Experts found a way to cure diabetes using human stem cells.


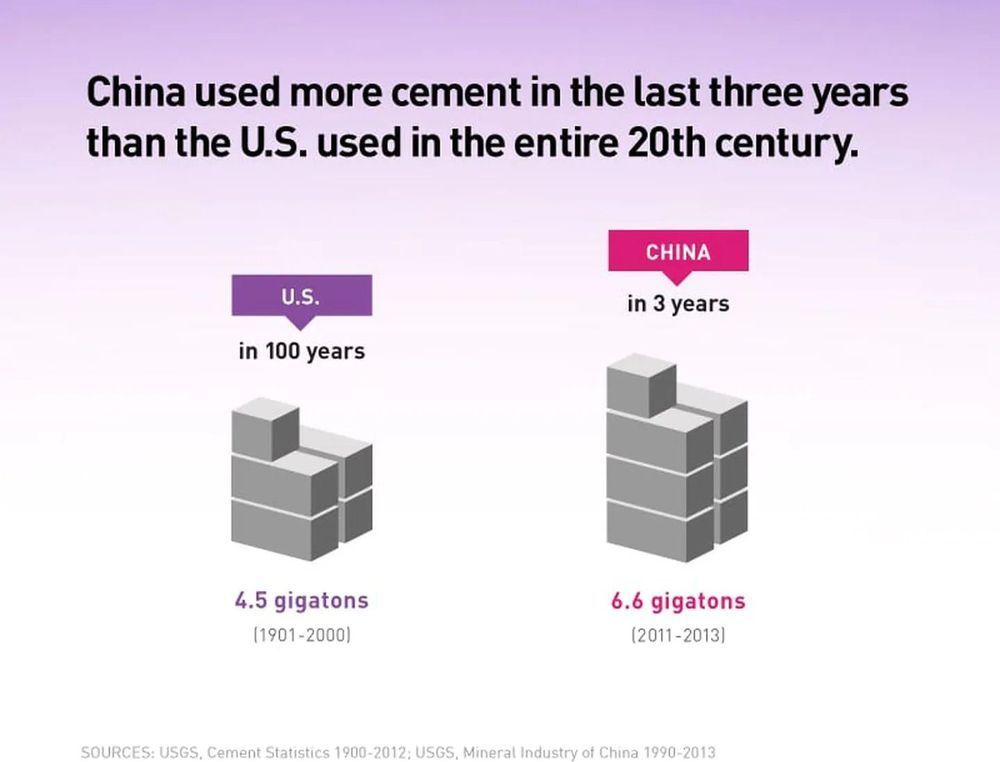
Of course, the computers and data centers that support AI’s complex algorithms are very much dependent on electricity. While that may seem pretty obvious, it may be surprising to learn that AI can be extremely power-hungry, especially when it comes to training the models that enable machines to recognize your face in a photo or for Alexa to understand a voice command.
The scale of the problem is difficult to measure, but there have been some attempts to put hard numbers on the environmental cost.
For instance, one paper published on the open-access repository arXiv claimed that the carbon emissions for training a basic natural language processing (NLP) model—algorithms that process and understand language-based data—are equal to the CO2 produced by the average American lifestyle over two years. A more robust model required the equivalent of about 17 years’ worth of emissions.

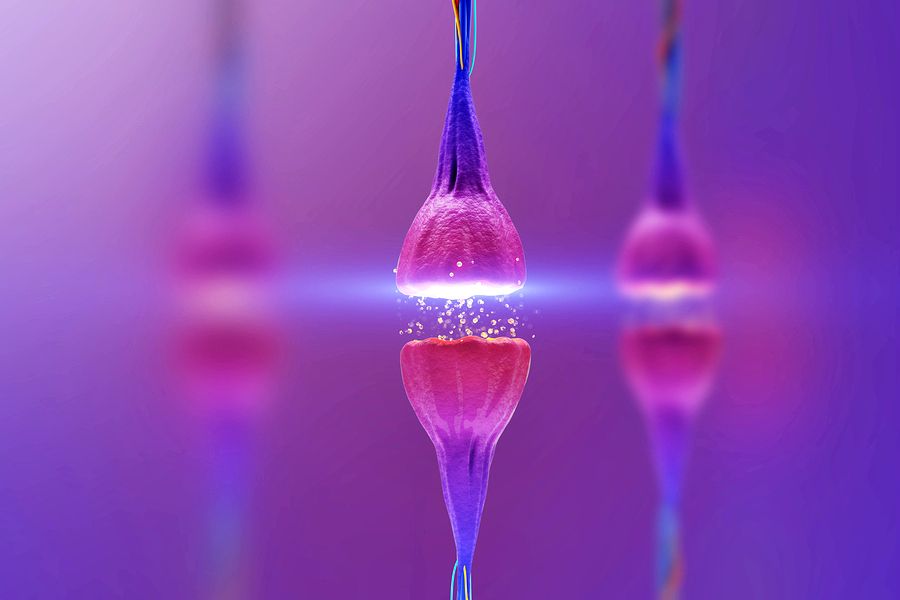
In focal brain diseases, a patient’s neural network loses key connections, preventing the brain from functioning as it miraculously should. But what if there was a way to restore those connections? An EU funded study is seeking to do just that by getting real biological neurons to synaptically communicate with artificial ones.
Though still in the early stages of study, SYNCH, a team of scientists from the U.K., Switzerland, Germany, and Italy, have created what they describe as a “synaptically connected brain-silicon Neural Closed-loop Hybrid system.” Basically, they’ve taken actual brain cells and artificial brain cells, and got them talking back and forth over the internet.

