Compared to existing shields, rust gives much better protection per unit weight.



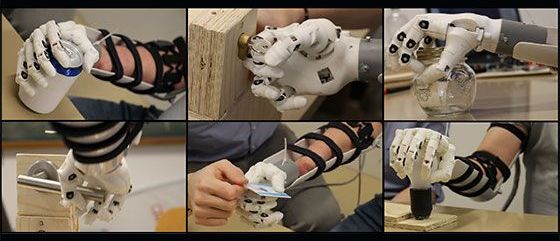
Prosthetic hands restore only some of the function lost through amputation. But combining electrical signals from forearm muscles with other sources of information, such as eye tracking, promises better prostheses. A study funded by the SNSF gives specialists access to valuable new data.
Page Content
The hand is a precious limb. Its 34 muscles and 20 joints enable movements of great precision and complexity which are essential for interacting with the environment and with others on a daily basis. Hand amputation thus has severe physical and psychological repercussions on a person’s life. Myoelectric prosthetic hands, which work by recording electrical muscle signals on the skin, allow amputees to regain some lost function. But dexterity is often limited and the variability of the electrical signals from the forearm alone makes the prosthetics sometimes unreliable. Henning Müller, professor of business informatics, is investigating how combining data from myoelectric signals with other sources of information could lead to better prosthetics. Müller has now made available to the scientific community a dataset that includes eye tracking and computer vision as well as other information (electromyography and acceleration sensor data).

Yes, you can detect another person’s consciousness. Christof Koch described a method called ‘zap and zip’. Transcranial magnetic stimulation is the ‘zap’. Brain activity is detected with an EEG and analyzed with a data compression algorithm, which is the ‘zip’. Then the value of the perturbational complexity index (PCI) is calculated. If the PCI is above 0.31 then you are conscious. If the PCI is below 0.31 then you are unconscious. If this link does not work then go to the library and look at the November 2017 issue of Scientific American. It is the cover story.
Zapping the brain with magnetic pulses while measuring its electrical activity is proving to be a reliable way to detect consciousness.
Do you suffer from knee pain?
Dr. Theodore Ho talks about the rapidly expanding possibilities of stem cells to be used in reversing or slowing the aging process. He discusses his previous and current work with the brain, including such methods as tissue clearing, multifiber photometry and optogenetics, and single resolution calcium imaging and control. Dr. Ho is a neuroscientist and stem cell biologist studying the mechanisms and causes of biological aging and potential strategies to slow or reverse them, in order to prevent the onset of age
Associated diseases to help us live healthier and longer lives.
He completed a four-year joint bachelor’s/master’s degree program in.
Human developmental and regenerative biology/bioengineering at.
Harvard University, and he received his PhD in Biophysics from the.
University of California San Francisco, studying stem cell aging in the lab of Dr. Emmanuelle Passegue. In college he developed a nanoparticle drug delivery system, in graduate school he discovered previously unknown mechanisms of cellular and molecular aging of stem cells, and now in the Deisseroth lab he is using optical recording and perturbation of neuronal activity to study neural circuit dynamics that control behavior. This talk was given at a TEDx event using the TED conference format but independently organized by a local community.
***Update: Launch is now scheduled for 3:21 p.m. EST on Saturday, Feb. 15. Live coverage begins at 2:45.
Watch a cargo spacecraft lift off from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on a resupply mission to the International Space Station! 🚀
Launch is targeted at 3:43 p.m. EST on Friday, Feb. 14 for Northrop Grumman’s 13th commercial resupply services mission. A previous launch attempt on Feb. 9 was scrubbed after off-nominal readings from a ground support sensor. The Cygnus cargo spacecraft, loaded with approximately 7,500 pounds of research, supplies and hardware, will launch atop an Antares rocket from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport. This Cygnus spacecraft is named the S.S. Robert H. Lawrence, in honor of the first African American to be selected as an astronaut.

