There are 70 coronavirus vaccines in development globally, with three candidates already being tested in human trials, according to the World Health Organization, as drugmakers race to find a cure for the deadly pathogen.



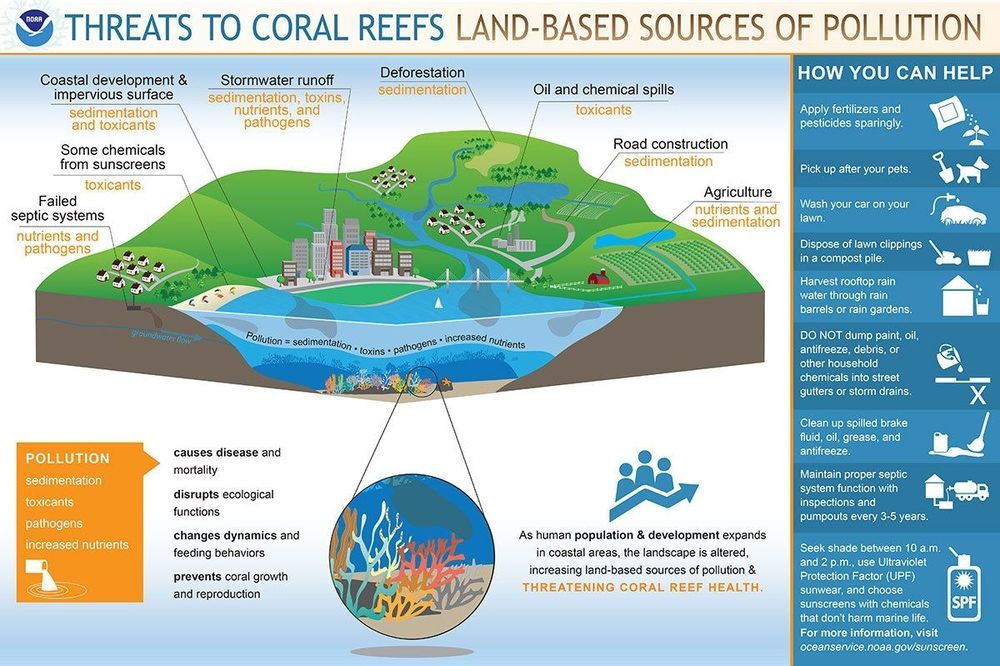
Most of us have heard that coral reefs around the world are dying, largely because of warmer ocean temperatures and the increased acidity of seawater, but few people realize why that is important to humans. Who really cares if the Great Barrier Reef off the coast of Australia is nearly lifeless? So a few rich scuba divers won’t get to see it. Boo-hoo. Actually, it’s a little more complicated than that.

