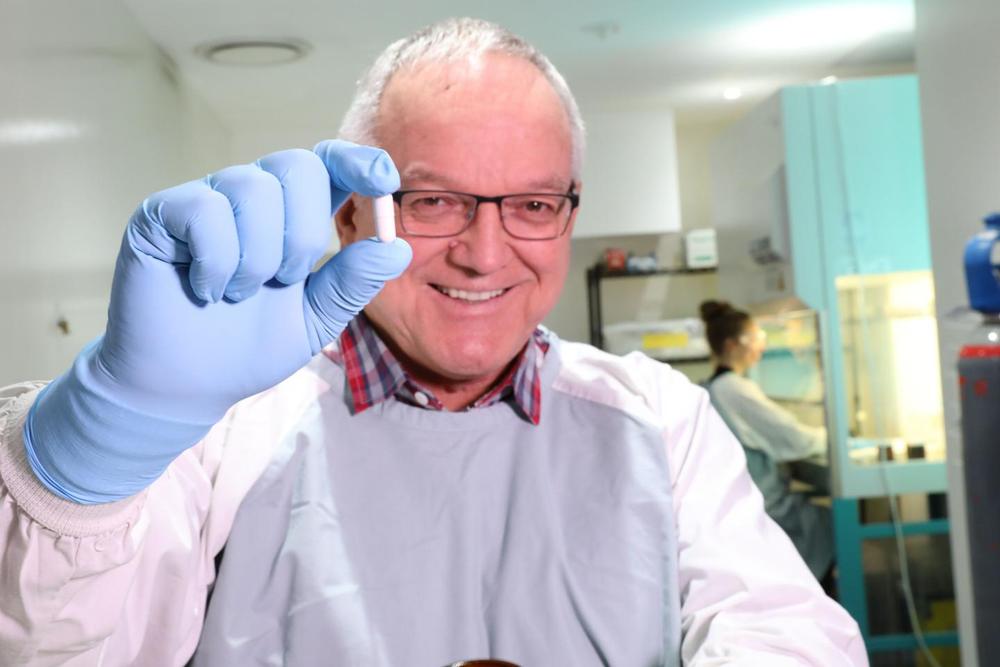
The Centre for Digestive Disease headed by Professor Thomas Borody has cured Crohn’s disease as reported today by Dr Gaurav Agrawal in Gut Pathogens.
Centre for Digestive Diseases.
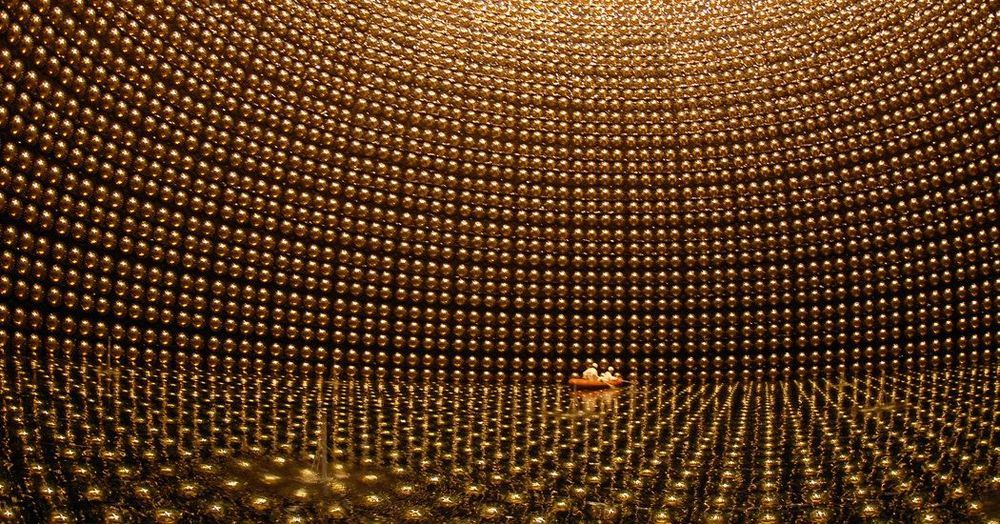
How did matter gain the edge over antimatter in the early universe? Maybe, just maybe, neutrinos.
The Super-Kamiokande Neutrino Observatory, located more than 3,000 feet below Mount Ikeno near the city of Hida, Japan. Credit… Kamioka Observatory, Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo.
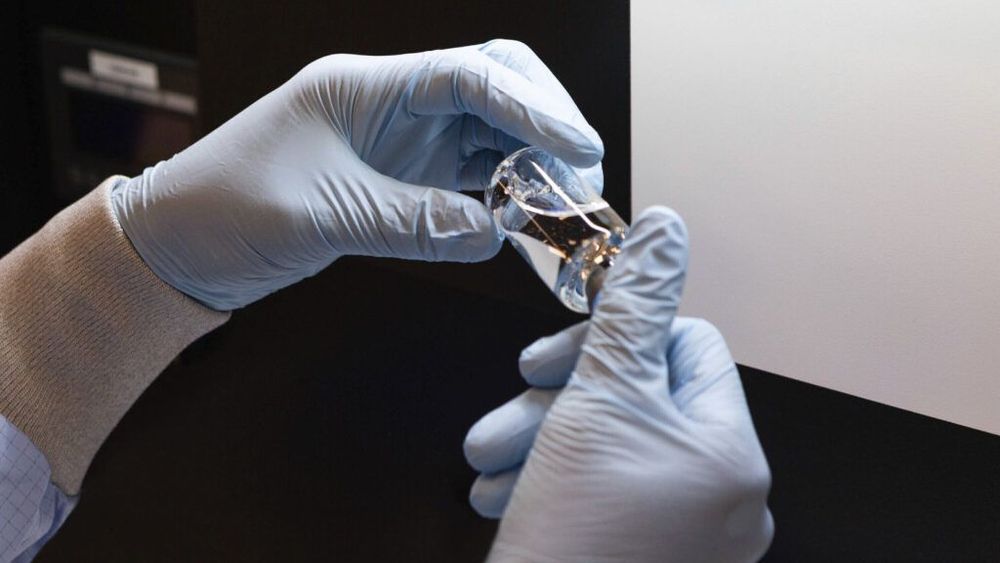
A Chicago hospital treating severe COVID19 patients with Gilead Sciences’ antiviral medicine remdesivir in a closely watched clinical trial is seeing rapid recoveries in fever and respiratory symptoms, with nearly all patients discharged in less than a week, STAT has learned.
Remdesivir was one of the first medicines identified as having the potential to impact SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes Covid-19, in lab tests. The entire world has been waiting for results from Gilead’s clinical trials, and positive results would likely lead to fast approvals by the Food and Drug Administration and other regulatory agencies. If safe and effective, it could become the first approved treatment against the disease.
The outcomes in patients at a Chicago hospital offer only a snapshot of remdesivir’s effectiveness, but are the first clinical data to surface to date.
We present a calculation of a neutrino decay scenario in the early Universe. The specific decay is ν_{2} \to ν_{1} + ϕ, where ϕis a boson. If there is a neutrino mass hierarchy, m_{ν_{e}} m_{ν_μ} m_{ν_τ}, we show that it is possible to generate stimulated decay and effects similar to atomic lasing without invoking new neutrinos, even starting from identical neutrino distributions. Under the right circumstances the decay can be to very low momentum boson states thereby producing something similar to a Bose condensate, with possible consequences for structure formation. Finally, we argue that this type of decay may also be important other places in early Universe physics.

