Polestar may be a young brand, but its direction is clear: be the “guiding star” for the Volvo and Geely Car Groups when it comes to technology, performance, and sustainability.
Just last year, its debut car, the hybrid-electric two-door Polestar 1, began its initial production run to satisfy approximately 150 pre-orders. Deliveries are now underway, but Polestar – naturally – is already sailing forth towards its next phase, the all-electric five-door fastback Polestar 2.
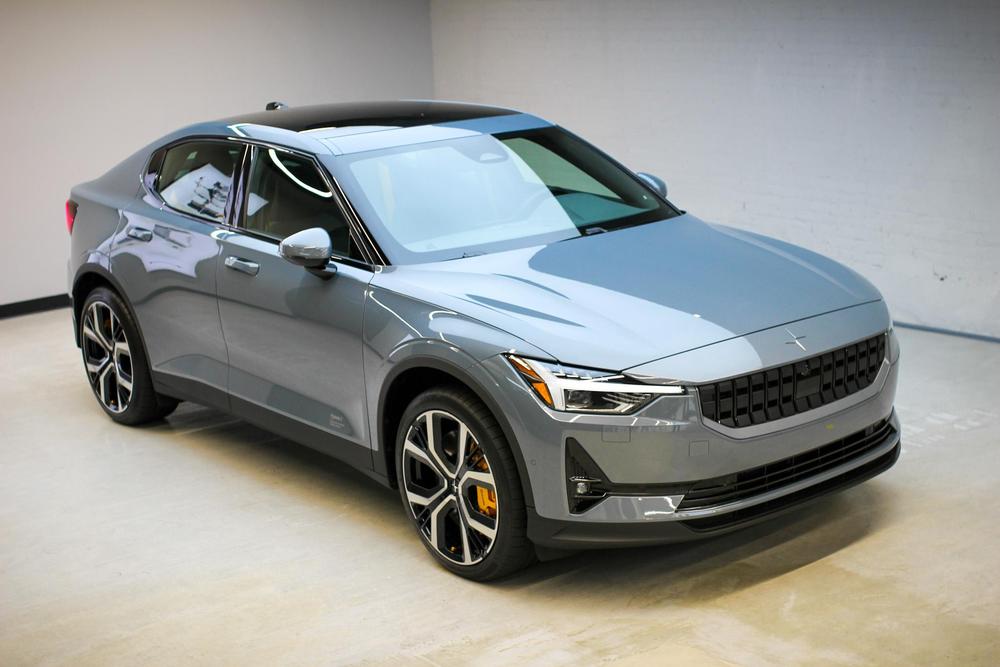
Polestar’s latest brings the young brand’s future into sharper focus, distinguishing itself from its sibling brand Volvo while quite possibly outshining the competition, too.