And he’s been searching for it for a decade.
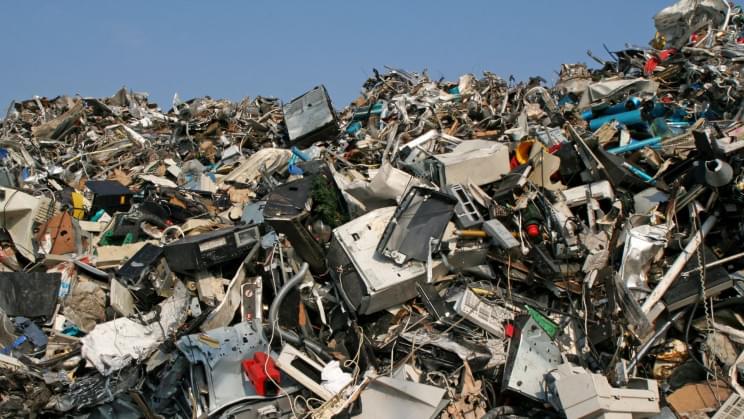
It’s a nightmare scenario that might become increasingly common in a world of digital currency. A man threw away an old PC hard drive while doing a quick spring clean of his home in Newport Wales, U.K., in 2013. Fast-forward almost a decade and he’s still desperately petitioning to be allowed to go through his local landfill.
The reason the man, 35-year-old IT engineer James Howells, wants to trawl through his local trash site is that the hard drive he threw out included a wallet with 7,500 Bitcoin.
At the time he threw out the hard drive, that amount of Bitcoin would have been worth 665 thousand dollars (500 thousand pounds). Today, it would have made him a millionaire, as it would be worth a total of 357 million dollars.
In an interview with The Guardian in 2013, Howells explained how he had been looking through the landfill, which is roughly the size of a football field. “I had a word with one of the guys down there, explained the situation. And he actually took me out in his truck to where the landfill site is, the current ditch they’re working on. It’s about the size of a football field, and he said something from three or four months ago would be about three or four feet down,” Howells explained.
Roughly $140 billion in ‘lost’ Bitcoin worldwide Following initial scavenging efforts for the lost hard drive, Howells seemed resigned to losing the digital fortune. More recently, however, he has recruited local residents in Newport to help him search for the device. Anyone who helps him find it, he says, is promised to be rewarded millions — if the hard drive is still readable, that is. The 35-year-old also offered to donate 25 percent of the potential findings — roughly 70 million dollars– to a “Covid Relief Fund” for his home city.
Full Story: