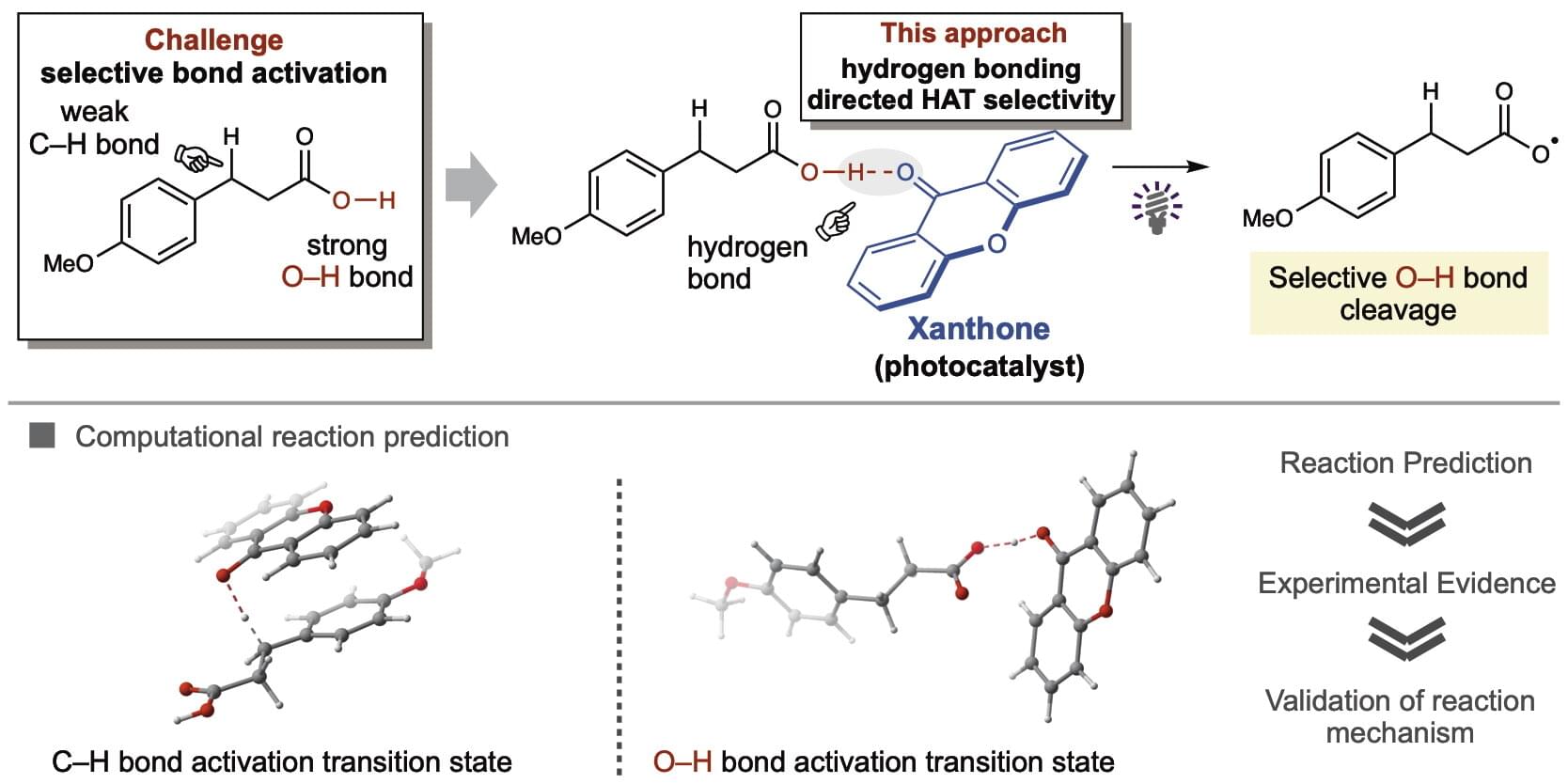
Carboxylic acids are ubiquitous in bioactive organic molecules and readily available chemical building blocks. Carboxylic acids can be converted into carboxy radicals that can initiate versatile carbon–carbon and carbon–heteroatom bond formations, which are highly desirable for developing materials and pharmaceuticals. Currently, however, there are few applicable methods that use inexpensive catalysts.
To this end, researchers from WPI-ICReDD and University of Shizuoka have developed a facile hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) method that selectively transforms carboxylic acids into carboxy radicals using xanthone, an inexpensive commercial organic ketone photocatalyst. This research was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
HAT converts substrates into radical species by removing a hydrogen atom and ketones are highly accessible, inexpensive, and known for HAT photocatalysis. However, selective HAT for carboxylic acids is challenging because the O–H bond is stronger than adjacent C–H bonds. Nonetheless, using the artificial force–induced reaction (AFIR) method, a computational technique developed at ICReDD, the authors identified xanthone as a promising ketone photocatalyst for selective O–H bond HAT.