SolarWinds releases critical security patches for Access Rights Manager software to prevent potential data breaches and code execution.
Airlines, banks and broadcasters were among the companies around the world reporting disruptions, citing technical issues.
How do you teach ChatGPT common sense? Train it on questions that adults would never think to ask. In this week’s “The Joy of Why,” computer scientist Yejin Choi talks with co-host Steven Strogatz about how training AI can mimic the “why-this, why-that” curiosity of a toddler.
Show The Joy of Why, Ep Will AI Ever Have Common Sense? — Jul 18, 2024.
A 64-year-old named Mark has spent the last year learning how to control devices like his laptop and phone using a brain implant. And thanks to OpenAI, it’s gotten a whole lot easier to do.
The neurotech startup Synchron said Thursday it’s using OpenAI’s latest artificial intelligence models to build a new generative chat feature for patients with its brain-computer interface, or BCI.
A BCI system decodes brain signals and translates them into commands for external technologies. Synchron’s model is designed to help people with paralysis communicate and maintain some independence by controlling smartphones, computers and other devices with their thoughts.
A survey of people in the US has revealed the widespread belief that artificial intelligence models are already self-aware, which is very far from the truth.
The path toward a cancer diagnosis is anything but fun. Among the least enjoyable aspects of the journey are the invasive and often excruciating biopsies that are needed to collect information about the genetic mutations or chromosomal abnormalities of the cells in a growing tumor. This information is critical for an accurate diagnosis of a patient’s cancer, as well as for prognosis predictions and treatment selections. At the recent Acoustical Society of America meeting in Ottawa, Canada, Roger Zemp of the University of Alberta reported on an alternative method that he and his colleagues have developed for extracting this genetic information that uses sound waves rather than tissue removal. “Traditional biopsies with their big needles are scary and painful,” says Joy Wang, a master’s student who works with Zemp. “Our method is pain free and can provide clearer information about a cancer’s genetics.”
Biopsy needles are akin to hole punches for the flesh. These long, hollow needles can be over 2 mm in diameter and typically punch out a core of flesh between 1 and 2 mm in diameter. For comparison, the average blood-draw needle is half a millimeter in diameter. The large holes made by the biopsy needles significantly increase the likelihood of pain, swelling, bruising, or infection at the biopsy site, both during the biopsy collection and for days afterward.
The prospect of being left black and blue can cause patients significant anxiety. The worry can become so high that it can stop a person from getting a questionable lump or bump checked out. Therefore, researchers have been searching for less invasive, less frightening methods to retrieve the information that biopsies provide. Alternative techniques could also allow for earlier detection of some cancers, Zemp says.
How Droplets Form Inside Cells
Posted in futurism
A new theory that accounts for disorder in a protein’s structure sheds light on the development inside a cell of tiny droplets that are vital to a cell’s function.
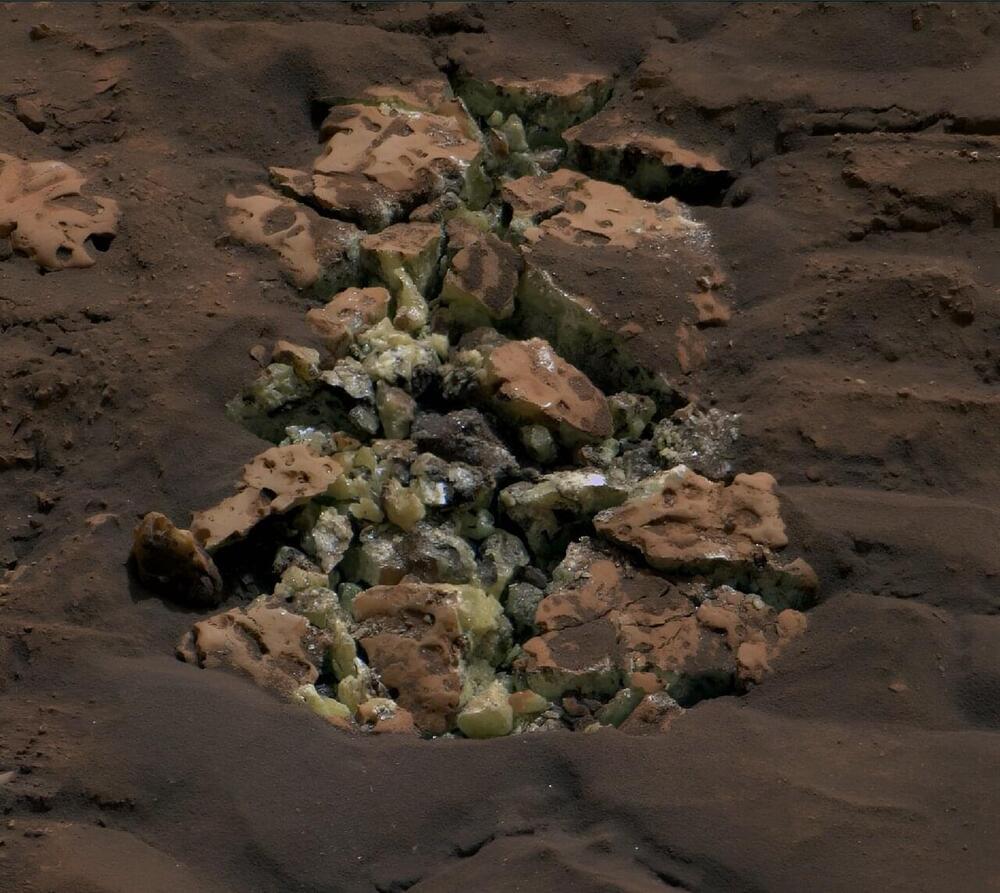
Scientists were stunned on May 30 when a rock that NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover drove over cracked open to reveal something never seen before on the Red Planet: yellow sulfur crystals.
Johns Hopkins engineers have created a new optical tool that could improve cancer imaging. Their approach, called SPECTRA, uses tiny nanoprobes that light up when they attach to aggressive cancer cells, helping clinicians distinguish between localized cancers and those that are metastatic and have the potential to spread throughout the body.
In a new Physical Review Letters study, scientists propose a new method for combining solid-state spin qubits with nanomechanical resonators for scalable and programmable quantum systems.