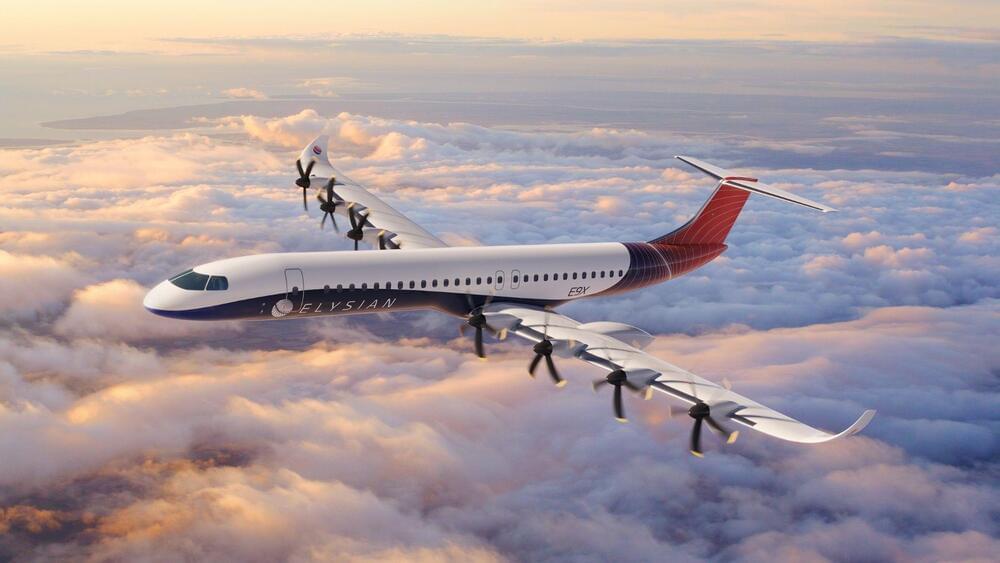
Zero-emissions long-distance aviation is absolutely possible… Provided you’re not in a hurry. Solar Airship One will take 20 days to fly all the way around the equator, some 40,000 km (~25,000 miles), in a single zero-emissions hop.
The 151-m (495-ft)-long airship will have its entire upper surface covered in solar film – some 4,800 square meters (51,700 sq ft) of it, or about nine-tenths of an NFL football field for those of you who prefer the standard units.
By day, the solar panels will run the airship’s electric propulsion systems, while also banking up extra power for the overnight haul by electrolyzing water into hydrogen. By night, the hydrogen will run through a fuel cell, providing the juice to keep going.