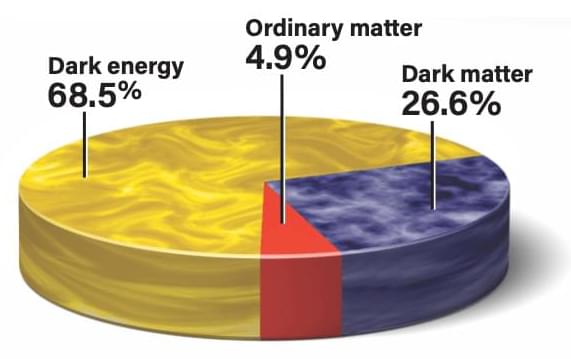
Are dark matter and dark energy stable and constant? Since we don’t understand their true physical nature, we can’t be sure. But astronomers can see if they vary depending on which direction in space they look. This is a test of whether the universe is lopsided or the same everywhere (the physics term for this is isotropic). It turns out that the amount of dark matter surrounding galaxies is the same in every direction, and the strength of dark energy is also the same in every direction.
To see whether the influence of dark matter and dark energy has changed over cosmic time, astronomers look deep into space. Distant light is old light, so telescopes act as time machines, probing billions of years into the past. By measuring the redshift and brightness of distant objects, astronomers map out the expansion history of the universe. Dark matter dominated for most of that history since the Big Bang. That’s because when the universe was smaller, the gravity exerted by dark matter was stronger, while the force exerted by dark energy has stayed the same. Now is the only time in the entire history of the universe when the two entities’ influences are about equal. In the future, the effects of dark energy will increasingly dominate, and the universe will accelerate forever.