The high-tech outfit’s features includes compatibility with vaping and a subwoofer soundsystem.



The Pentagon has created top secret military artificial intelligence that has a higher intellect than humans.
A Defense Intelligence Agency experiment shows AI and humans have different risk tolerances when data is scarce.
In the 1983 movie WarGames, the world is brought to the edge of nuclear destruction when a military computer using artificial intelligence interprets false data as an imminent Soviet missile strike. Its human overseers in the Defense Department, unsure whether the data is real, can’t convince the AI that it may be wrong. A recent finding from the Defense Intelligence Agency, or DIA, suggests that in a real situation where humans and AI were looking at enemy activity, those positions would be reversed.
Artificial intelligence can actually be more cautious than humans about its conclusions in situations when data is limited. While the results are preliminary, they offer an important glimpse into how humans and AI will complement one another in critical national security fields.


GE offshore wind: massive offshore turbine Haliade-X 12MW looks like a winner.
GE-Hitachi Nuclear Energy may be a receding opportunity.
GE might sell its steam power business and rationalise its fossil fuel interests.
The power and renewables businesses are important in considering investment in GE.

The Newtonian laws of physics explain the behavior of objects in the everyday physical world, such as an apple falling from a tree. For hundreds of years Newton provided a complete answer until the work of Einstein introduced the concept of relativity. The discovery of relativity did not suddenly prove Newton wrong, relativistic corrections are only required at speeds above about 67 million mph. Instead, improving technology allowed both more detailed observations and techniques for analysis that then required explanation. While most of the consequences of a Newtonian model are intuitive, much of relativity is not and is only approachable though complex equations, modeling, and highly simplified examples.
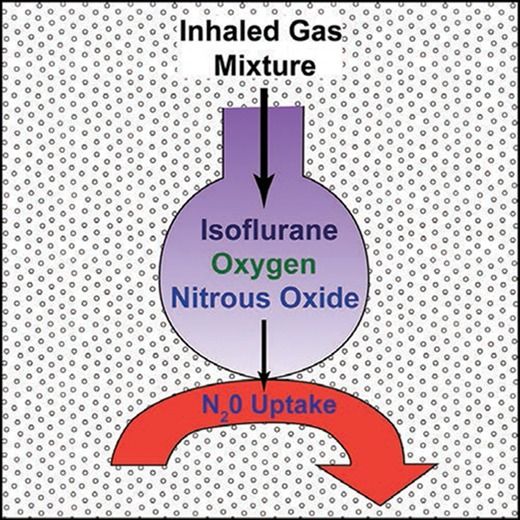
In this issue, Korman et al.1 provide data from a model of the second gas effect on arterial partial pressures of volatile anesthetic agents. Most readers might wonder what this information adds, some will struggle to remember what the second gas effect is, and others will query the value of modeling rather than “real data.” This editorial attempts to address these questions.
The second gas effect2 is a consequence of the concentration effect3 where a “first gas” that is soluble in plasma, such as nitrous oxide, moves rapidly from the lungs to plasma. This increases the alveolar concentration and hence rate of uptake into plasma of the “second gas.” The second gas is typically a volatile anesthetic, but oxygen also behaves as a second gas.4 Although we frequently talk of inhalational kinetics as a single process, there are multiple steps between dialing up a concentration and the consequent change in effect. The key steps are transfer from the breathing circuit to alveolar gas, from the alveoli to plasma, and then from plasma to the “effect-site.” Separating the two steps between breathing circuit and plasma helps us understand both the second gas effect and the message underlying the paper by Korman et al.1

DisplayPort Alt Mode 2.0 is a new standard from the Video Electronics Standards Association that allows USB 4 to offer all the bells and whistles of the DisplayPort 2.0 standard as well as transmitting USB data. That means support for 8K displays at 60Hz with HDR, 4K displays at 144Hz with HDR, or even 16K (15360×8460) displays at 60Hz with compression. It’s a big step towards USB Type-C becoming a true jack-of-all trades connector.
The USB 4 spec can already transmit DisplayPort data, but AnandTech reports that the new standard remaps USB-C’s high speed data pins to unlock more bandwidth for video. USB 4 is bidirectional, meaning it can carry up to 40Gbps of data in either direction. However, video doesn’t need to go both ways — you only really need data to pass from your laptop to your monitor (for example). This alt mode means that all that bandwidth can be used to just send video one way, meaning you get a maximum raw bandwidth of up to 80Gbps.
“Everybody here’s been vaccinated anyway”
“It’s a hoax”
Given that I can’t see the man talking’s mouth due to his face mask I have trouble blindly assuming this video is true. Is that my own cognitive dissonance though? Was awfully weird to see Pence walking around the Mayo Clinic face mask less. Almost seemed to me like he felt like he had protection against the virus. Was it just his religious faith that inspired him to act with such little caution or is there something big here that we aren’t being told?
Fox News’ John Roberts Caught on Hot Mic Discussing COVID-19 as a Hoax.
& said “everyone here has been vaccinated anyway!”
Video became Viral after it captured an informal exchange between Roberts and New York Times photographer Doug Mills.

What are some of ways that technology can be used to combat things like racism, bipartisan politics, Islamophobia, antisemitism, and extreme prejudice? Especially when these things are systemically embedded in certain cultures to the point that rationality seems to fly out the window? I see conversations on social media in peaceful international groups such as this one as a great potential stepping stone to mediate the tension between groups who seem to be devoted to blind hatred for one another. What are some other ways technology can advance social and political sciences?
“This article analyzes the narratives of Islamophobia in Hindu Nationalism (Hindutva). Specifically, it analyzes how Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, from the Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), articulates Islamophobia in his speeches, interviews, and podcasts. In total, a discourse analysis of 35 such documents has been conducted. Conceptually, this article applies the notion of language-games to understand how Modi articulates Islamophobia. The article contends that while Modi’s Islamophobia is executed subtly, it is nonetheless a function of the way in which Hindutva conceives of Muslims as subordinate to Hindus. Two Islamophobic narratives in Modi’s political discourse have been mapped out: the erasure of Indian Muslim histories in Modi’s economic development agenda, and the characterization of Hinduism as having a taming effect on Islam in India. The article provides a conceptual overview of language-games and a review of how Hindutva defines Hindus and Muslims, before analyzing how Modi articulates Islamophobia. The article concludes by suggesting that a Hindutva-driven Islamophobia may have permeated into the Hindu mainstream.”