A new approach to water treatment could be cheaper, produce less waste and possibly help fix nitrate pollution in California.
- By Meg Wilcox on June 27, 2019
They used to call it RoboBee—a flying machine half the size of a paperclip that could flap its pair of wings 120 times a second. It was always tethered to a power source, limiting its freedom. Now, though, RoboBee becomes RoboBee X-Wing, as Harvard researchers have added solar cells and an extra pair of wings, freeing the robot to blast off to a galaxy far, far away. Or at least partway across the room, as it can sustain flight for only half a second, and only indoors.
But hey, baby steps. The teeniest of quadrotors measure a few inches across and weigh a third of an ounce. RoboBee X-Wing is about the same size as those untethered fliers, but weighs a hundredth of an ounce, which earns it the distinction of being the lightest aerial vehicle to manage sustained untethered flight. One day that could make it ideal for navigating tight, sensitive spaces in a galaxy very, very near.
You’ve read your last complimentary article this month. To read the full article, SUBSCRIBE NOW. If you’re already a subscriber, please sign in and and verify your subscription.
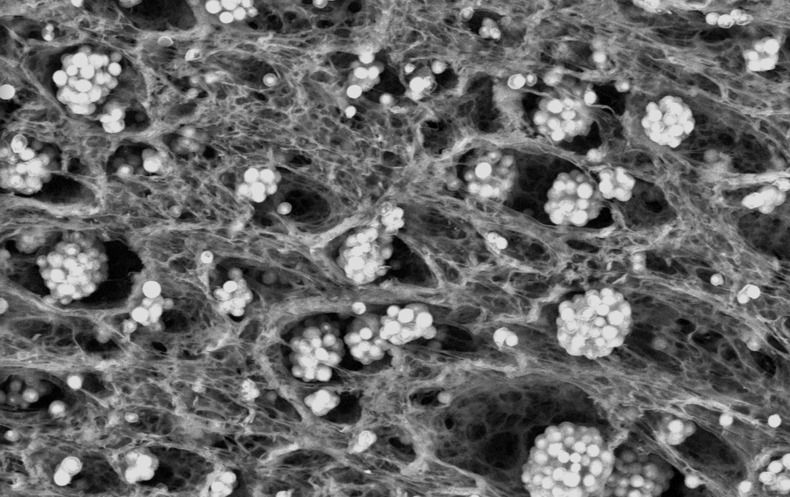
An exciting breakthrough from Columbia University researchers demonstrates a new way to grow human hair follicles using 3D printed molds. This is the first time human hair follicle cells have been grown completely in lab conditions, opening up a potentially unlimited source of hair follicles for future hair restoration surgical procedures.
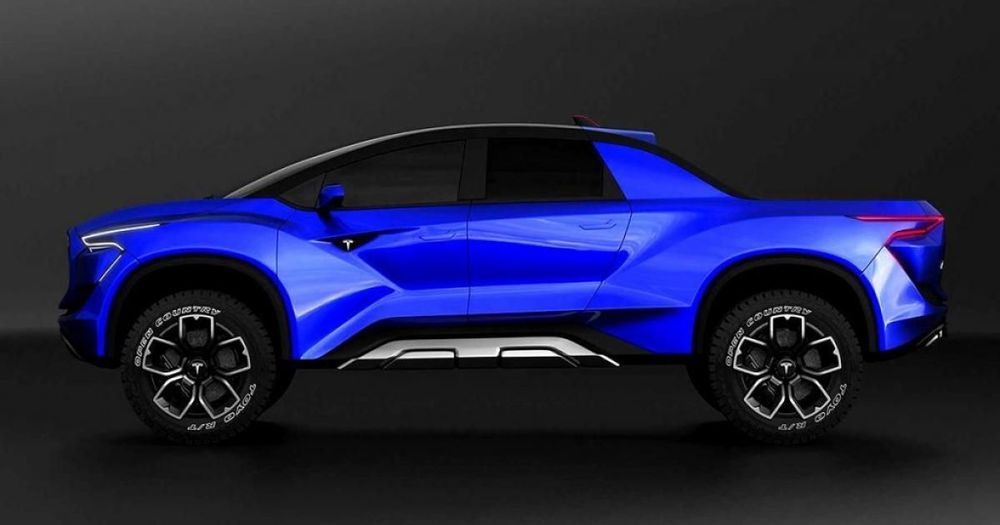

Tesla and the electric cars they produce are renowned for their sleek design and high tech capabilities. There is currently a saloon car (Model S), a budget version (Model 3), an SUV (Model X) and of course, the famous Roadster model which was launched into space by Elon Musk himself. There’s also a mid-sized car which is planned to be released later this year — the model Y, which is in between an S and an X. So, what’s missing from this luxury vehicle line-up? A pickup truck, of course! Tesla’s got that covered as well!
