http://www.blogtalkradio.com/georgewilderjr/2017/10/24/ceo-i…er-jr-show
Even as autonomous robots get better at doing things on their own, there will still be plenty of circumstances where humans might need to step in and take control. New software developed by Brown University computer scientists enables users to control robots remotely using virtual reality, which helps users to become immersed in a robot’s surroundings despite being miles away physically.
The software connects a robot’s arms and grippers as well as its onboard cameras and sensors to off-the-shelf virtual reality hardware via the internet. Using handheld controllers, users can control the position of the robot’s arms to perform intricate manipulation tasks just by moving their own arms. Users can step into the robot’s metal skin and get a first-person view of the environment, or can walk around the robot to survey the scene in the third person—whichever is easier for accomplishing the task at hand. The data transferred between the robot and the virtual reality unit is compact enough to be sent over the internet with minimal lag, making it possible for users to guide robots from great distances.
“We think this could be useful in any situation where we need some deft manipulation to be done, but where people shouldn’t be,” said David Whitney, a graduate student at Brown who co-led the development of the system. “Three examples we were thinking of specifically were in defusing bombs, working inside a damaged nuclear facility or operating the robotic arm on the International Space Station.”
Freshly discovered malware called Triton can compromise safety systems that control many kinds of industrial processes.
For years, security experts have been warning that hackers can disable systems that control critical infrastructure we all rely on, such as dams and power plants. Now researchers at Mandiant, which is part of the security firm FireEye, have revealed that a new form of malware, dubbed Triton, closed down the operations of a business in the Middle East belonging to Schneider Electric, a French company. The researchers say that they haven’t attributed the hack to a particular attacker, but they do say it bore hallmarks of threats from a nation-state.
Triton appears to have targeted a so-called safety instrumented system, or SIS, which monitors the operation of a physical process using sensors and acoustics. By taking control of it, hackers can destroy or damage the process the SIS is monitoring by tricking it into thinking everything’s normal, when in fact the process is operating at unsafe levels.
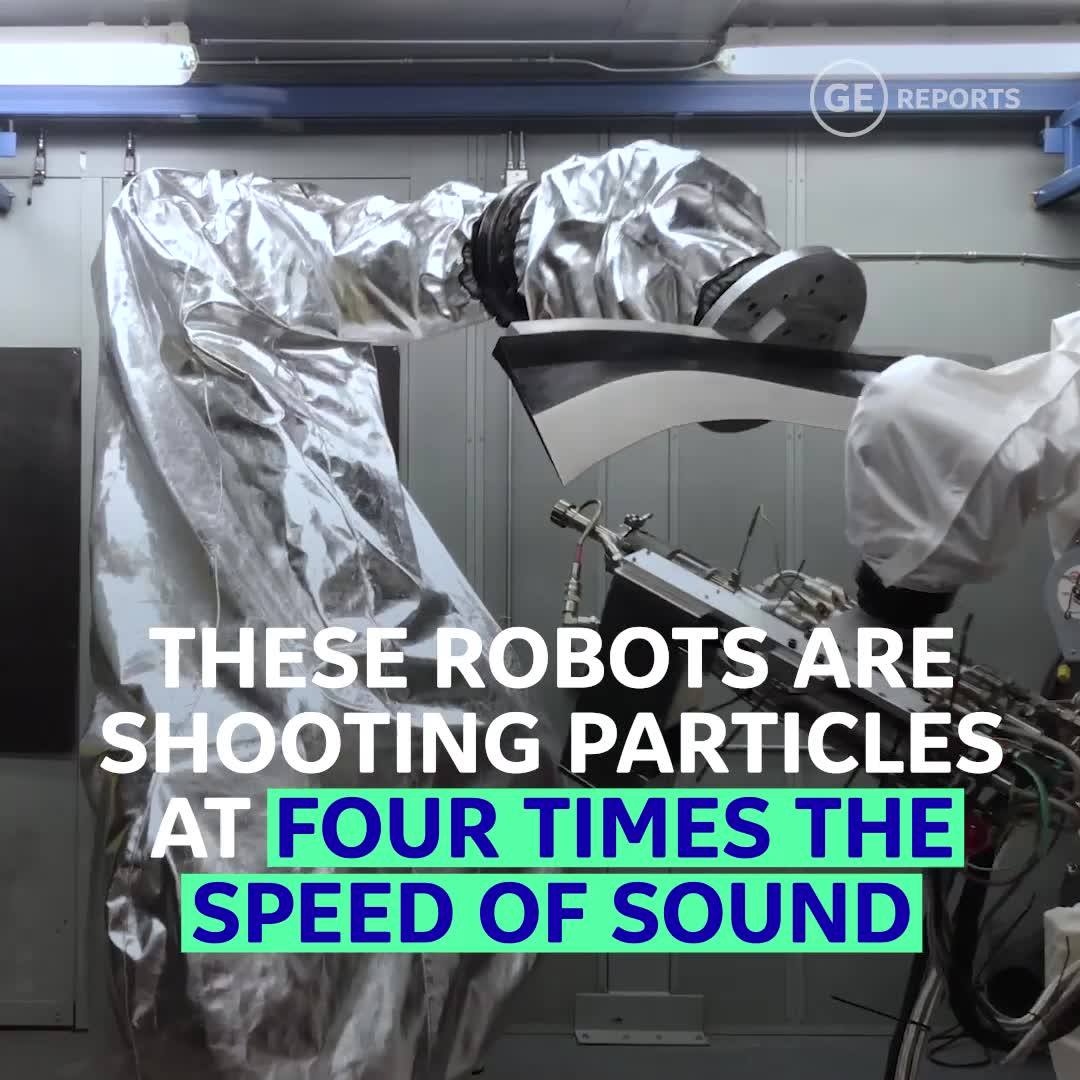
GE researchers are using cold spray to repair and build new parts for aviation, energy, and other applications. http://invent.ge/2iqaKra
Reminds me of a movie I once saw …the Matrix???
Posted by Cointelegraph. Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency News.
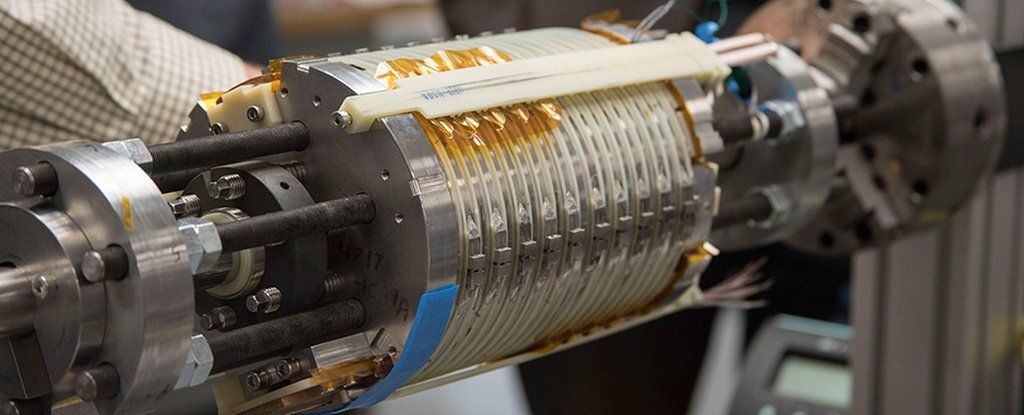
If you want to stick something on your fridge, like really get it stuck on hard there, you might want to talk to the scientists at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory. They’ve just build the most powerful superconducting magnet ever, shattering the world record.
Its magnetic field clocks in at 32 tesla in strength. That’s 33 percent higher than the previous record, and 3,000 times stronger than a small fridge magnet, making this a larger increase than all the improvements in superconducting magnets from the last 40 years combined.
“This is a transformational step in magnet technology, a true revolution in the making,” said MagLab Director Greg Boebinger.