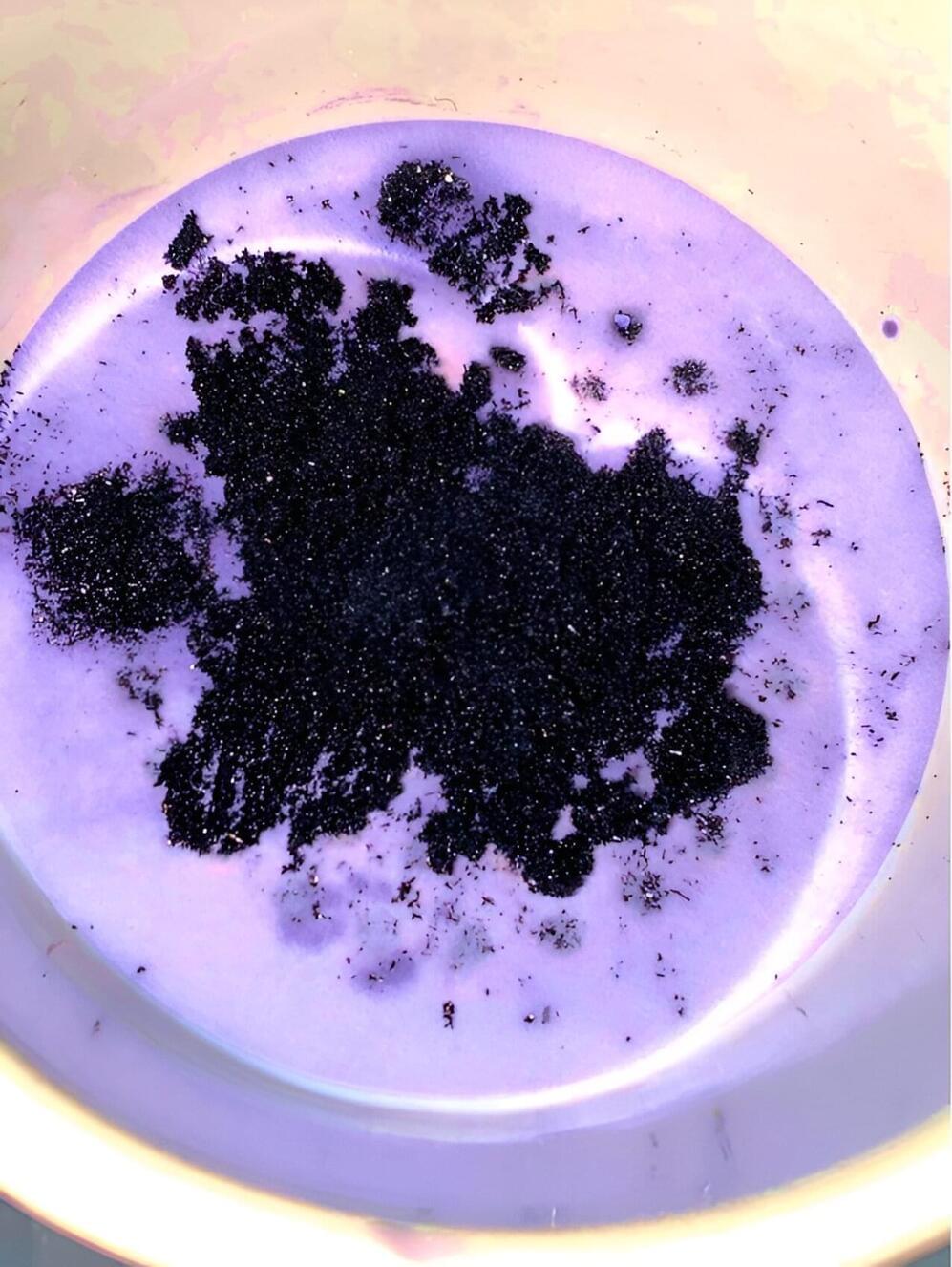
The team leveraged ground-state electron transfer to develop water-based conductive ink for use in flexible electronics.
A major trend in electronics has been the emergence of flexible electronics in devices such as solar cells and energy storage. The technology enabling these devices to be flexible and lightweight is organic electronics. However, concerns about the sustainability of producing organic electronics are growing.
Recently, researchers in Sweden tackled the sustainability challenges head-on by developing water-based conductive inks in organic electronics.