Devising renewable sources of energy is a key concern for scientists, political leaders and communities as the world comes to terms with the realities of climate change and the limits of the Earth’s natural resources. In an exciting new development, scientists from the Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research (SANKEN) at Osaka University have demonstrated that electricity may be obtainable from water with a high salt concentration, such as seawater.
Some people think about “osmosis” as just a science term they were forced to learn in elementary school biology class. However, the spontaneous motion of dissolved ions or molecules through a semi-permeable membrane when there is a concentration difference between the two sides can be harnessed to generate electricity. And luckily for us, the oceans are filled with salty water, which may be used to help alleviate humanity’s ever-growing demand for energy. However, in order to be practical, this membrane needs to be very thin and highly selective to allow ions—but not water molecules—to pass through.
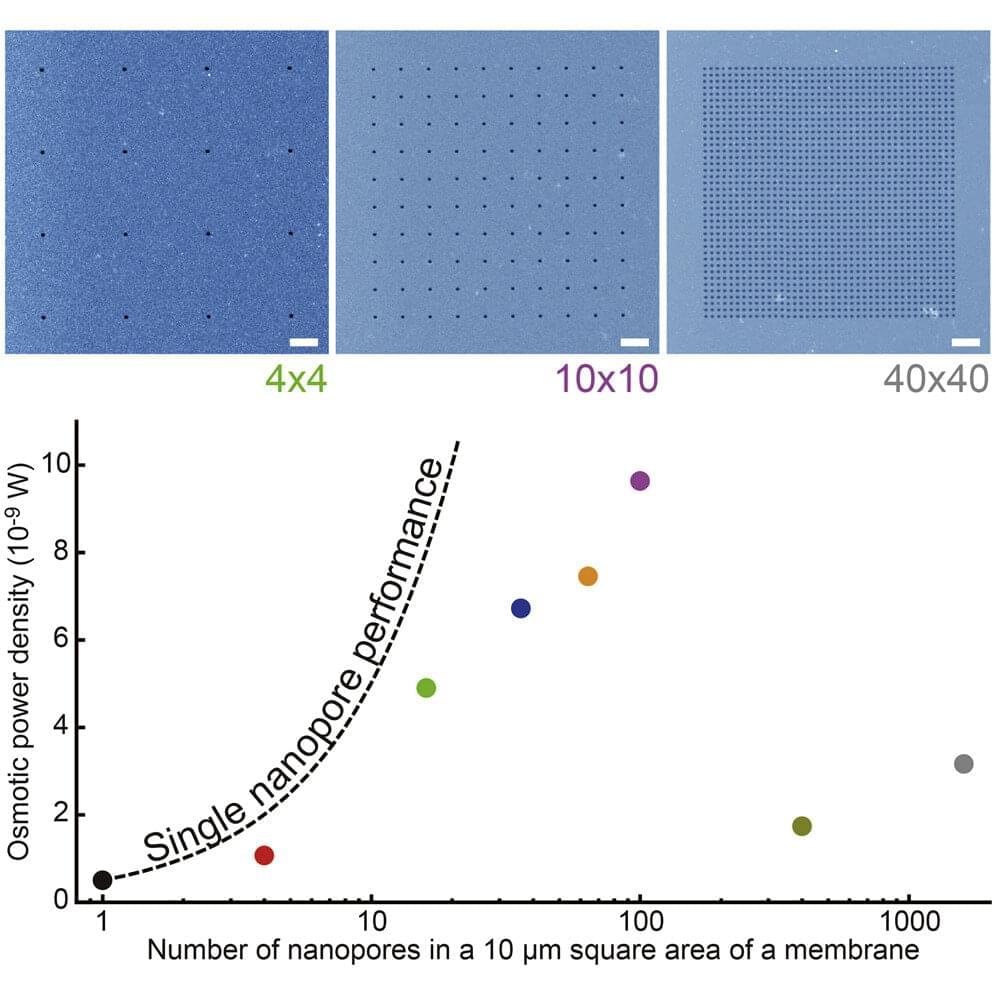
Now, a research team led by Osaka University has used conventional semiconductor processing technology to precisely control the structure and arrangement of nanopores in an ultrathin silicon membrane. Because these fabrication methods have been around for decades, the costs and design complexities were minimized. Moreover, the size and location of the pores could be precisely controlled.