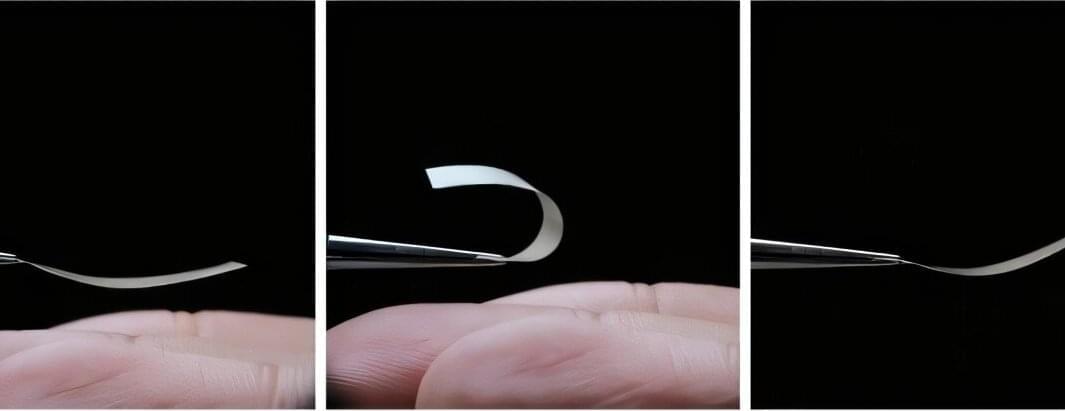
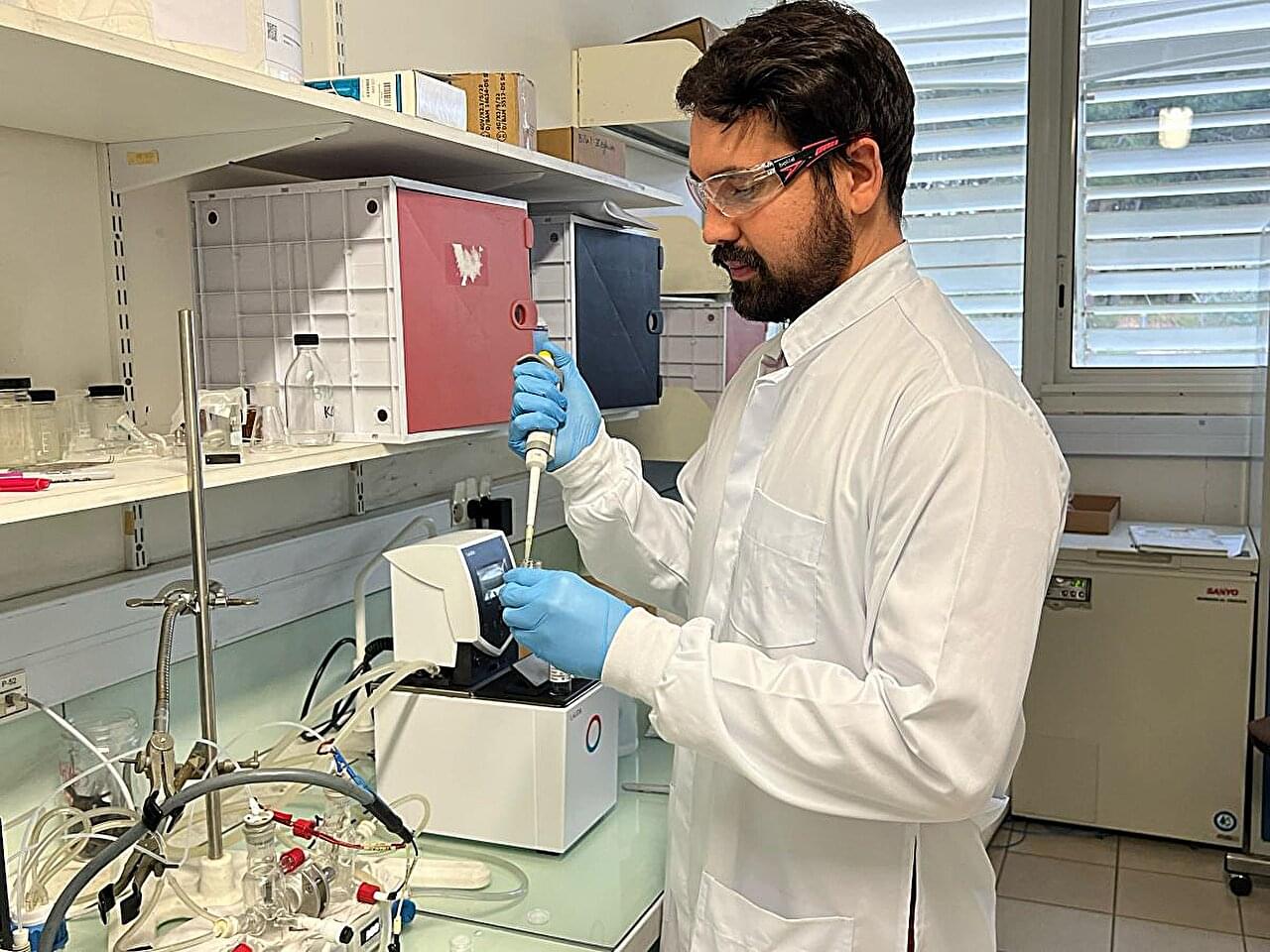
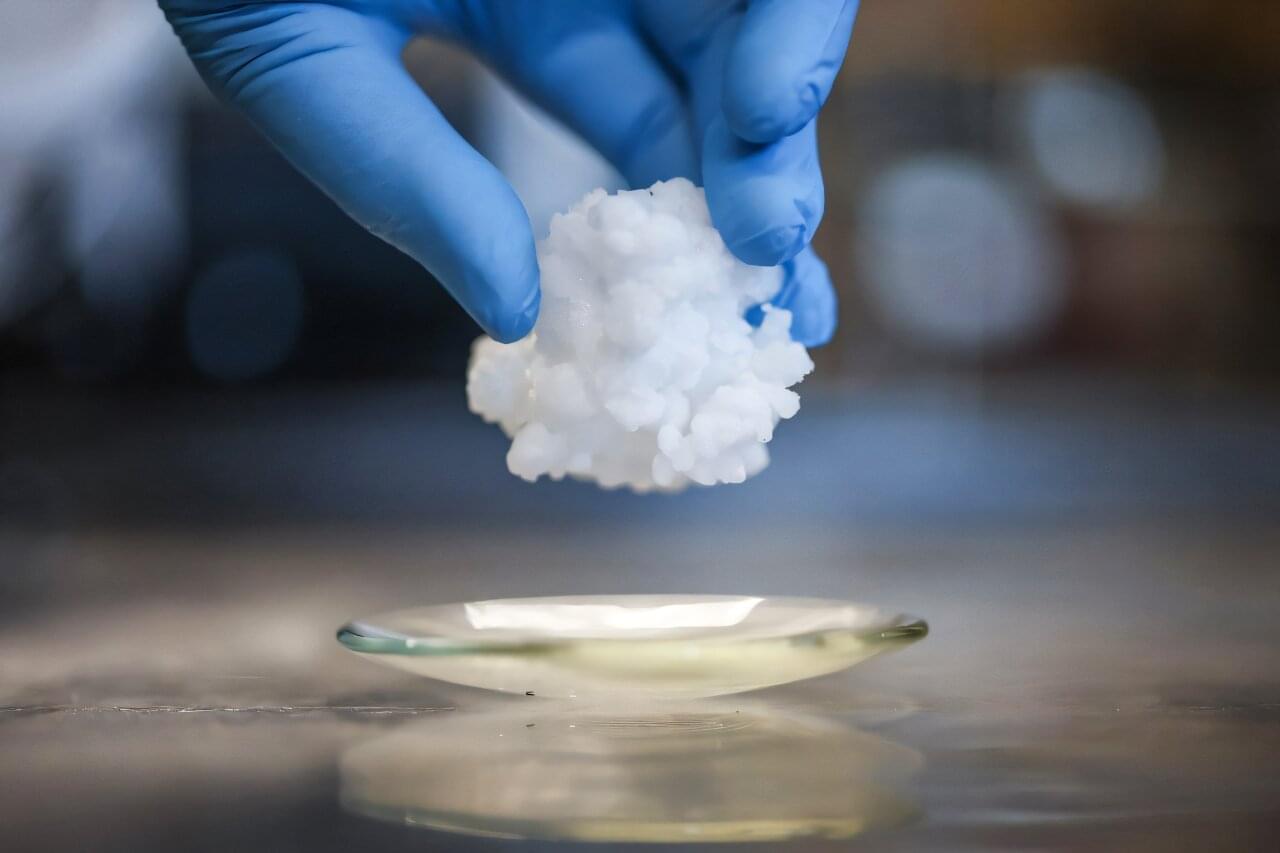
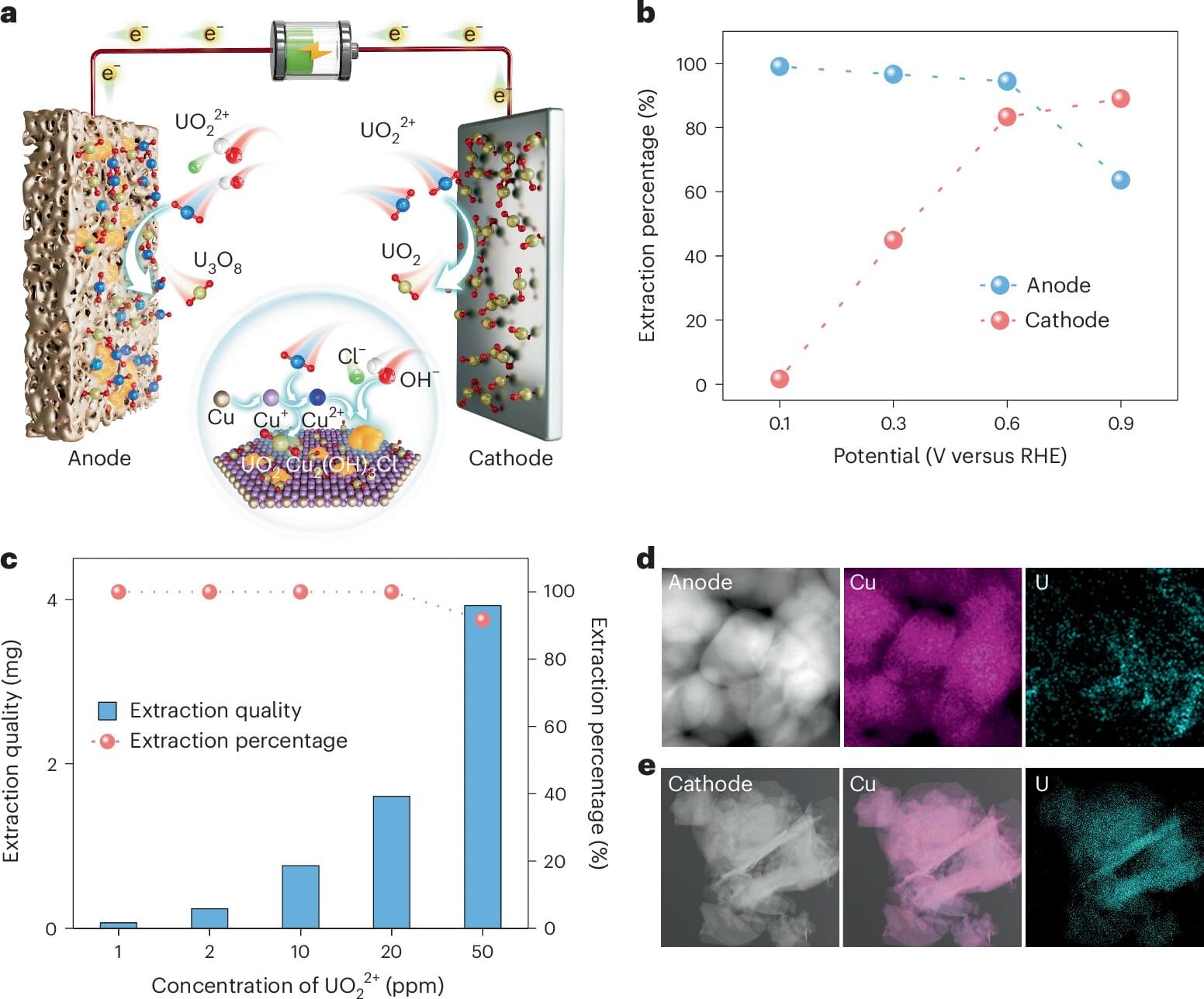
A team of chemists, materials scientists and engineers affiliated with several institutions in China, working with a colleague from Taiwan, has developed a new way to remove uranium from seawater that is much more efficient than other methods. Their paper is published in the journal Nature Sustainability.
The current method for obtaining uranium for use in nuclear power plants is mining it from the ground. Canada, Kazakhstan and Australia are currently the largest producers of uranium, accounting for nearly 70% of global production. Other countries such as the U.S., China and Russia would like to overcome their reliance on foreign providers of the radioactive element, and have been looking for ways to efficiently extract it from seawater.
The world’s oceans have far more uranium than ground sources, but it is highly dilute, which makes harvesting difficult and expensive. In this new effort, the team working in China has found a way to do it much more efficiently, resulting in lower costs. Notably, China builds more nuclear power plants than any other country and would very much like to be able to produce its own uranium.