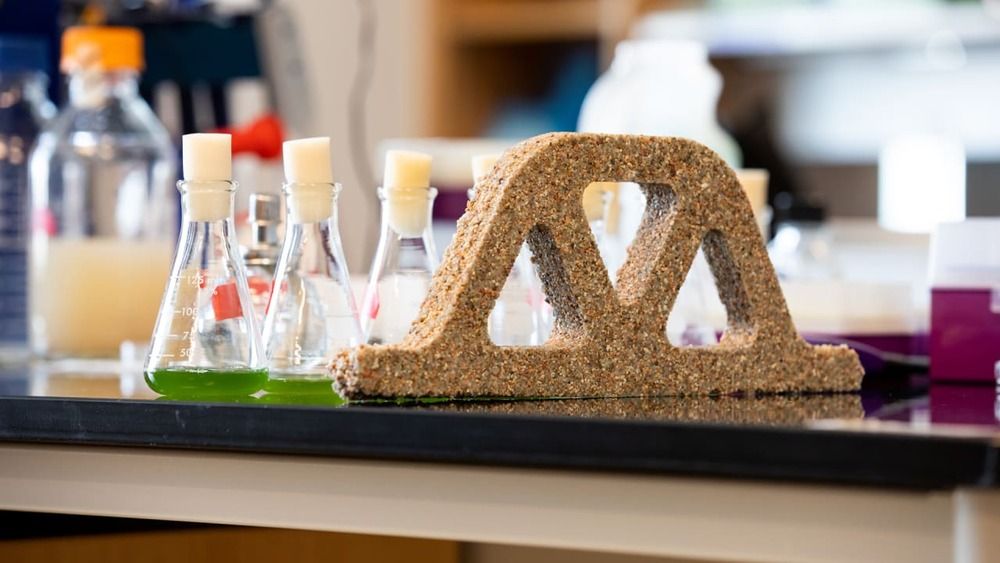
While not as strong as concrete, the bricks could reduce the CO2 footprint of a building, self-heal, and even reproduce.
[Photo: University of Colorado Boulder College of Engineering and Applied Science].



Grey hair seems to be driven by stem cell exhaustion, one of the suggested reasons we age. One researcher believes we can turn back the clock on greying hair.

Melissa Harris’s research points to a new paradigm for hair graying. “We thought that once you go gray the stem cells are all lost — there’s no going back,” Harris said. “But presumably they can be reactivated.”
Molecular biology is not usually the kind of science you can do with the naked eye. Sure enough, Melissa Harris, Ph.D., runs a lab that leans into CRISPR gene-editing tools, single-cell sequencing studies and network-analysis algorithms. But all she needs is a glance to diagnose the state of your melanocyte stem cells.
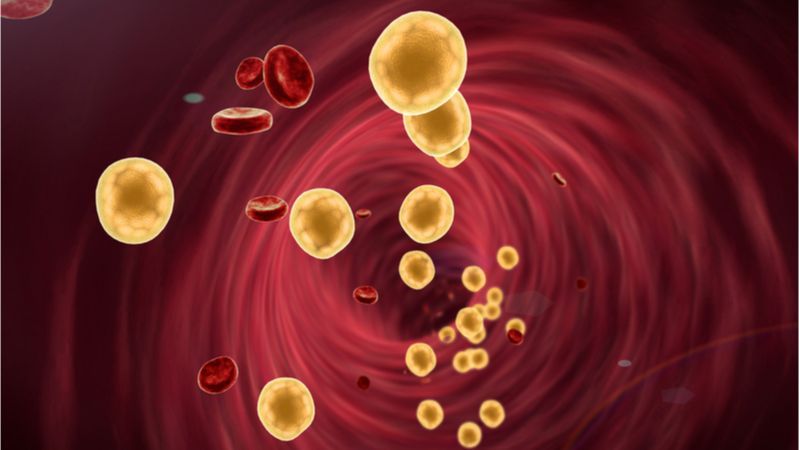
The mitochondria are well known as being the powerhouses of the cell, as they convert nutrients into the energy that our cells need in order to function and remain alive. Until recently, it was believed that they remain within our cells all their lives, but a new discovery by researchers at the Montpellier Cancer Research Institute has turned our understanding on its head.
Introducing the mitochondria
Mitochondria, which are often called the powerhouses of cells, act like miniature factories, converting the food we eat into usable energy in the form of a chemical called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP provides energy to fuel a myriad of cellular processes, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and protein synthesis. ATP is common to all forms of life and is often referred to as the “molecular unit of currency” of intracellular energy transfer.

Drug development is an extremely arduous and costly process, and failure rates in clinical trials that test new drugs for their safety and efficacy in humans remain very high. According to current estimates, only 13.8% of all tested drugs demonstrate ultimate clinical success and obtain approval by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). There are also increasing ethical concerns relating to the use of animal studies. As a result, there has been a world-wide search to find replacements for animal models.
To help address this bottleneck in drug development, Donald Ingber, M.D., Ph.D., and his team at Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, developed the first human “Organ-on-a-Chip” (Organ Chip) model of the lung that recapitulates human organ level physiology and pathophysiology with high fidelity, which was reported in Science in 2010. Organ Chips are microfluidic culture devices composed of a clear flexible polymer the size of a computer memory stick, which contains two parallel hollow channels that are separated by a porous membrane. Organ-specific cells are cultured on one side of the membrane in one of the channels, and vascular endothelial cells recapitulating a blood vessel line the other, while each channel is independently perfused with cell type-specific medium.

For those of you who are unaware of why David Sinclair is viewed with ambivalence. The headline seems complimentary, but the details paint a more complex picture that implies one shouldn’t take what Sinclair says and writes without a grain of salt.
Not yet—but Harvard Medical School professor David Sinclair sure is getting rich, famous, and having a blast while trying.


Zero to 658 in 50 seconds without emissions.
The Bloodhound LSR team has announced plans to challenge for the land speed record using a zero-emissions rocket as part of the next phase of its programme, following successful high-speed tests in South Africa last November.
The land speed record car has returned to the UK Land Speed Centre, Bloodhound’s HQ in Gloucestershire, after having successfully completed its crucial high-speed tests in South Africa.
These tests took place on the Hakskeenpan: a dry lake bed in the Kalahari Desert, during which the land speed record vehicle notched speeds of 628mph (1,010km/h), placing the Bloodhound LSR car, unofficially, as the sixth-fastest car of all time.
“We’re doing a lot better than people think.”–Jerome Glenn “Change is the process by which the future invades our life, and it is important to look at it closely.̶…