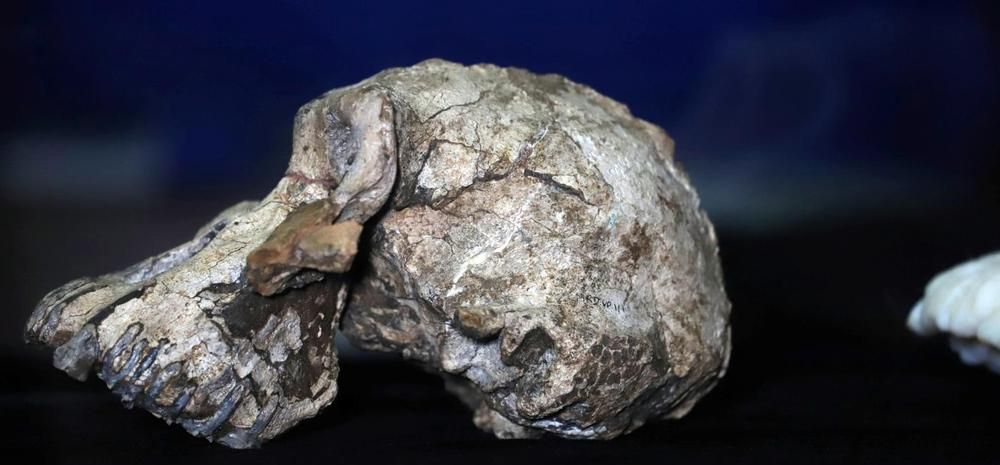
The recent discovery of a 3.8m-year-old cranium (skull without the lower jaw) is the hottest topic of conversation among palaeoanthropologists right now. But fossils are found all the time, so why is the cranium of this small, old man so important? It turns out the discovery is changing our view of how early hominin species evolved – and how they led to humans. To understand how, let’s start at the beginning.
In 1995, researchers found several partial jaws, isolated teeth and limb bones in Kenya, dated between 4.2m and 3.9m years old, and assigned them to a brand new species: Australopithecus anamensis. All these fossils were found in sediments associated with an ancient lake – “anam”, which means lake in the local language. A number of additional specimens were then found in Ethiopia, thought to belong to the same species.
The primitive features of A. anamensis have led to the widespread view that this species is the ancestor of Australopithecus afarensis, a younger hominin from Tanzania, Ethiopia and perhaps Kenya, dated between 3.8m and 3m years old. The most iconic fossil of A. afarensis is probably the partial skeleton known as Lucy, which was for a long time viewed as the oldest known human ancestor.