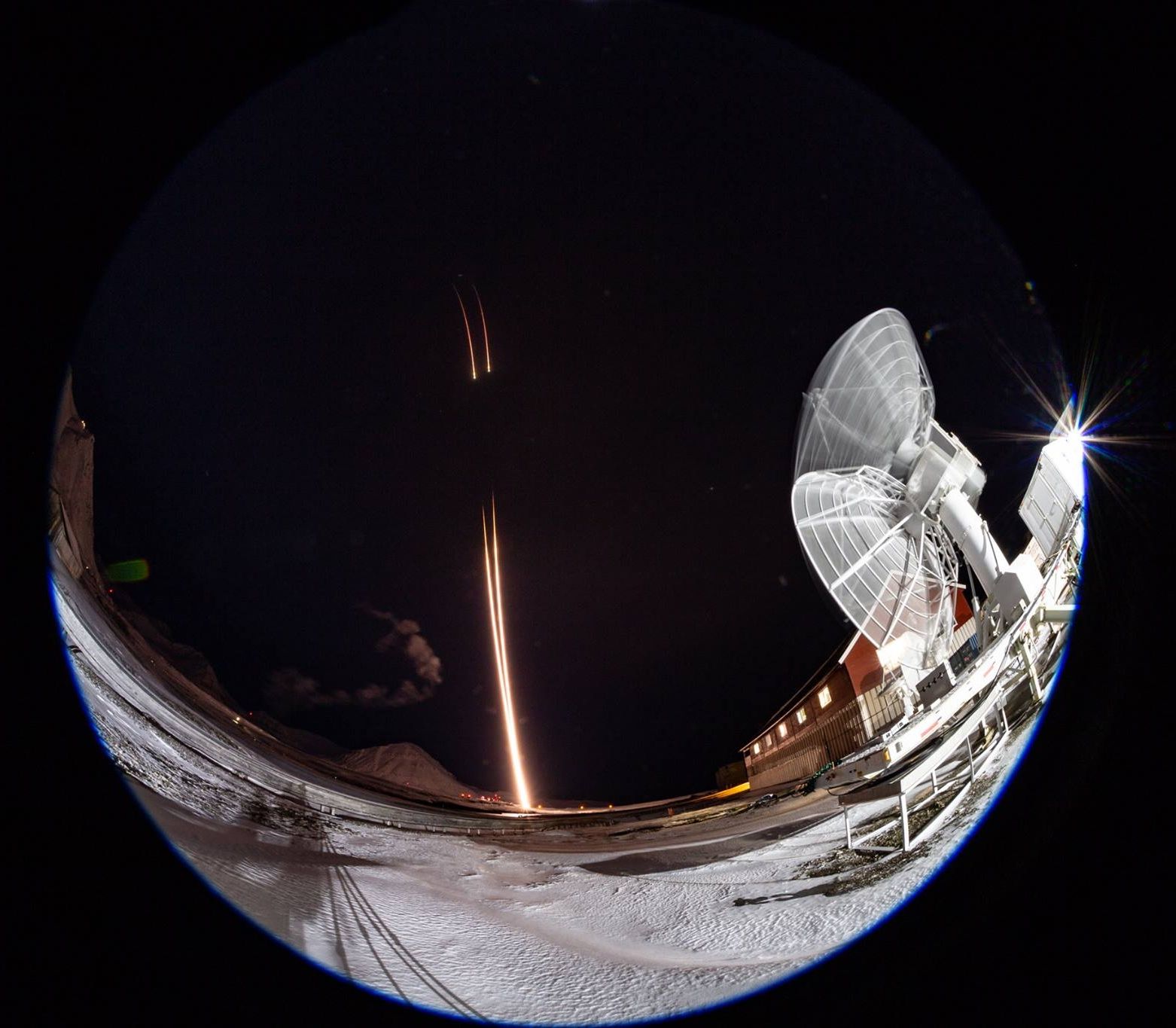
We launched two sounding rockets that will help scientists understand atmospheric escape on our home planet that has applications all over the universe — from predicting which far off planets might be habitable, to piecing together how Mars became the desolate, exposed landscape it is today.
