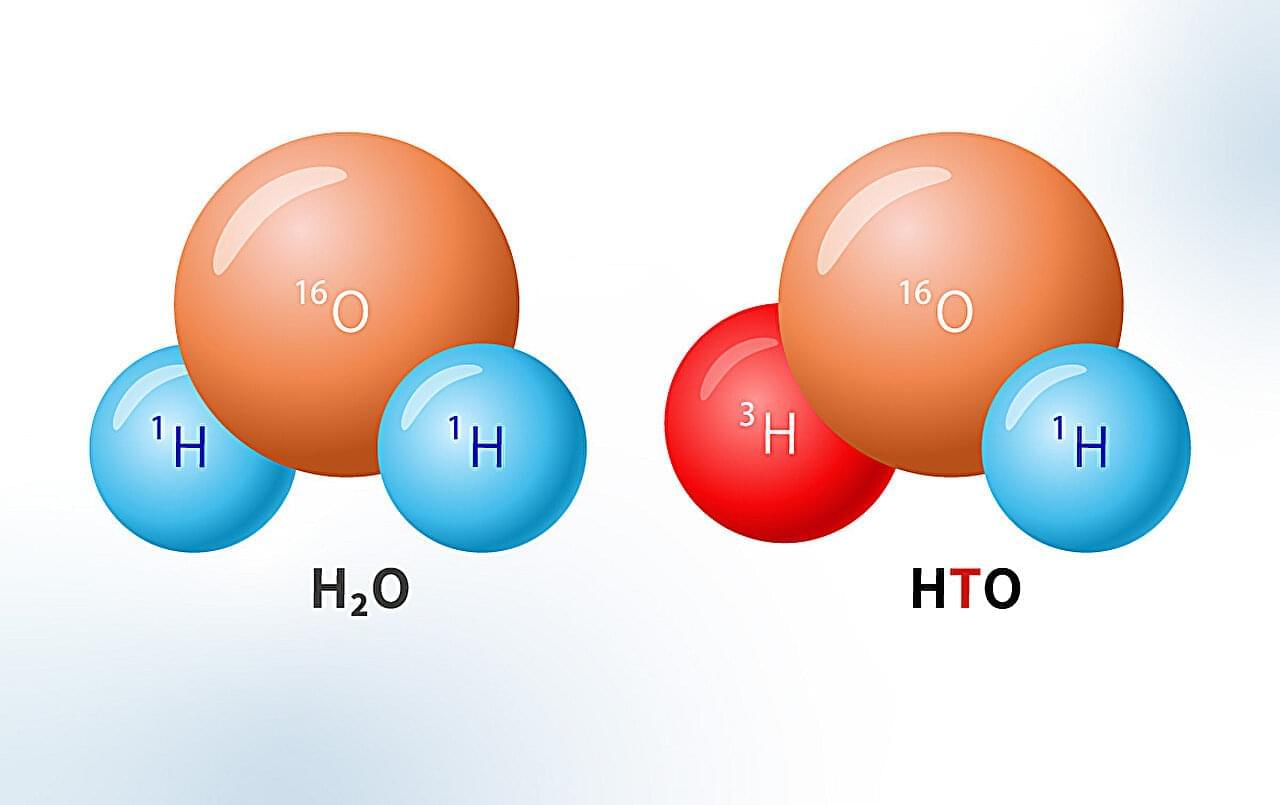
Operators have pumped water to cool the nuclear reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) since the accident in 2011 and treated this cooling water with the Advanced Liquid Processing System (ALPS), which is a state-of-the-art purification system that removes radioactive materials, except tritium.
As part of the water molecule, tritium radionuclide, with a half-life of 12.32 years, is very costly and difficult to remove. The ALPS-treated water was accumulating and stored at the FDNPP site and there is limited space to store this water. Therefore, in 2021, the Government of Japan announced a policy that included discharging the ALPS-treated water via an approximately one-kilometer-long tunnel into the ocean. Planned releases of the ALPS-treated water diluted with ocean water began in August 2023 and will be completed by 2050.
In a new numerical modeling study, researchers have revealed that the simulated increase in tritium concentration in the Pacific Ocean due to the tritium originating from the ALPS-treated water is about 0.1% or less than the tritium background concentration of 0.03−0.2 Bq/L in the vicinity of the discharge site (within 25 km) and beyond.