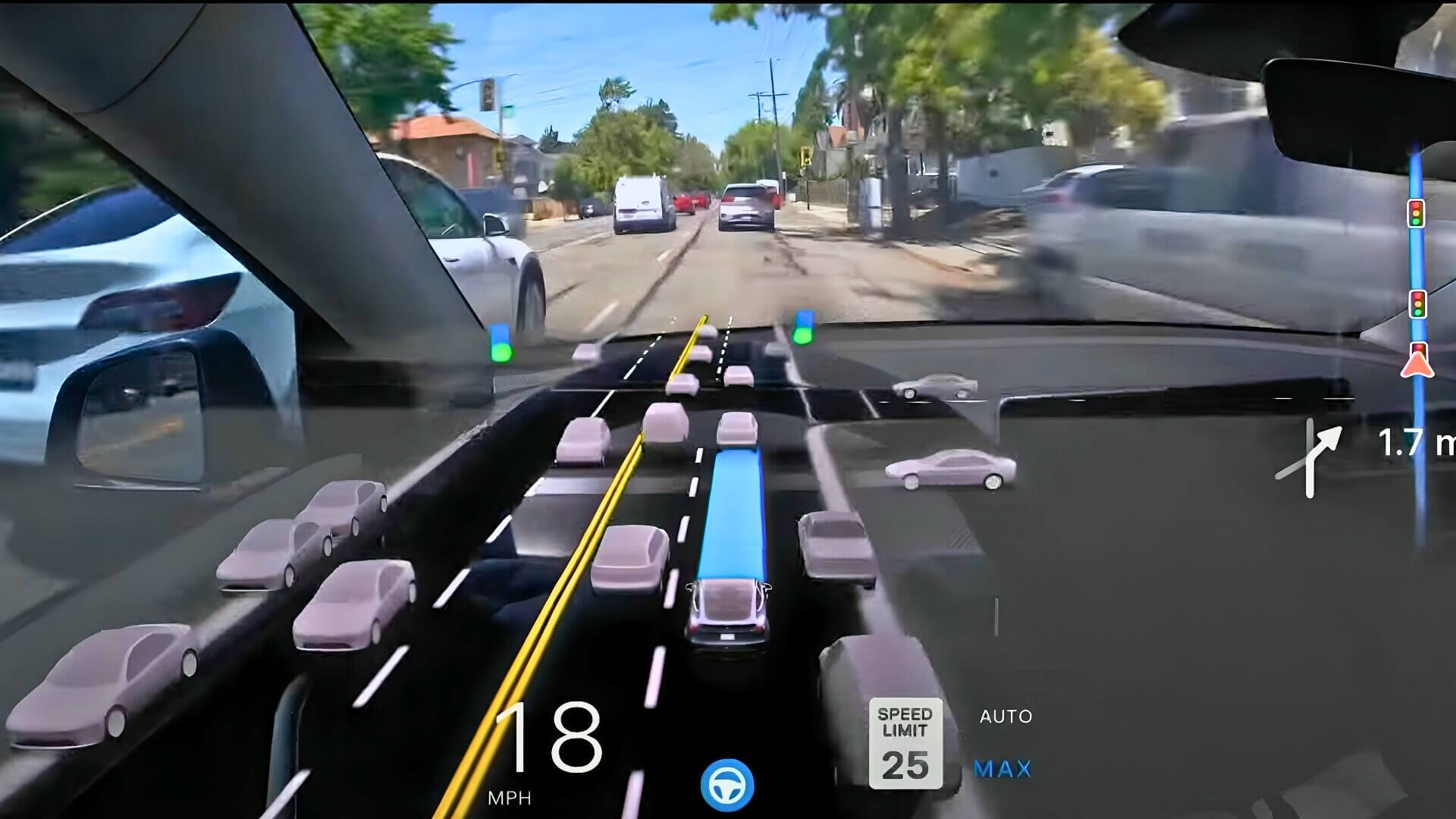
Tesla is now shipping the Full Self-Driving (FSD) (Supervised) Early Access Program to the USA. This is a big step forward in Tesla’s work to improve and project its autonomous driving technology. Tesla expects that the capability will eventually extend to all FSD owners in North America, letting them try out pre-release versions of the automaker’s most sophisticated automotive-driving-assistance software.
Enrolling in this program will allow Tesla owners to test out high-end upgrades before the rest of the public gains access. Most importantly, participants will offer useful info and vehicle data that will aid in refining and fine-tuning future versions.