The entire US coastline is in for a one-two punch from the lunar cycle and climate change.


Most plastic persists in the environment. A recently developed polymer degrades in a week and doesn’t leave microplastics behind. Image credit: Larina Marina/ Shutterstock.
Plastic trash chokes shorelines and oceans, in part because plastic polymers do not easily decompose. But a new kind of environmentally degradable plastic could help change that: It breaks down in about a week in sunlight and air, according to a recent study in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS). Chemical characterization using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectroscopy, among other techniques, revealed that the plastic decomposed rapidly in sunlight from a petroleum-based polymer into succinic acid, a naturally occurring nontoxic small molecule that doesn’t leave microplastic fragments in the environment.
Although a sun-sensitive plastic might not be a good choice for bottles or bags that need to last more than a week on shelves, integrating the environmentally degradable polymer as a minor ingredient, or with other biodegradable polymers, could help speed breakdown of these materials in landfills, says coauthor Liang Luo, an organic materials scientist at Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China. The flexible and degradable material would be potentially useful inside electronics, he says. Sealed inside a cell phone or other flexible electronic device, the polymer could last for years isolated from light and oxygen, Luo notes, while making smartphones easier to dispose of at the end of their service life. And the byproduct succinic acid could be upcycled for commercial uses in the pharmaceutical and food industries, Luo adds.
WTF?! On Thursday the Security Service of Ukraine (SSU) reported that they had shut down a cryptomining operation in the city of Vinnytsia, seizing over 500 GPUs and 50 processors — and a bunch of Playstation 4s. Consoles built on 2013-era technology might not be great at mining, but they don’t need to be when you have 3800 of them.
Although the market for GPUs is starting to improve, and dedicated ASICs might be on the way to relieve demand, it seems that one group of enterprising cryptocurrency miners have turned to last-gen console hardware to get things done.
From the photos provided by the SSU, it looks like these consoles are of the PS4 Slim variety, the 2016 refresh of the original console from three years prior. Mostly obsolete for newer games, it’s not at all surprising that so many could be sourced en masse so easily.

A new laser that generates quantum particles can recycle lost energy for highly efficient, low threshold laser applications.
Scientists at KAIST have fabricated a laser system that generates highly interactive quantum particles at room temperature. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics, could lead to a single microcavity laser system that requires lower threshold energy as its energy loss increases.
The system, developed by KAIST physicist Yong-Hoon Cho and colleagues, involves shining light through a single hexagonal-shaped microcavity treated with a loss-modulated silicon nitride substrate. The system design leads to the generation of a polariton laser at room temperature, which is exciting because this usually requires cryogenic temperatures.
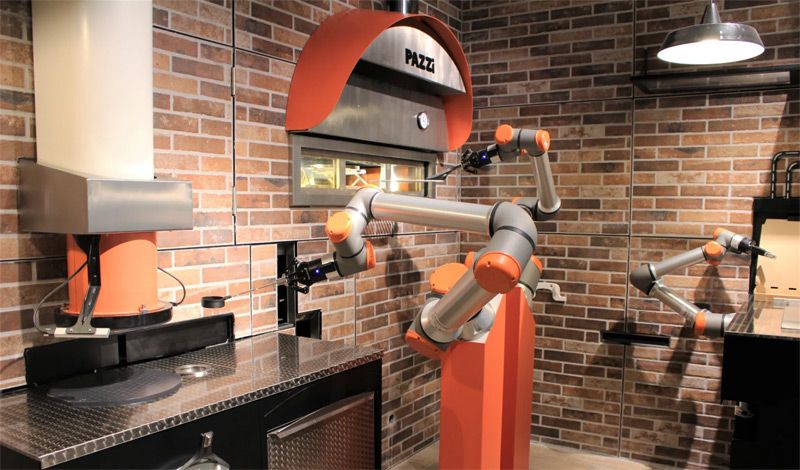