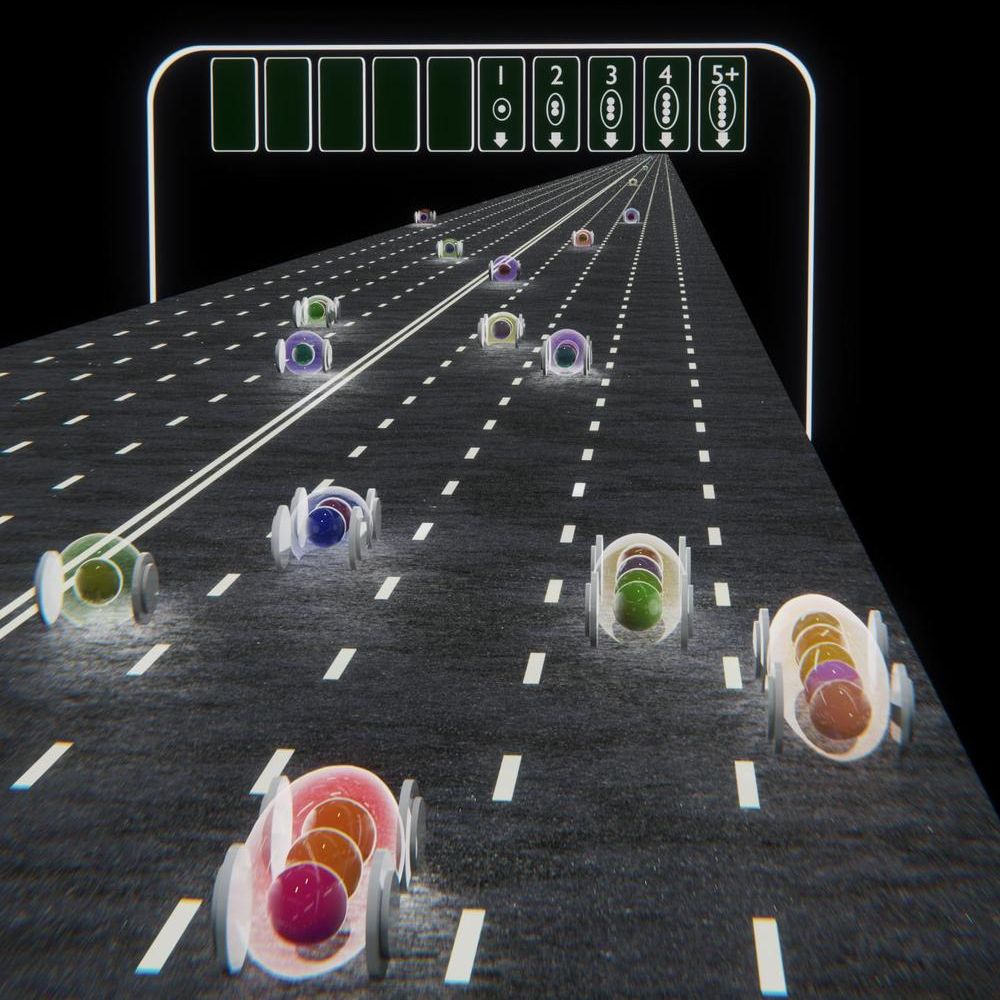
A research team led by professors from the University of Pittsburgh Department of Physics and Astronomy has announced the discovery of a new electronic state of matter.
Jeremy Levy, a distinguished professor of condensed matter physics, and Patrick Irvin, a research associate professor are coauthors of the paper “Pascal conductance series in ballistic one-dimensional LaAIO3/SrTiO3 channels.” The research focuses on measurements in one-dimensional conducting systems where electrons are found to travel without scattering in groups of two or more at a time, rather than individually.
The study was published in Science on Feb. 14. A video outlining the paper’s findings can be seen here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kDjGiH8OnqU&feature=youtu.be