The outside world is scary enough right now. The internet doesn’t have to be scary, too.



“The listing was posted on November 15, 2019”
🤔
The job listing is for positions in Dallas, El Paso, Houston, Seattle, Anchorage, Los Angeles, San Diego, San Francisco, Miami, Atlanta, Honolulu, Chicago, Boston, Detroit, Minneapolis, Newark, New York, Philadelphia, and San Juan.
The job description reads, “Serves as a project representative for a program responsible for preventing the importation and spread of communicable diseases.”
All cities currently dealing with coronavirus fears in the U.S. are listed on the job application.

The Japan Maritime Self Defense Force’s latest diesel-electric attack submarine was commissioned on March 5.
By Franz-Stefan Gady for The Diplomat.

A mind-bending new paper suggests our entire Milky Way galaxy could be located inside an enormous bubble where matter is much less dense than everywhere else.
If research bears the theory out, it’d mean that our galactic neighborhood is very different from the rest of the universe — and it could potentially solve a huge problem looming over the astrophysics field.
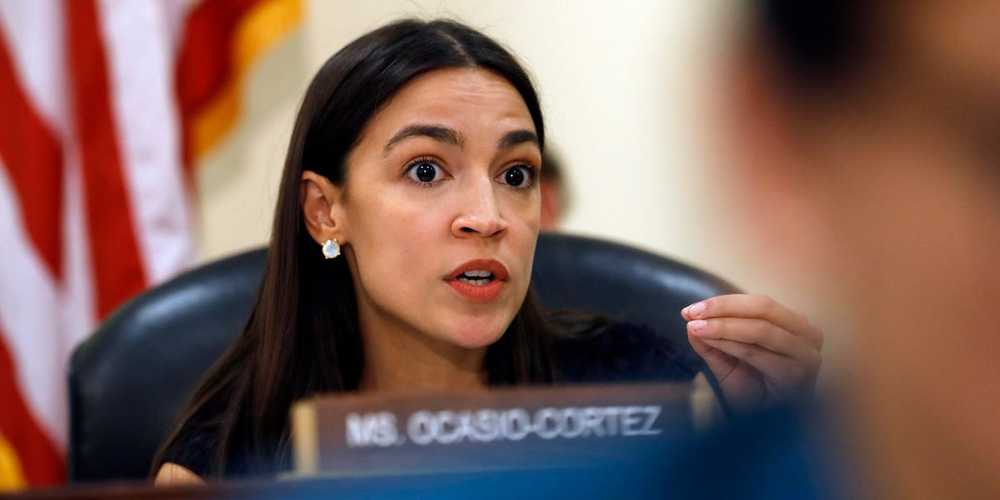


The House is preparing to vote on Thursday on a coronavirus-relief bill that would provide Americans with paid sick leave, food assistance, free coronavirus testing, and more substantial unemployment benefits.
But Ocasio-Cortez pushed for a more sweeping response, including expanding Medicare or Medicaid to cover all Americans, a freeze on evictions, a universal basic income, ending work requirements for food-assistance programs, criminal-justice reform, and freezing student-debt collection.
“This is not the time for half measures,” she tweeted on Thursday. “We need to take dramatic action now to stave off the worst public health & economic affects. That includes making moves on paid leave, debt relief, waiving work req’s, guaranteeing healthcare, UBI, detention relief (pretrial, elderly, imm).”
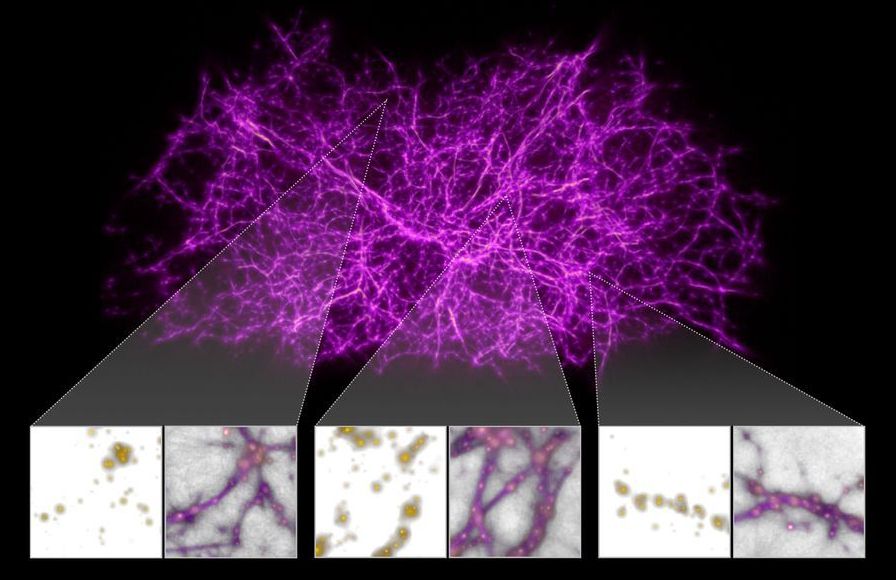
The behavior of one of nature’s humblest creatures is helping astronomers probe the largest structures in the universe.
The single-cell organism, known as slime mold (Physarum polycephalum), builds complex filamentary networks in search of food, finding near-optimal pathways to connect different locations. In shaping the universe, gravity builds a vast cobweb structure of filaments tying galaxies and clusters of galaxies together along faint bridges hundreds of millions of light-years long. There is an uncanny resemblance between the two networks: one crafted by biological evolution, and the other by the primordial force of gravity.
The cosmic web is the large-scale backbone of the cosmos, consisting primarily of the mysterious substance known as dark matter and laced with gas, upon which galaxies are built. Dark matter cannot be seen, but it makes up the bulk of the universe’s material. The existence of a web-like structure to the universe was first hinted at in the 1985 Redshift Survey conducted at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Since those studies, the grand scale of this filamentary structure has grown in subsequent sky surveys. The filaments form the boundaries between large voids in the universe.
First wave 🌊.
Your questions answered — an update (11−03−2020): Professor Neil Ferguson on the current status of the COVID-19 Coronavirus outbreak, case numbers, intervention measures and challenges countries are currently facing.
Read all reports including estimates of epidemic size, transmissibility, severity, phylogenetics, undetected cases, prevalence and symptom progression here: https://www.imperial.ac.uk/mrc-gida
The Abdul Latif Jameel Institute for Disease and Emergency Analytics (J-IDEA) brings together global health researchers in the School of Public Health at Imperial College London. Drawing on Imperial’s expertise in data analytics, epidemiology and economics, J-IDEA improves our understanding of diseases and health emergencies in the most vulnerable populations across the globe. The Institute links governments, research institutions and communities to develop practical and effective long-term solutions, shape health policy and deliver better quality of life for all.
Abdul Latif Jameel Institute for Disease and Emergency Analytics (J-IDEA)