KELVIN OGBA DAFIAGHOR is inviting you to a scheduled Zoom meeting.
Topic: COVID 19, China cover up, conspiracy theories, was the C.I.A complicent? should China be punished? Lessons learnt. OIN NOW Time: Apr 16, 2020 06:00 PM West Central Africa.
Join Zoom Meeting https://us04web.zoom.us/j/79182052546
Meeting ID: 791 8205 2546
Zoom is the leader in modern enterprise video communications, with an easy, reliable cloud platform for video and audio conferencing, chat, and webinars across mobile, desktop, and room systems. Zoom Rooms is the original software-based conference room solution used around the world in board, conference, huddle, and training rooms, as well as executive offices and classrooms. Founded in 2011, Zoom helps businesses and organizations bring their teams together in a frictionless environment to get more done. Zoom is a publicly traded company headquartered in Sanose, CA.
Circa 2015
A “dialysis for cancer,” which cleanses blood of cancer, has been developed by a team of scientists from Australia.
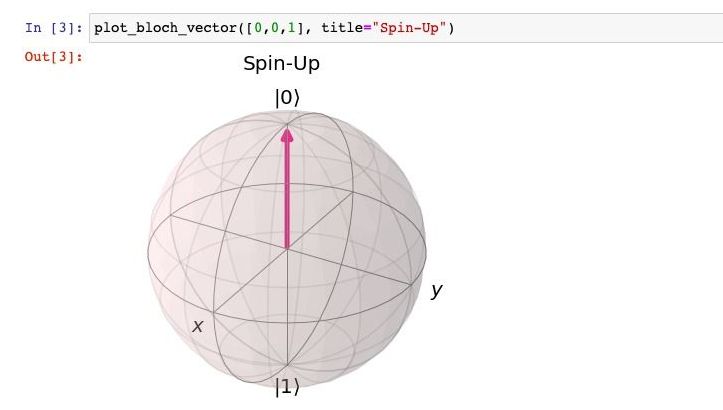
It is a common misconception that quantum computers are not yet ready for applications and the technology still has many years before becoming useful. In this article we will take a look at some of the basic principles of programming a quantum computer and address this misconception. We will look at free, open-source software such as QISKit from IBM, as well as the Quantum Machine Learning software PennyLane. We will also explain how you can run your programs on actual quantum computers in the cloud at IBM. In a follow-up article we will talk about some applications in machine learning that are ready for use currently to anyone with a bit of curiosity.
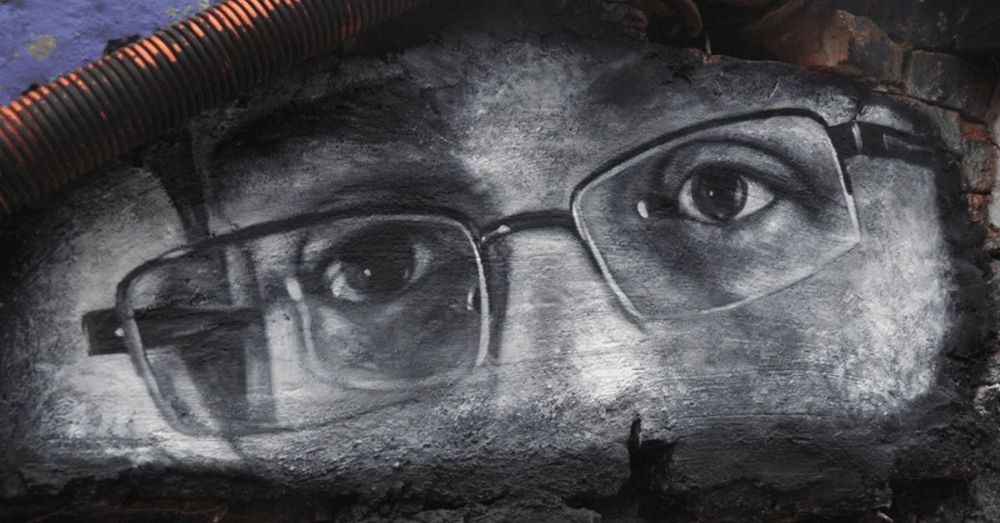


Governments around the world are using high-tech surveillance measures to combat the coronavirus outbreak. But are they worth it?
Edward Snowden doesn’t think so.
The former CIA contractor, whose leaks exposed the scale of spying programs in the US, warns that once this tech is taken out of the box, it will be hard to put it back.
Nowadays, artificial neural networks have an impact on many areas of our day-to-day lives. They are used for a wide variety of complex tasks, such as driving cars, performing speech recognition (for example, Siri, Cortana, Alexa), suggesting shopping items and trends, or improving visual effects in movies (e.g., animated characters such as Thanos from the movie Infinity War by Marvel).
Traditionally, algorithms are handcrafted to solve complex tasks. This requires experts to spend a significant amount of time to identify the optimal strategies for various situations. Artificial neural networks — inspired by interconnected neurons in the brain — can automatically learn from data a close-to-optimal solution for the given objective. Often, the automated learning or “training” required to obtain these solutions is “supervised” through the use of supplementary information provided by an expert. Other approaches are “unsupervised” and can identify patterns in the data. The mathematical theory behind artificial neural networks has evolved over several decades, yet only recently have we developed our understanding of how to train them efficiently. The required calculations are very similar to those performed by standard video graphics cards (that contain a graphics processing unit or GPU) when rendering three-dimensional scenes in video games.

The digital court could open up commercial opportunities to those who cannot access traditional legal services. Image CC-0.
In a move to save time, money and effort, economics researchers utilized existing blockchain methodologies to create what they call a digital court. This would provide enforcement of contracts wherever a traditional legal court would currently settle disputes. Examples of areas which could make use of this would be auctions, business contracts and sales. As it is based on existing technology, it could be implemented right now.
Blockchain technology has great potential to impact many areas of life, commerce in particular. Put simply it is a way to ensure that information can be recorded in such a way that it cannot be manipulated afterwards. Blockchain is what is known as a distributed ledger, that is, there is no central authority, it is peer-to-peer, and its most famous application at this time is the online currency bitcoin. However, people find other uses for it.