A new pizzeria, called Pazzi, is staffed entirely by robots, which can handle everything from order-taking to prepping the dough, to boxing the finished meal.
The restaurant, found in the Beaubourg area of Paris, has taken eight years of research and development. Its creators are two inventors, Cyril Hamon and Sébastien Roverso – both passionate about robotics and electronics since childhood – who began designing the machines in a family garage. Their goal has been to reinvent the fast food experience with a fully automated system that is more convenient and empowering to customers, while maintaining the same or better quality food as conventional restaurants and also being environmentally sustainable.
Pazzi builds on the success of a pilot, tested at the Val d’Europe shopping centre in 2019. The 120m² establishment is more visible and centrally located than that earlier demonstration, being opposite the famous Pompidou centre, benefiting from a high attendance.
Adding absorbent nanoparticles to polymer membranes simplifies desalination.
University of California, Berkeley, chemists have discovered a way to simplify the removal of toxic metals. like mercury and boron. during desalination to produce clean water, while at the same time potentially capturing valuable metals, such as gold.
Desalination — the removal of salt — is only one step in the process of producing drinkable water, or water for agriculture or industry, from ocean or waste water. Either before or after the removal of salt, the water often has to be treated to remove boron, which is toxic to plants, and heavy metals like arsenic and mercury, which are toxic to humans. Often, the process leaves behind a toxic brine that can be difficult to dispose of.
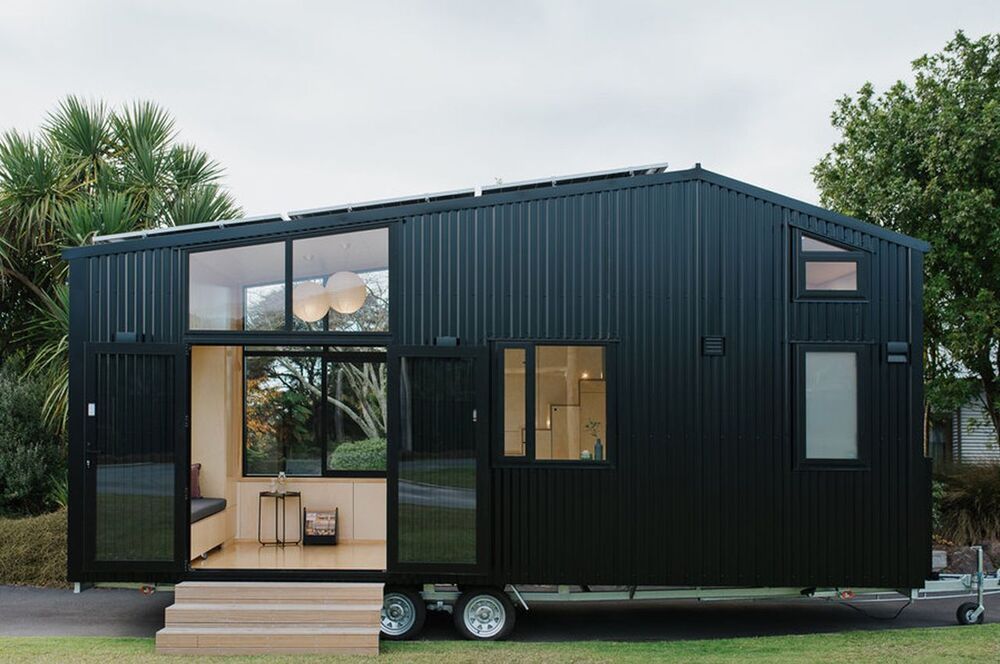

Transportable tiny homes are complex operations, to say the least. Designing them to be sustainable makes building them that much more of an intricate process. First Light Studio, a New Zealand-based architecture group built their own tiny home with help from a local company Build Tiny, Ohariu, checking all of the above boxes. Built to be net-zero through several sustainable features and compact enough to meet all NZTA regulations for mobile homes.
Ohariu was built by First Light Studio and Build Tiny from a client’s brief calling for, “a refined tramping lodge on wheels.” That’s code for hiking, for all us Americans. Since the tiny home would primarily be used for hiking trips and traveling throughout the outdoors, Ohariu was built to be adaptable and versatile above all else. Inside, the living spaces are described by the architects at First Light Studio as being, “more a large and very detailed piece of furniture than a traditional house build, the fit-out [focusing] on the things that are important and necessary.”
Catering to the necessities and casual family pastimes, the tiny home is doused in modular and multifunctional design that’s surrounded by creamy poplar plywood walls and silvery fittings that add a touch of refinement to an otherwise bare interior. Each furniture piece inside Ohariu doubles as storage to maintain an open, clutter-free interior where the tiny home’s family would bond over pastimes like cooking, playing card games, and enjoying the surrounding landscape. Featuring a chef’s kitchen, Ohariu comes with plenty of prep space for cooking and integrates tilt-up tabletops to make even more for when there’s company. Outside, Ohariu is coated in a stealthy ebony corrugate to match its lightweight mobility, supported by aluminum joinery, lights, and utilities that were given the same ebony finish. Ohariu’s roof is asymmetrical with six solar panels lined up on its longer side and a mezzanine bedroom cozying up beneath its sloped short side.
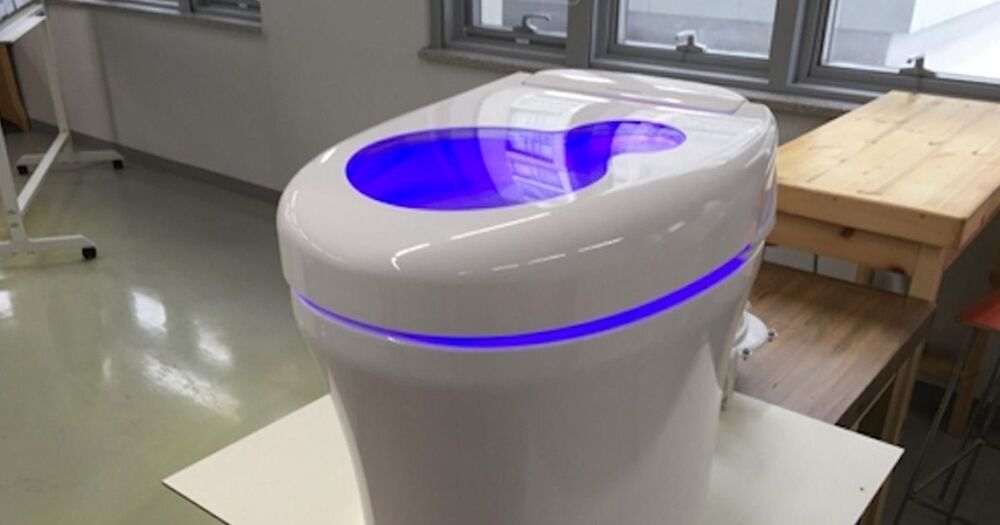

