Breaking the limits of light control: non-hermitian silicon photonic switching.
Imagine a new way of controlling [#light](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/light?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXWUWLMvFSlCWqwebCELVs4-fbCMnldCKnIVGZrgtNUTRTTYSpzFXQZE36EXaisrk4LktWLvfOHDWvPYLl3repY1GFTT1cBs7NW6b5tSZsCm6hrhxySUves0ATBtZTjr9RkS4buJBybFVuHrOjdR8CZM25CUC_y1s-Pyhej3ftz6g&__tn__=*NK-R) that defies conventional expectations, enabling faster and more efficient communication networks. This is the promise of non-Hermitian photonics, a cutting-edge field that manipulates light using the full range of complex optical properties, including gain and loss. By carefully balancing these properties, researchers have unlocked surprising behaviors, such as the ability for light to flow in counterintuitive ways.
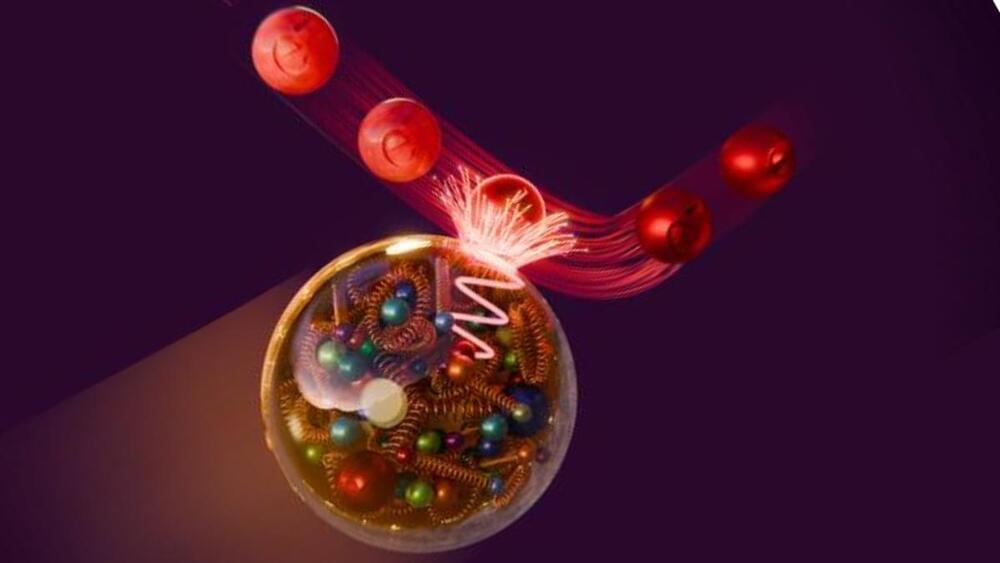
In this study, scientists have created a revolutionary non-Hermitian switching network on a tiny, two-layer photonic chip. The chip is a hybrid design, combining a bottom silicon layer with a top layer made of indium gallium arsenide phosphide (InGaAsP), a material that amplifies light. This combination allows light to be controlled with remarkable precision.
The secret lies in a phenomenon called exceptional points, where the interaction of gain and loss reaches a critical balance, resulting in unique optical effects. By adjusting the light amplification in the top layer, the researchers can dynamically switch light between the two layers of the chip. This switching occurs in an astonishingly short time—just 100 picoseconds (a picosecond is one-trillionth of a second).
What’s even more impressive is the scalability of this system. The researchers demonstrated that the chip could handle large networks of switches, enabling flexible and diverse connections. These connections support both single-wavelength and wavelength-selective operations, crucial for modern optical communication systems. The switches also achieve high extinction ratios, meaning they are exceptionally efficient at directing light where it needs to go.
This breakthrough adds a powerful new tool to the [#photonics](https://www.facebook.com/hashtag/photonics?__eep__=6&__cft__[0]=AZXWUWLMvFSlCWqwebCELVs4-fbCMnldCKnIVGZrgtNUTRTTYSpzFXQZE36EXaisrk4LktWLvfOHDWvPYLl3repY1GFTT1cBs7NW6b5tSZsCm6hrhxySUves0ATBtZTjr9RkS4buJBybFVuHrOjdR8CZM25CUC_y1s-Pyhej3ftz6g&__tn__=*NK-R) design arsenal, paving the way for ultrafast, compact, and high-bandwidth integrated photonic systems. Such advancements could transform next-generation optical networks, enabling faster internet speeds, more reliable communication, and improved data handling in our increasingly connected world.