Transparent electronic devices could have numerous valuable real-world applications. Among other things, they could enable the creation of new optical devices, smart gear or wearables, invisible solar panels and integrated communication systems.
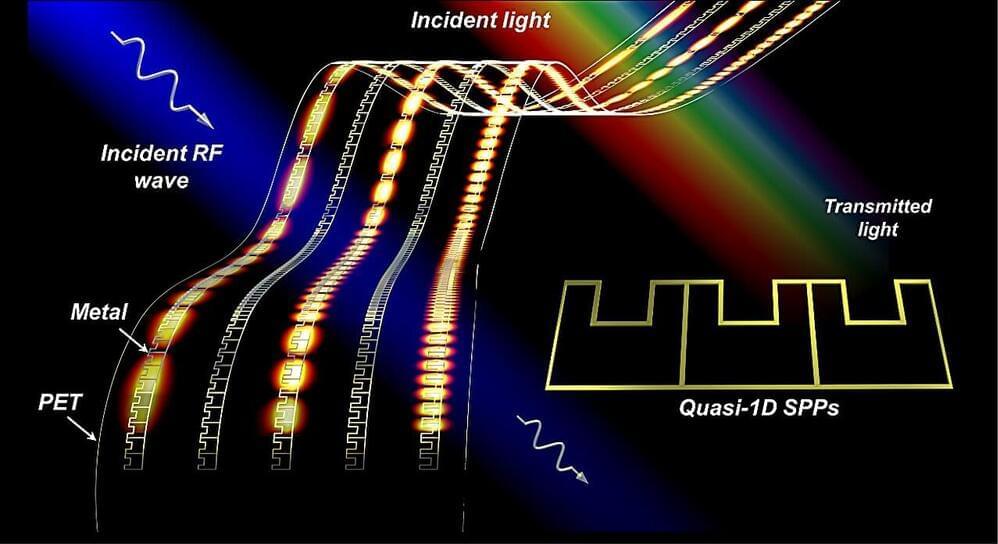
Researchers at Xidian University, Southeast University and Wuhan University of Technology recently developed new, highly promising, transparent metadevices based on quasi-one-dimensional surface plasmon polariton (quasi-1D SPP) structures. These devices, introduced in a paper published in Nature Electronics, could be used to develop optically and radiofrequency transparent wireless communication systems and other promising technologies.
“Transparent and invisible electronic device is a fascinating goal that scientists and engineers are enthusiastically pursuing,” Prof. Bian Wu, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Tech Xplore. “Currently, transparent electronics typically rely on the intrinsic properties of optically conductive materials, which are not radiofrequency transparent and have low operating efficiency. SSPs can be used to concentrate, channel and enhance energy. However, the use of SPPs in the development of optical and radiofrequency transparency remains blank.”