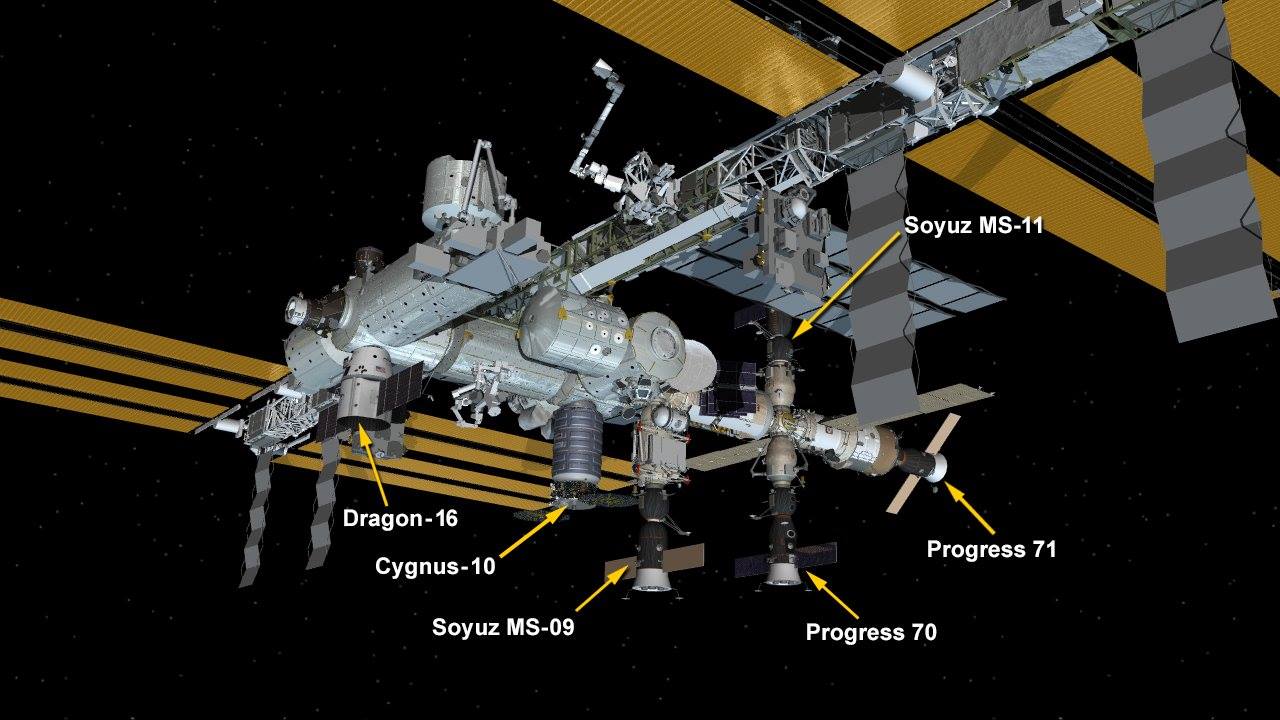
SpaceX’s #Dragon cargo spacecraft was successfully installed on the Earth-facing side of the International Space Station’s Harmony module at 10:36 a.m. EST. While there are now six spaceships attached at the station, the Dragon will spend about five weeks there and return to Earth in January 2019 with more than 4,000 pounds of research, hardware and crew supplies.
