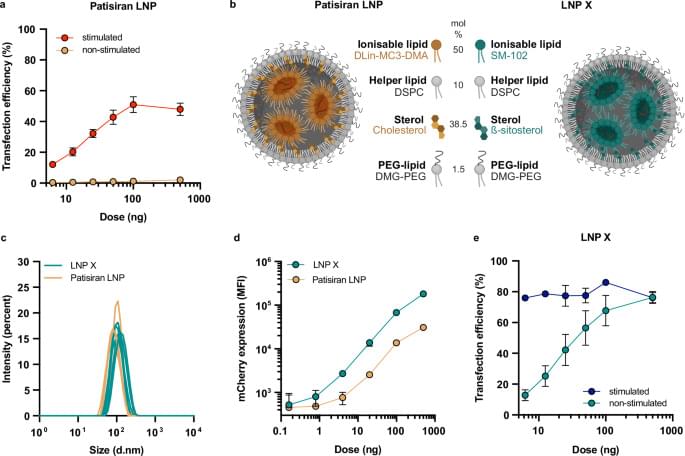
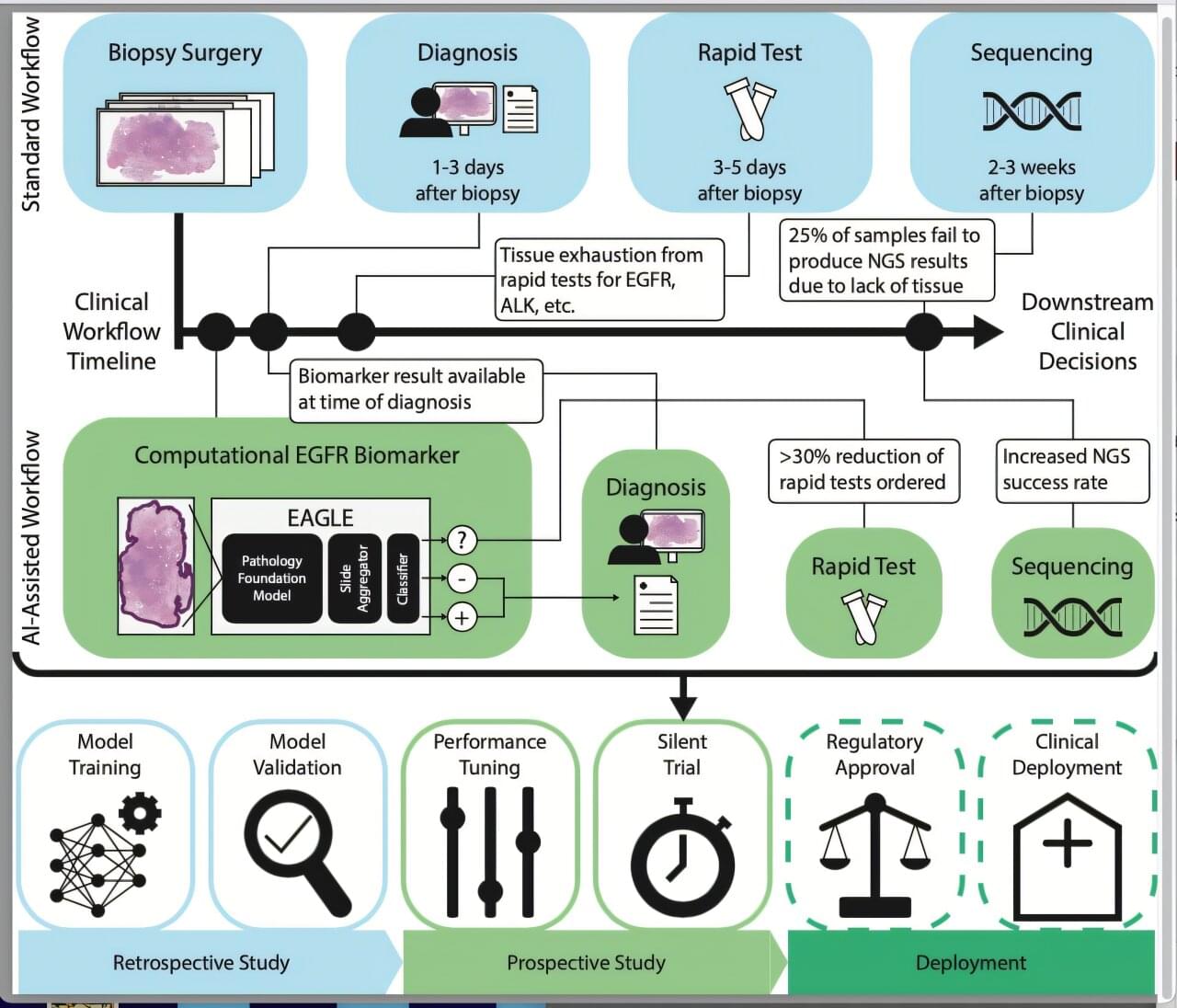
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be made more sustainable by making practical changes, such as reducing the number of decimal places used in AI models, shortening responses, and using smaller AI models, according to research from UCL published in a new UNESCO report.
In recent years, the use of generative AI has expanded rapidly, with large language models (LLMs) developed by companies such as OpenAI, Meta and Google becoming household names. For example, OpenAI’s ChatGPT service, powered by the GPT-4 LLM, receives about 1 billion queries each day.
Each generation of LLMs has become more sophisticated than the last, better able to perform tasks like text generation or knowledge retrieval. This has led to a vast and increasing demand on resources such as electricity and water, which are needed to run the data centers where these AI models are trained and deployed.