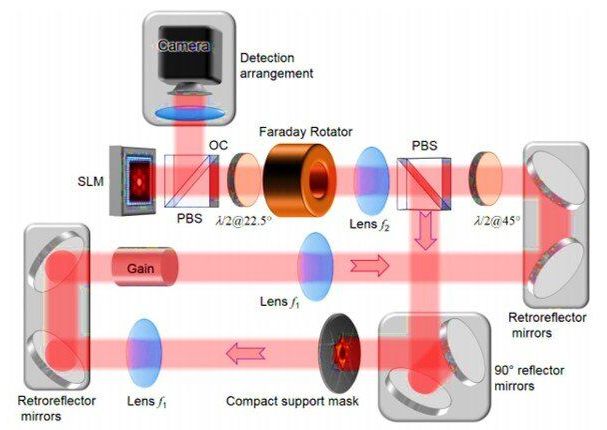
Physicists can explore tailored physical systems to rapidly solve challenging computational tasks by developing spin simulators, combinatorial optimization and focusing light through scattering media. In a new report on Science Advances, C. Tradonsky and a group of researchers in the Departments of Physics in Israel and India addressed the phase retrieval problem by reconstructing an object from its scattered intensity distribution. The experimental process addressed an existing problem in disciplines ranging from X-ray imaging to astrophysics that lack techniques to reconstruct an object of interest, where scientists typically use indirect iterative algorithms that are inherently slow.
In the new optical approach, Tradonsky et al conversely used a digital degenerate cavity laser (DDCL) mode to rapidly and efficiently reconstruct the object of interest. The experimental results suggested that the gain competition between the many lasing modes acted as a highly parallel computer to rapidly dissolve the phase retrieval problem. The approach applies to two-dimensional (2-D) objects with known compact support and complex-valued objects, to generalize imaging through scattering media, while accomplishing other challenging computational tasks.
To calculate the intensity distribution of light scattered far from an unknown object relatively easily, researchers can compute the source of the absolute value of an object’s Fourier transform. The reconstruction of an object from its scattered intensity distribution is, however, ill-posed, since phase information can be lost and diverse phase distributions in the work can result in different reconstructions. Scientists must therefore obtain prior information about an object’s shape, positivity, spatial symmetry or sparsity for more precise object reconstructions. Such examples are found in astronomy, short-pulse characterization studies, X-ray diffraction, radar detection, speech recognition and when imaging across turbid media. During the reconstruction of objects with a finite extent (compact support), researchers offer a unique solution to the phase retrieval problem, as long as they model the same scattered intensity at a sufficiently higher resolution.