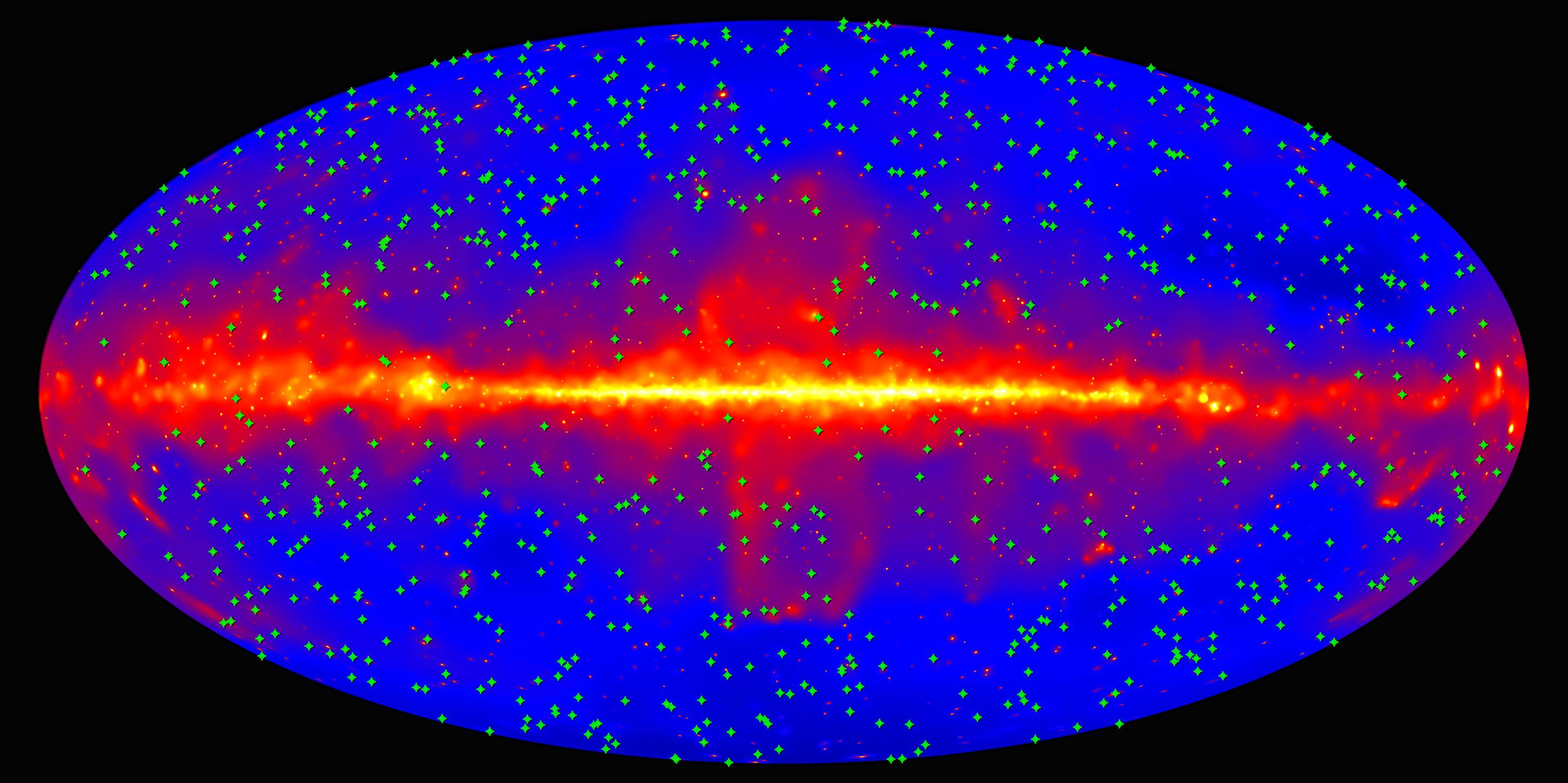
Starlight continues to travel across the cosmos long after its sources have burned out — which means that we can see stars that no longer exist. It also means that our astronomers can study stellar formation without looking at the stars at all, but by observing the gamma rays that shoot out from distant galaxies interacting with the starlight. Take a closer look: https://go.nasa.gov/2G33gsA&h=AT2mbPrj5N1YVp76caneadyE80cXxz…q-2PIES2mQ
Project for Awesome (P4A) 2018 is finally here, and you can help us to win much-needed funds at no cost to you by voting for the videos supporting our charity.
Every year, a number of charities are chosen through voting, and they each receive a sum of money based on what the fundraiser at P4A has raised. In the past, charities have received around $25,000 each, which is a considerable sum, especially for a small non-profit org such as LEAF.
With these funds, we can purchase new equipment to support reporting at conferences and events and to bring our audience the best media experience possible. We are also planning to host a second conference in New York City in 2019, and this will be far more ambitious in scale and will be a two-day event rather than the single-day conference we held this year; with your support, we can make this one of the top conferences supporting the field of rejuvenation biotechnology and make high-quality footage available to the public. Finally, we can use the funds to hire new writers in order to bring you even more high-quality news articles and educational pieces about aging and research.
