Cancer treatment could be revolutionised by the discovery of the origin cells which divide first.
United Neuroscience’s Alzheimer’s vaccine candidate UB-311 was found safe and well-tolerated, triggering an antibody response against beta-amyloid in most of the patients, according to Phase 2a trial results.
https://alzheimersnewstoday.com/…/ub-311-safe-effective-ph…/
For better or worse, robots with humanoid features are often compared to humans—we want to know if they’re anywhere close to doing the same kinds of things that we do, and with a few exceptions, the answer is “probably not.” Humanoid robots are difficult to build and program, but we keep doing it because it makes some amount of sense to have robots that look and function like we do operating in the same environments that we operate in. However, one of the great things about robots is that they don’t have to be constrained by the same boring humanoid-ness that we are, and we can do all kinds of things to them to make them more capable than we’ll ever be.
Leonardo augments humanoid legs with thrusters to help it run and jump.
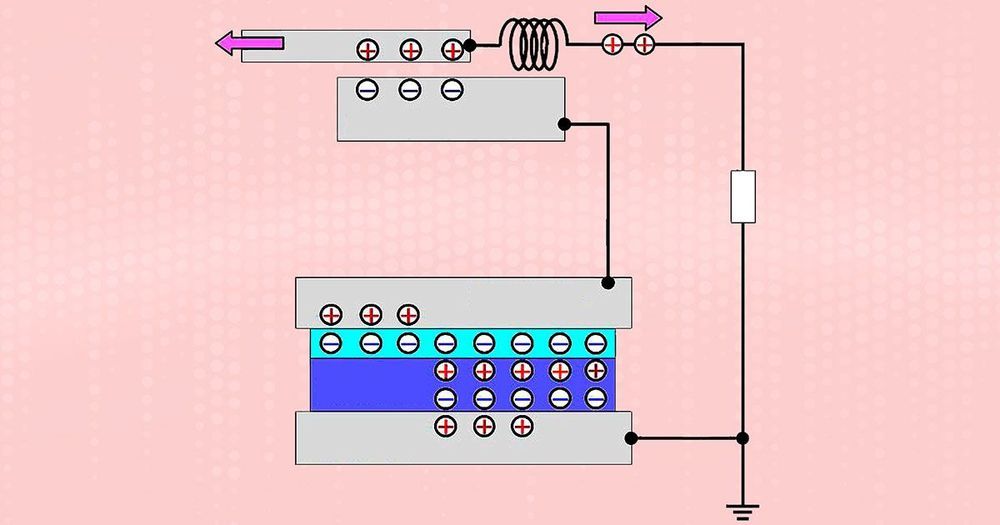
Vibration-based energy harvesting has long promised to provide perpetual power for small electronic components such as tiny sensors used in monitoring systems. If this potential can be realized, external energy sources such as batteries would no longer be needed to power these components.
Scientists at the Tokyo Institute of Technology and the University of Tokyo in Japan believe they have taken a step toward achieving self-powered components by developing a new type of micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) energy harvester. Their approach enables far more flexible designs than are currently possible— something, they say, that is crucial if such systems are to be used for the Internet of Things (IoT) and wireless sensor networks.
Scientists in Japan have developed a MEMS energy harvester charged by an off-chip electret.
Plant-e: roots, shoots, leaves
Posted in futurism
Combining Machine Learning and Your Gut
The link between the gut biome and age is described by longevity researcher Alex Zhavoronkov and a team of his colleagues at Insilico Medicine, an artificial intelligence startup focused on drug discovery, biomarker development, and aging research.
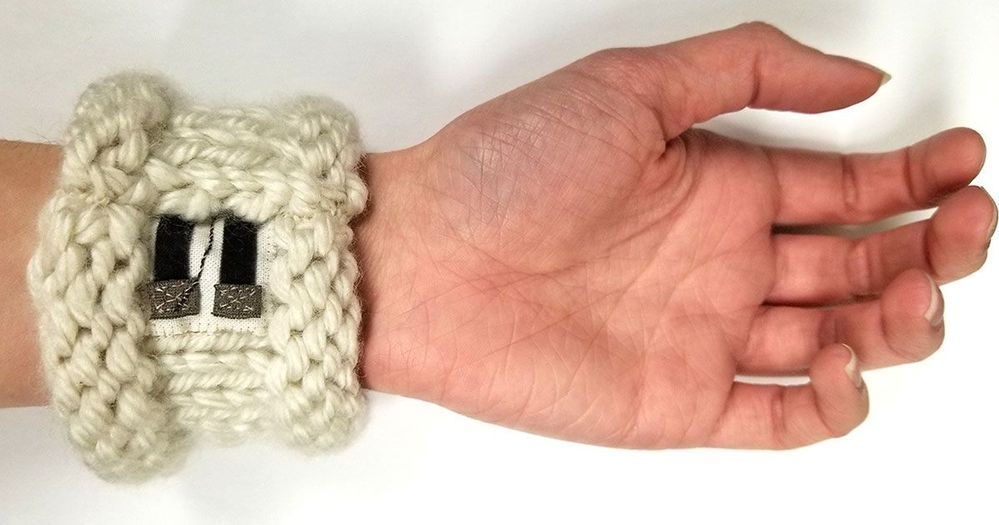
A new way to harvest electricity from body heat could inspire new wearable devices that never need to be plugged in. The millivolts of electricity this thermoelectric technology produces mandates slim power usage from any electronics plugged in to its feed. However, the developers say there already are fitness trackers and medical monitors today that could work within their device’s power envelope. The new, wearable thermoelectric generator is also sourced from non-toxic and non-allergenic substances, making it a viable candidate for wearable technology.
Made with cotton, this generator harvests body heat to power wearable electronics.
Researchers have found bees can do basic mathematics, in a discovery that expands our understanding of the relationship between brain size and brain power.
Building on their finding that honeybees can understand the concept of zero, Australian and French researchers set out to test whether bees could perform arithmetic operations like addition and subtraction.
Solving maths problems requires a sophisticated level of cognition, involving the complex mental management of numbers, long-term rules and short term working memory.
If the forecast calls for rain, you’ll probably pack an umbrella. If it calls for cold, you may bring your mittens. That same kind of preparation happens in buildings, where sophisticated heating and cooling systems adjust themselves based on the predicted weather.
But when the forecast is imperfect—as it often is—buildings can end up wasting energy, just as we may find ourselves wet, cold or burdened with extra layers we don’t need.
A new approach developed by Fengqi You, professor in energy systems engineering at Cornell University, predicts the accuracy of the weather forecast using a machine learning model trained with years’ worth of data on forecasts and actual weather conditions. You combined that predictor with a mathematical model that considers building characteristics including the size and shape of rooms, the construction materials, the location of sensors and the position of windows.
Miracle material graphene – considered the strongest substance known to science – has been used to make eco-friendly paint by manufacturer Graphenstone.
The paint is made from a pure lime base that has been combined with graphene – a recently engineered material hailed as the thinnest, strongest and most conductive ever developed.
It will be distributed in the UK through The Graphene Company, which claims Graphenstone is the most environmentally friendly paint in the world.