Read updates in Chinese: 新冠病毒疫情最新消息汇总
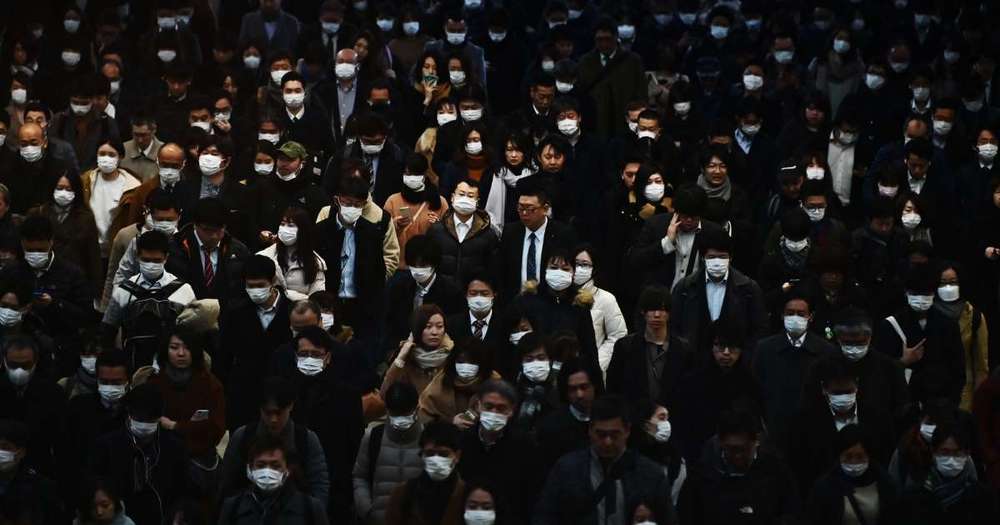
Fears take hold that a global pandemic is inevitable.
From eastern Asia, Europe, the Middle East, the Americas and Africa, a steady stream of new cases on Friday fueled the sense that the new coronavirus epidemic may be turning into a global pandemic, with some health officials saying it may be inevitable.
Dr. Frank Sabatino is currently the Health Director of the Balance for Life Health Retreat, a lifestyle education center specializing in plant based nutrition, health rejuvenation, stress management, therapeutic fasting and detoxification.
“Our task is to make nature, the blind force of nature, into an instrument of universal resuscitation and to become a union of immortal beings.“
- Nikolai F. Fedorov
We hold faith in the technologies & discoveries of humanity to END AGING and Defeat involuntary Death within our lifetime.
Working to Save Lives with Age Reversal Education.
========== Perpetual Life Creed ==========
We believe that all of life is sacred and that we have been given this one life to make unlimited. We believe in our Creator’s divine plan for all of humanity to have infinite lifespans in perfect health and eternal joy, rendering death to be optional.
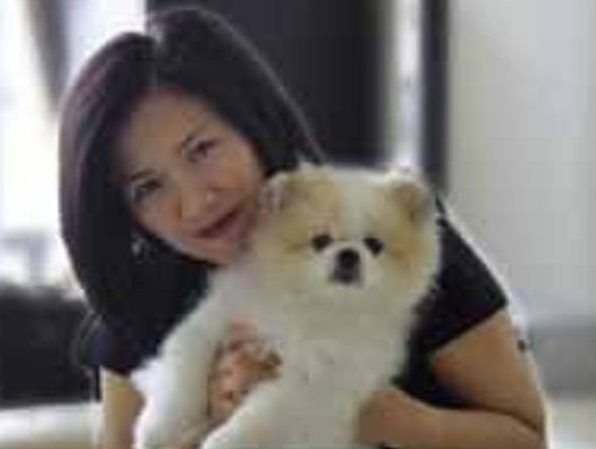

THE PET dog of a coronavirus patient in Hong Kong has tested positive for the deadly disease.
The owner of the dog, Yvonne Chow Hau Yee, who lives with her beloved Pomeranian, tested her pet pooch after being diagnosed with COVID-19.
The dog has been quarantined by officials, suggesting they have concerns that the pet could pass on the disease.

There are decisions being made right now that could have an effect on global populations for generations to come. As part of this project, we commissioned an artist to investigate some of the themes raised in the podcasts. This work of fiction imagines a future where gene editing has become mainstream and discusses the moral, ethical and political divides that this might create.