Intel and AMD could be looking at some stiff competition in the processor game. Fresh off announcing its new Snapdragon 855 mobile chip, the company has announced the Snapdragon 8cx. It’s for laptops instead of smartphones and is by far the most powerful processor the company has ever made. How can you tell? The “X” in the name stands for “extreme.”
While the Snapdragon 8cx is not the company’s first PC chip (that honor goes to the quickly forgotten Snapdragon 850), it’s the first one that could make Intel take note. Like the 855, the Snapdragon 8cx uses a 7nm manufacturing process. It has the same octa-core design with four high-performance cores based on the Cortex A76 and four low-power cores based on the A55. That’s really the end of the similarities, though.
Qualcomm has cranked the clock speed of all of its “Kryo 495” cores way up in the Snapdragon 8cx, but it won’t say exactly how high. The chip has 10MB of cache between L2 and L3 — the 855 only has 3MB. That makes the Snapdragon 8cx better at running heavy apps, and there’s support for up to 16GB of system memory. You can also check the boxes for NVMe and UFS3.0 storage.
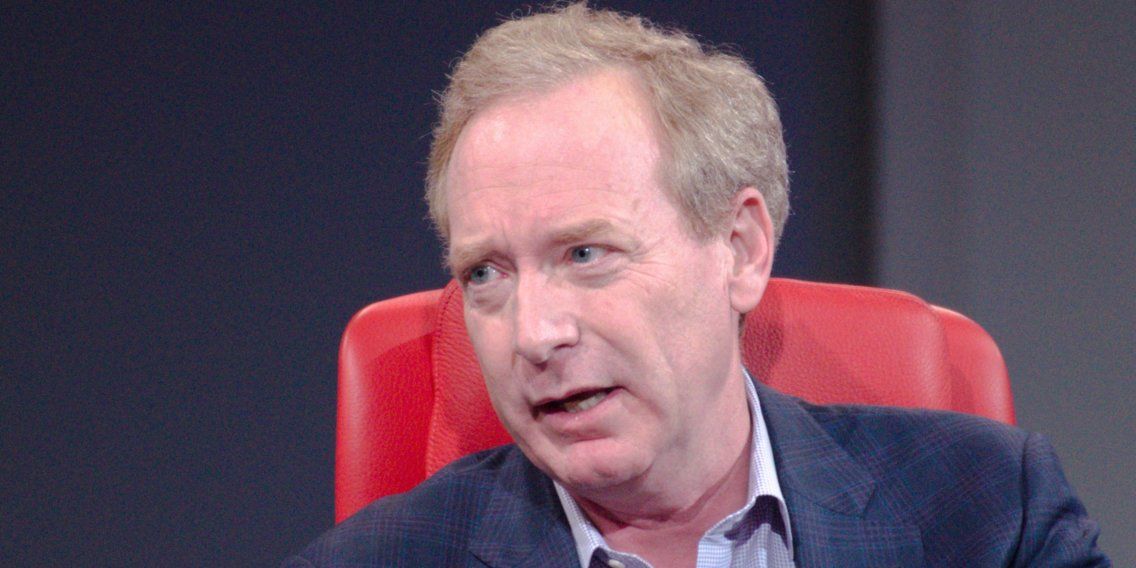
Microsoft said Thursday it was adopting a set of ethical principles for the use of its facial recognition technology, and urged the government to follow its lead with regulations barring unlawful discrimination and focusing on transparency.
In a blog post, Microsoft president Brad Smith pushed for the government, as well as tech companies, to regulate facial-recognition technology and ensure it “creates broad societal benefits while curbing the risk of abuse.”
“The facial recognition genie, so to speak, is just emerging from the bottle,” Smith said in the post. “Unless we act, we risk waking up five years from now to find that facial recognition services have spread in ways that exacerbate societal issues.”
Newborns with vitamin D deficiency have an increased risk of schizophrenia later in life, a team of Australian and Danish researchers has reported.
The discovery could help prevent some cases of the disease by treating vitamin D deficiency during the earliest stages of life.
The study, led by Professor John McGrath from The University of Queensland (UQ) in Australia and Aarhus University in Denmark, found newborns with vitamin D deficiency had a 44 per cent increased risk of being diagnosed with schizophrenia as adults compared to those with normal vitamin D levels.