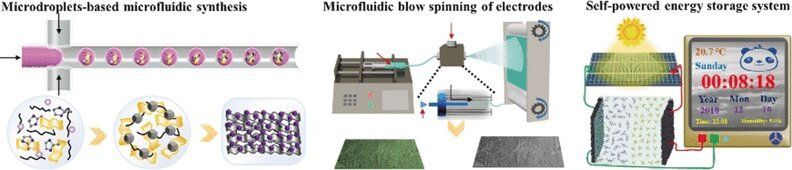
Evening gowns with interwoven LEDs may look extravagant, but the light sources need a constant power supply from devices that are as well wearable, durable, and lightweight. Chinese scientists have manufactured fibrous electrodes for wearable devices that are flexible and excel by their high energy density. Key for the preparation of the electrode material was a microfluidic technology, as shown in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
Dresses emitting sparkling light from hundreds of small LEDs may create eye-catching effects in ballrooms or on fashion shows. But wearable electronics can also mean sensors integrated in functional textiles to monitor, for example, water evaporation or temperature changes. Energy storage systems powering such wearable devices must combine deformability with high capacity and durability. However, deformable electrodes often fail in long-term operation, and their capacity lags behind that of other state-of-the-art energy storage devices.
Electrode materials usually benefit from a fine balance of porosity, conductivity, and electrochemical activity. Material scientists Su Chen, Guan Wu, and their teams from Nanjing Tech University, China, have looked deeper into the material demands for flexible electrodes and developed a porous hybrid material synthesized from two carbon nanomaterials and a metal-organic framework. The nanocarbons provided the large surface area and excellent electrical conductivity, and the metal-organic framework gave the porous structure and the electrochemical activity.



 Malignant tumors release cells into a patient’s blood, meaning that researchers could detect the presence of cancer through a blood sample. The problem is that the cancerous cells enter the bloodstream and circulate so quickly that they may not appear in one single blood sample. This issue is what sparked Dr. Hayes and his team to develop a device that actually searches for the cancerous cells.
Malignant tumors release cells into a patient’s blood, meaning that researchers could detect the presence of cancer through a blood sample. The problem is that the cancerous cells enter the bloodstream and circulate so quickly that they may not appear in one single blood sample. This issue is what sparked Dr. Hayes and his team to develop a device that actually searches for the cancerous cells.