The latest Tesla model that Elon Musk has revealed is an electric pickup truck. Currently, it’s just a rumor and there has been no leak of the design or any details about this truck. That said, there is no shortage of speculation and many people seem to have their own opinions on the appearance of the new Tesla truck. However, one thing that is known is Tesla’s are expensive. Not only the design but the interior and the technology they scream luxury and offer amazing comfort. They are arguably some of the best electric vehicles on the market today but costs can run upwards of $100,000 for the latest models.
So, as anyone would expect, the new pickup truck was predicted to cost in the region of high five-, maybe even low six-figures. However, the price range has been revealed and it’s shocked everyone — apart from the Model 3, this could be one of the cheapest Tesla cars ever produced.


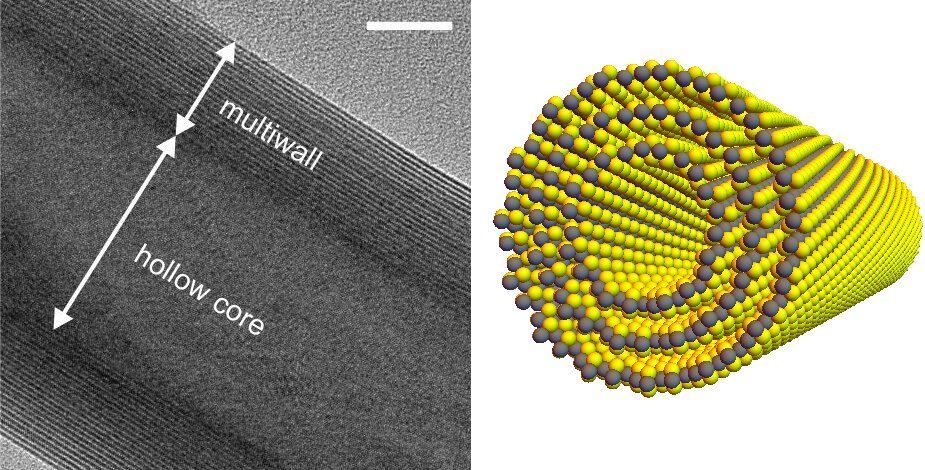
Physicists have discovered a novel kind of nanotube that generates current in the presence of light. Devices such as optical sensors and infrared imaging chips are likely applications, which could be useful in fields such as automated transport and astronomy. In future, if the effect can be magnified and the technology scaled up, it could lead to high-efficiency solar power devices.
Rice University’s solar-powered approach for purifying salt water with sunlight and nanoparticles is even more efficient than its creators first believed.
Researchers in Rice’s Laboratory for Nanophotonics (LANP) this week showed they could boost the efficiency of their solar-powered desalination system by more than 50% simply by adding inexpensive plastic lenses to concentrate sunlight into “hot spots.” The results are available online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“The typical way to boost performance in solar-driven systems is to add solar concentrators and bring in more light,” said Pratiksha Dongare, a graduate student in applied physics at Rice’s Brown School of Engineering and co-lead author of the paper. “The big difference here is that we’re using the same amount of light. We’ve shown it’s possible to inexpensively redistribute that power and dramatically increase the rate of purified water production.”