The toilet could turn roughly a pound of solid human waste, the average amount a human poops in a day, into an impressive 50 liters of methane gas, according to Cho. That means it can generate half a kilowatt hour of electricity, enough to drive an electric car for three quarters of a mile.
And because its 2021 — a day and age in which nothing is safe from the world of cryptocurrencies — Cho came up with a virtual currency called Ggool, or “honey” in Korean. Every use of the toilet scores you 10 Ggool per day, which can be used to buy stuff on the university’s campus.
“I had only ever thought that feces are dirty, but now it is a treasure of great value to me,” a postgraduate student Heo Hui-jin who’s both earned and spent Ggool, told Reuters. “I even talk about feces during mealtimes to think about buying any book I want.”
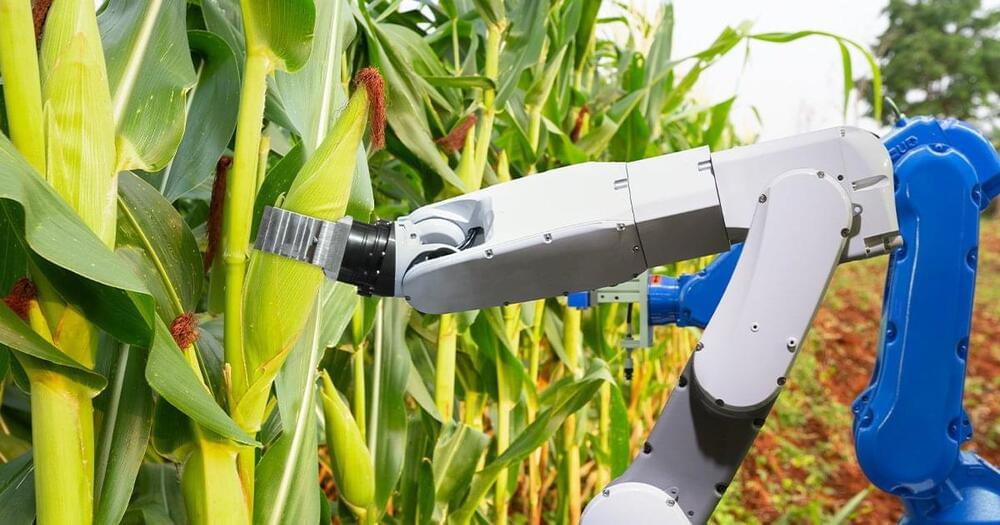

The smart farm: To show just how much these technologies could help farmers, CSU and Food Agility have partnered to create the Global Digital Farm (GDF).
The smart farm will be built at CSU’s Wagga Wagga campus, and it will feature autonomous tractors, harvesters, and other farming robots, as well as AI programs designed to help with farm management and more.
Teachable moments: The plan isn’t for the GDF to simply demonstrate what a smart farm can look like — CSU and Food Agility want to use it to teach Australia’s farmers how to take advantage of all the tech that will be on display.