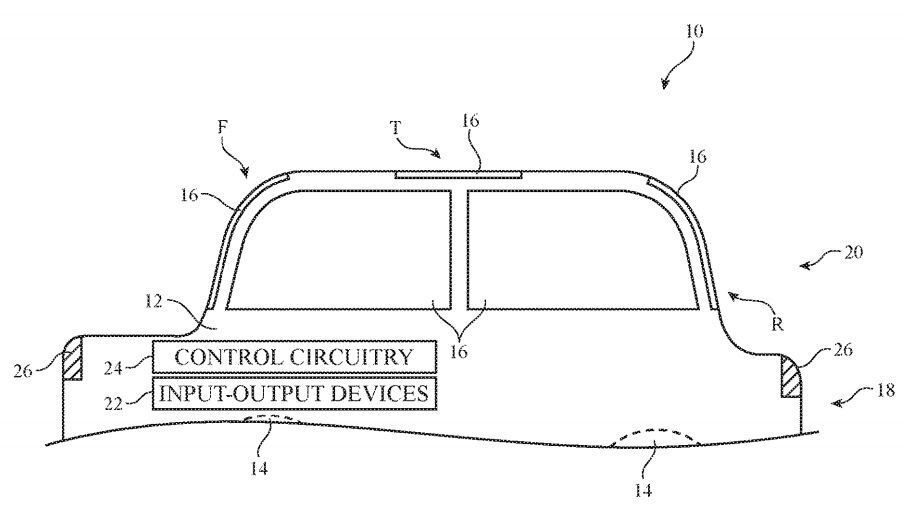
A recent patent filing offers a window into future forays by Apple into automotive design. Apple is exploring artificial intelligence systems that will enable future motorists to enjoy windows that continuously change characteristics as they drive.
Titled “Systems with adjustable windows,” U.S. Patent No. 10,625,580 envisions glass components that control light, reflection and heat conductance based on both user preference and sensory input.
The smart windows would contain multiple adjustable layers sandwiched between two panes of glass that could perform such functions as keeping a cool interior, providing privacy to occupants, allowing viewing through haze and blocking harmful sunlight radiation.