Rain, seas and a surface of eroding organic material can be found both on Earth and on Saturn’s largest moon, Titan. However, on Titan it is methane, not water, that fills the lakes with slushy raindrops.
Here is a vegetable weeding robot designed to increase efficiency on large-scale vegetable farms. It works autonomously and can cover up to 12 acres in 9 hours. It uses GPS and camera to get the job done with accuracy.

Dino is designed to reduce labor costs and free up time for farming teams to focus on more important tasks. It can be put on a schedule and since it’s electric, only minimal maintenance is required.
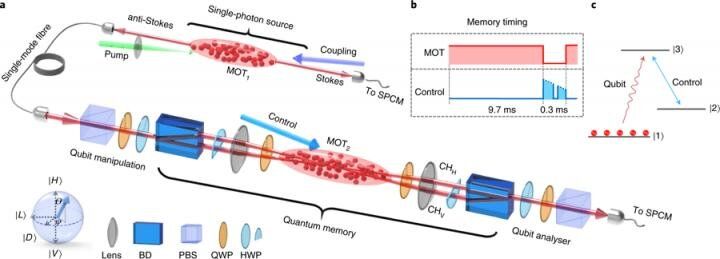
Like memory in conventional computers, quantum memory components are essential for quantum computers—a new generation of data processors that exploit quantum mechanics and can overcome the limitations of classical computers. With their potent computational power, quantum computers may push the boundaries of fundamental science to create new drugs, explain cosmological mysteries, or enhance accuracy of forecasts and optimization plans. Quantum computers are expected to be much faster and more powerful than their traditional counterparts as information is calculated in qubits, which, unlike the bits used in classical computers, can represent both zero and one in a simultaneous superstate.
Photonic quantum memory allows for the storage and retrieval of flying single-photon quantum states. However, production of such highly efficient quantum memory remains a major challenge as it requires a perfectly matched photon-matter quantum interface. Meanwhile, the energy of a single photon is too weak and can be easily lost into the noisy sea of stray light background. For a long time, these problems suppressed quantum memory efficiencies to below 50 percent—a threshold value crucial for practical applications.
Now, for the first time, a joint research team led by Prof. Du Shengwang from HKUST, Prof. Zhang Shanchao from SCNU, Prof. Yan Hui from SCNU and Prof. Zhu Shi-Liang from SCNU and Nanjing University has found a way to boost the efficiency of photonic quantum memory to over 85 percent with a fidelity of over 99 percent.
Although the many experiments searching for evidence of dark matter have yet to turn up any solid proof of the stuff yet, they are making other amazing discoveries. The XENON1T experiment has now revealed the longest half-life ever seen in an element, which is far, far longer than the age of the universe.
To help put the first generation of space colonists on the right footing, Purdue University’s Resilient ExtraTerrestrial Habitats (RETH) Institute is building a one-quarter-scale space habitat similar to ones that may one day be built on the Moon and Mars. It is hoped habitats boasting a combination of “resilience, intelligence, and autonomy” will stand up to the many hazards space can throw at them.
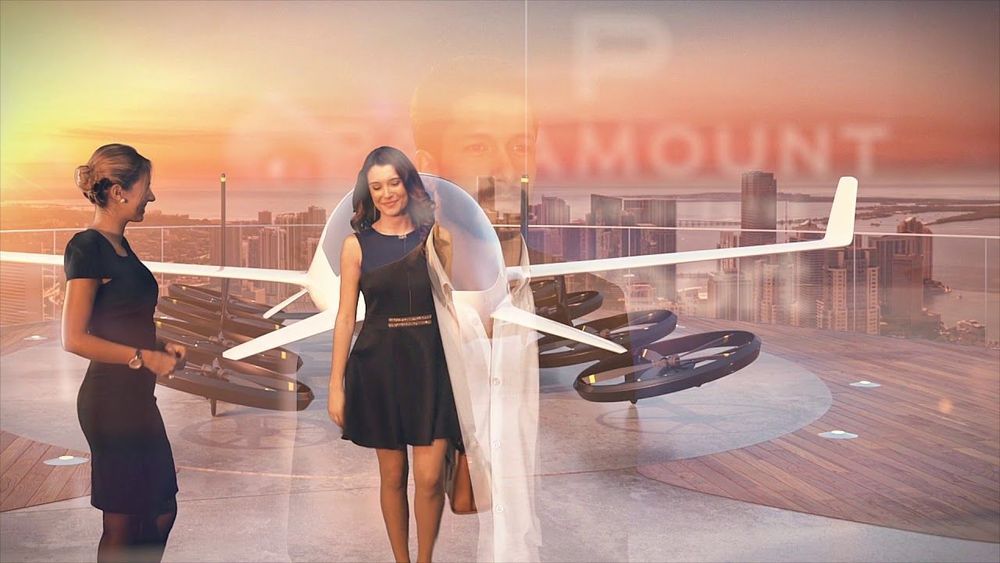
Future residents of Paramount Miami World Center, a 600-unit condominium building now under construction, may be the first in the world with a private skyport for their use, television station WSVN reports.
Infrastructure matters. Flying cars will never, um, get off the ground if they don’t have places to land. Helicopter landing pads and heliports are apparent answers to the question of where to touch down. However, landing spots or sky ports built specifically for flying cars could offer convenience and amenities specifically applicable for or adapted to flying cars.
“Ever since ‘The Jetsons’ came out, America’s been talking about flying cars,” Daniel Kodsi, Paramount Miami World Center’s CEO and developer, said in a statement. “It’s something that inspires you, something that you think about when you’re building a project. You’re saying, ‘Well, what is the future? What’s going to happen in the future?’”
Jose Cordeiro is promoting the development of rejuvenation biotechnologies in Spain and the integration of Latin American immigrants into Spain’s aging society to maintain the country’s productivity. He was at the recent Undoing aging conference in Berlin and gave us an interview about his political goals.
At Undoing Aging 2019, jointly organized by SENS Research Foundation and Forever Healthy Foundation, there was a session focused on the ways to make healthy life extension and medical progress a greater part of the global agenda. Among the speakers there was Jose Cordeiro, the vice chair of Humanity Plus, director of The Millennium Project, fellow of the World Academy of Art and Science, and board member of the Lifeboat Foundation.
Jose earned his Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Mechanical Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts. His thesis was focused on the modeling of the International Space Station. Jose has also studied International Economics and Comparative Politics at Georgetown University in Washington, D.C., and received his MBA in France at INSEAD, where he focused on Finance and Globalization.
Last year, Jose decided to begin his political activities in order to foster the development of rejuvenation biotechnologies in Spain and to work on the integration of Latin American immigrants into Spain’s aging society and thus maintain the country’s productivity. He kindly agreed to give me an interview to discuss more about his ambitious initiative.