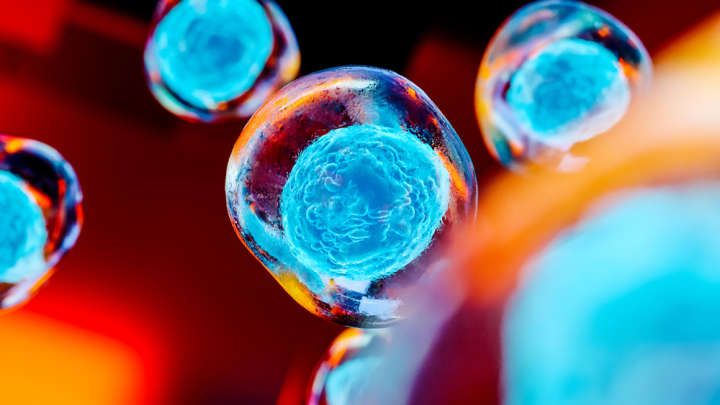
For the first time, scientists have reprogrammed cells from a 114-year-old woman into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), a move which they describe as a significant step toward understanding “the underlying mechanisms of extreme longevity and disease resistance.”
iPS cells are adult cells that have been genetically reprogrammed into an embryonic stem cell-like state and are able to give rise to any of the specialized cell types of the body, whether it’s neurons, blood cells, or heart cells.
Until this new project, researchers weren’t even certain whether they could create viable iPS cells from someone so elderly, let alone a supercentenarian. Now they have shown it’s possible to effectively make these aged cells resemble young pluripotent cells, the researchers believe they might have made a step towards the reversal of cellular aging.