Coyote malware uses Windows UI Automation to target 75 banks and crypto sites in Brazil, risking credential theft.





Vanderbilt University Medical Center researchers have developed a groundbreaking new method for the recovery of hearts from deceased organ donors after circulatory death (DCD). The method (rapid recovery with extended ultra-oxygenated preservation [REUP]), which involves flushing the donor heart with a cold oxygenated preservation solution after death, avoids the disadvantages of two existing preservation methods, both of which reanimate the heart, one that has ethical questions and another that

Optical sensors have undergone significant evolution, transitioning from discrete optical microsystems toward sophisticated photonic integrated circuits (PICs) that leverage artificial intelligence (AI) for enhanced functionality. This review systematically explores the integration of optical sensing technologies with AI, charting the advancement from conventional optical microsystems to AI-driven smart devices. First, we examine classical optical sensing methodologies, including refractive index sensing, surface-enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA), surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), surface plasmon-enhanced chiral spectroscopy, and surface-enhanced fluorescence (SEF) spectroscopy, highlighting their principles, capabilities, and limitations. Subsequently, we analyze the architecture of PIC-based sensing platforms, emphasizing their miniaturization, scalability, and real-time detection performance. This review then introduces the emerging paradigm of in-sensor computing, where AI algorithms are integrated directly within photonic devices, enabling real-time data processing, decision making, and enhanced system autonomy. Finally, we offer a comprehensive outlook on current technological challenges and future research directions, addressing integration complexity, material compatibility, and data processing bottlenecks. This review provides timely insights into the transformative potential of AI-enhanced PIC sensors, setting the stage for future innovations in autonomous, intelligent sensing applications.
Naked mole rats are well known for living far longer lives than any rodent ought to have. It’s just one of their amazing talents for surviving in a challenging, even hostile underground environment.
A fascinating new study led by researchers from the University of Rochester in the US has shown a single gene could play a significant role in their longevity, one that could be transferred into other mammals to give their own life spans a nudge.
The gene – a version of what’s known as hyaluranon synthase 2 – produces an abundance of high-molecular-mass hyaluronic acid (HMM-HA), a compound already thought to mediate the risk of cancer in naked mole rats (Heterocephalus glaber).
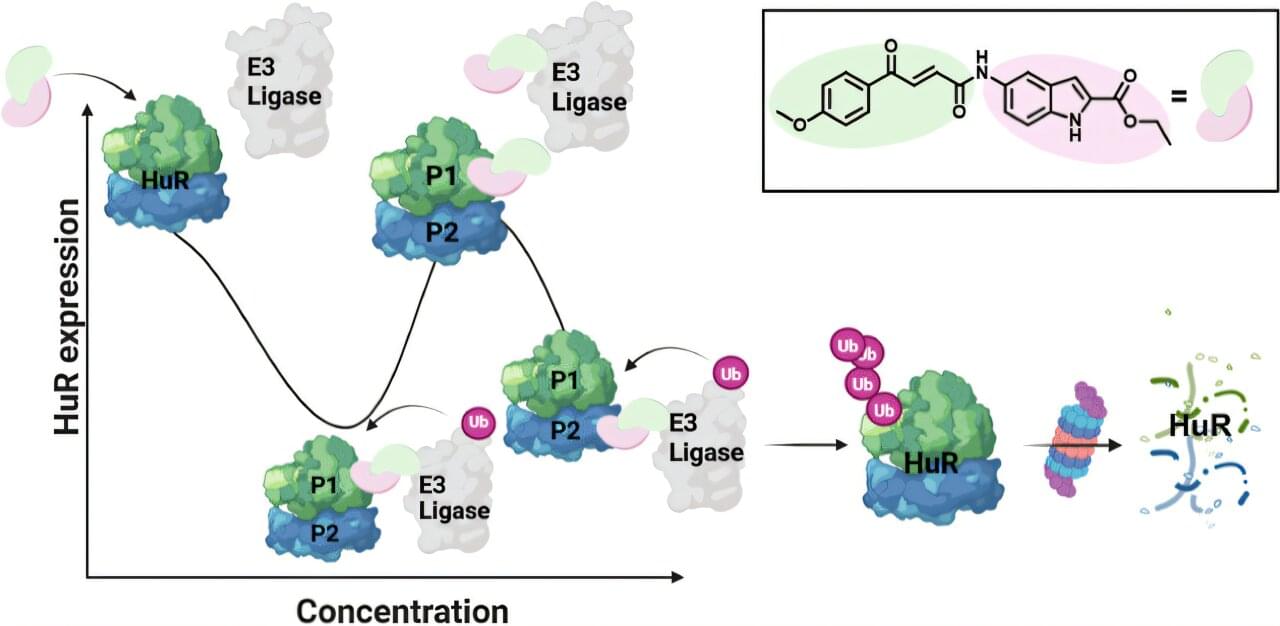
In the battle against aggressive breast cancer, a once-elusive target is now within reach—thanks to a breakthrough from a team from the Faculty of Medicine at Hebrew University. Dr. Raphael Benhamou and M.Sc. student Liann Kassabri have developed innovative druglike molecules capable of degrading HuR, a key RNA-binding protein that stabilizes oncogenes and fuels cancer progression.
HuR (also known as ELAVL1) has long been labeled “undruggable” due to its structural flexibility and lack of a conventional active site. Overexpressed in many cancer types—particularly breast cancer—HuR fortifies malignant cells by protecting mRNAs that drive cell growth and survival.
“We knew that simply blocking HuR wasn’t enough,” says Dr. Benhamou. “We needed to eliminate it altogether.” Strikingly, this elimination led to a three to four orders of magnitude improvement in anticancer properties compared to traditional HuR-binding molecules that do not induce degradation.

Remote, scalable cognitive behavioral therapy–based chronic pain programs are effective for treating individuals with high-impact chronic pain.
Importance Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) skills training interventions are recommended first-line nonpharmacologic treatment for chronic pain, yet they are not widely accessible.
Objective To examine effectiveness of remote, scalable CBT-based chronic pain (CBT-CP) treatments (telehealth and self-completed online) for individuals with high-impact chronic pain, compared with usual care.
Design, Setting, and Participants This comparative effectiveness, 3-group, phase 3 randomized clinical trial enrolled 2,331 eligible patients with high-impact chronic musculoskeletal pain from 4 geographically diverse health care systems in the US from January 2021 through February 2023. Follow-up concluded in April 2024.
An over-the-counter cough medicine may be the key to slowing the progression of Parkinson’s disease.
Called Ambroxol, the drug is commonly used to break up phlegm, but early studies have shown it can also prevent the build-up of misfolded clumps of protein in the brain, known as Lewy bodies – a hallmark of Parkinson’s and other types of dementia.
Robarts scientist Dr. Stephen Pasternak is leading a phase 2 clinical trial to further study Ambroxol’s potential as a disease-modifying drug.
“Current treatments for Parkinson’s target the symptoms of the disease, such as movement, but don’t change the long-term progression of pathology in the brain,” he explained. “We hope Ambroxol will be a disease-changing drug.”
Dr. Stephen Pasternak is leading a phase 2 clinical trial to study Ambroxol, an over-the-counter cough medicine, with the goal of slowing or stopping the progression of Parkinson’s Disease Dementia.