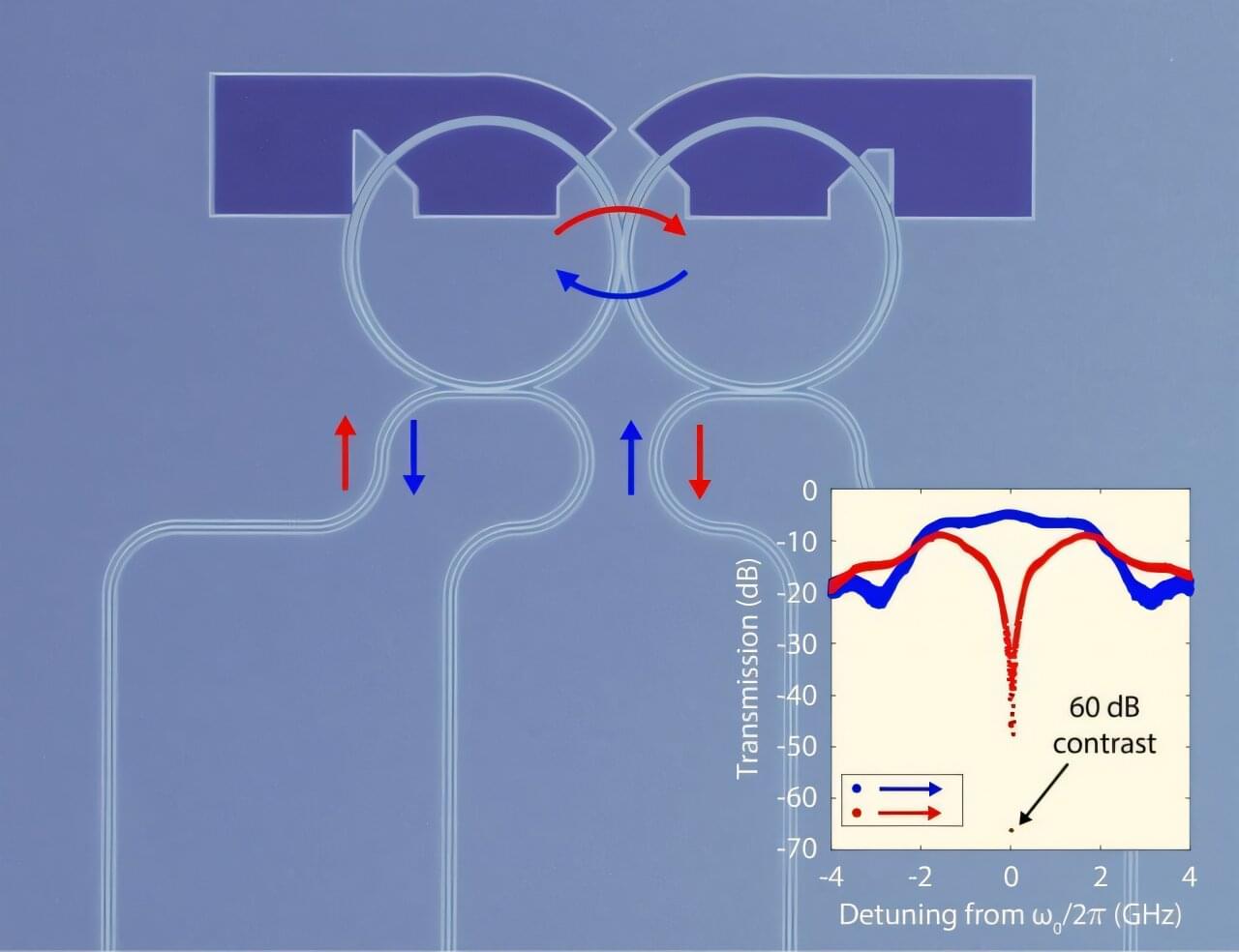
The original goal of the study was to get this asymmetry to a point of perfect isolation—that is, where there is zero interaction in one direction. They successfully achieved this goal by demonstrating a giant optical isolation effect, where the propagation of light in one direction was a million times easier than in the opposite direction.
But while exploring their test devices, the engineers encountered a surprise. Their approach was so efficient that they could even get past the isolation point to where the sign of the coupling simply flipped and the phase became direction dependent. This was something that had not been seen before in time modulated coupling and is an easy path to photonic gyration.
Going forward, the Illinois researchers will work to expand their findings. They are working with their partners specializing in condensed matter to explore how longer and more elaborate chains of resonators with this kind of tunable couplings could answer fundamental questions on topological physics. Simultaneously, from an engineering standpoint, they aim to create a pure gyrator which is a universal building block of many nonreciprocal devices.