AT&T is connecting IoT robots, in new partnerships with Xenex and Brain Corp., that aim to help hospitals and retail establishments like grocery stores keep facilities clean, kill germs and keep shelves stocked more efficiently.
Chris Penrose, SVP of Advanced Solutions at AT&T, told FierceWireless that the robots are riding on the carrier’s 4G LTE network, rather than narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) or LTE-M networks. That’s because of the large amounts of data they need to push, along with latency and speed requirements for these particular use cases.
In the robotics space, AT&T is typically leaning more toward using LTE and potentially 5G in the future, Penrose noted.


Editor’s note: The story has been updated.
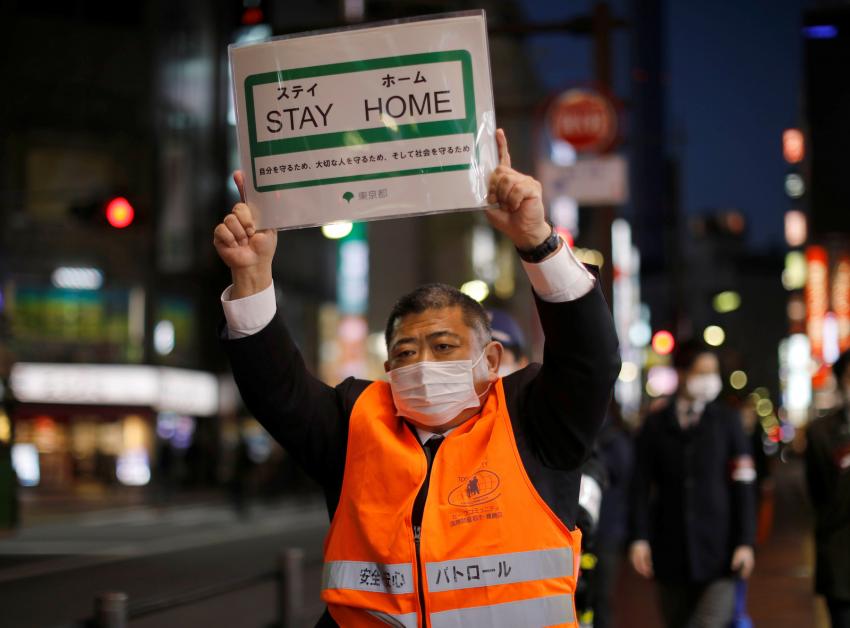
Japan could see some 850,000 people seriously sickened by the coronavirus and almost half of them dying if no social distancing or other measures are followed, according to an expert estimate released Wednesday.
Japan has the world’s oldest population, which is a particular concern since COVID-19 can be especially serious and fatal in the elderly. And there are concerns that Japan’s government has done too little and acted too late to stave off high numbers of seriously ill patients.

Cool read…hhh.
The emergence of Bitcoin as one of the hottest new investment assets has surprised many who once believed the blockchain-driven cryptocurrency would never have real-world value. It has also generated immense amounts of interest from those who had either never heard of Bitcoin before or who knew relatively little about it. As a result, there are now incredible opportunities for making extra money in the cryptocurrency niche.
In the following article, you’ll find out how to make money with Bitcoin and discover a few of the many different ways to capitalize on the cryptocurrency trend and earn Bitcoin in lots of different ways.

Remember, keeping your bitcoins or altcoins on your exchange wallets is highly insecure. You should never store then on the exchange for longer than is necessary. To make your Bitcoins, LiteCoins or any other crypto currency safe, you will need a hardware wallet like the Ledger Nano S or Trezor.
Click here for the latest coronavirus news, which the BDN has made free for the public. You can support our critical reporting on the coronavirus by purchasing a digital subscription or donating directly to the newsroom.
Until now, Aroostook County native Jessica Meir has watched the unfolding coronavirus pandemic from orbit.
That changes on Friday, when she and two fellow astronauts return to a changed planet.