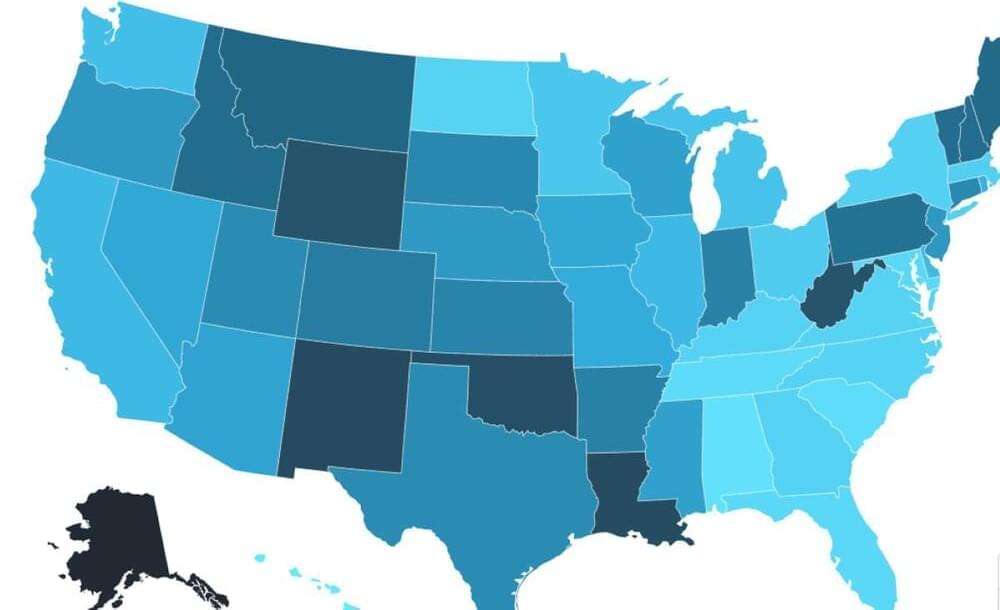
Newsweek ranked which states had the fewest health-related water safety violations based on data from the Environmental Protection Agency.

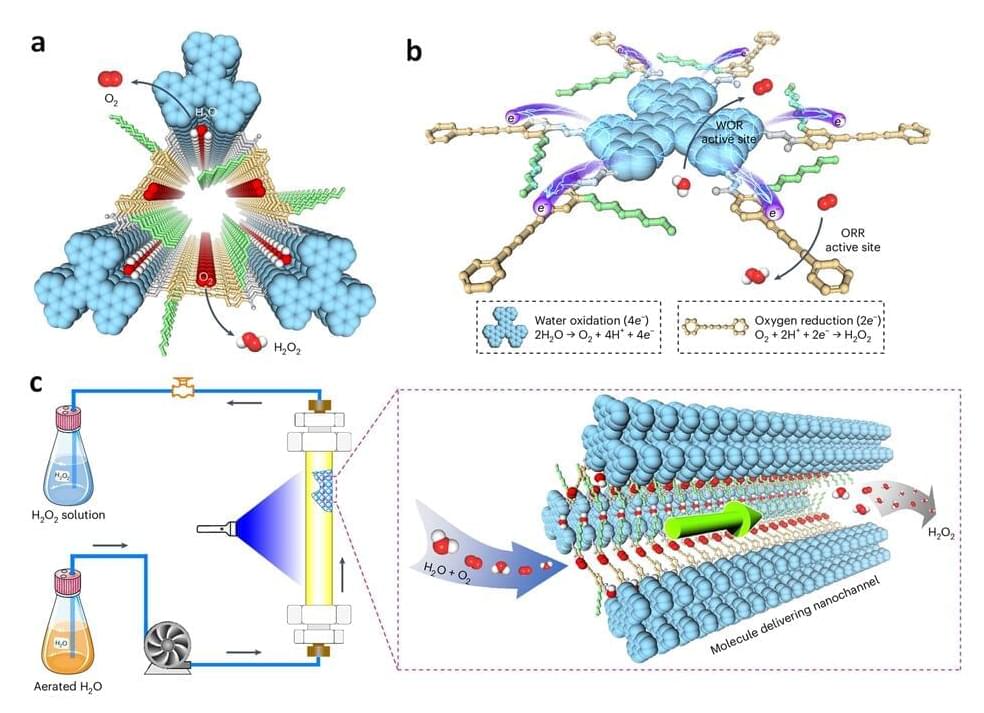
National University of Singapore (NUS) chemists have developed hexavalent photocatalytic covalent organic frameworks (COFs) which mimic natural photosynthesis for the production of hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2), an important industrial chemical.
The conventional method of H 2 O 2 production involves using anthraquinone as a catalyst to convert air and hydrogen into H 2 O 2. However, this process requires substantial energy, costly noble metal catalysts, high-pressure hydrogen gas and hazardous solvents. Artificial photosynthesis of H 2 O 2, resembling the natural photosynthesis process with the use of sunlight as an energy source and abundant water and air as feedstocks, presents a sustainable and promising alternative to the conventional anthraquinone process.
However, such an artificial system faces three key challenges: insufficient charge carrier generation and fast charge recombination, which lowers the efficiency; limited number of available catalytic sites, which results in low productivity; and lack of efficient delivery of charges and reactants to the catalytic sites, which causes sluggish reaction kinetics.

Brighter with Herbert.

O.o!!!! Woah even the news is talking about Dyson spheres now o.o
By Jacopo Prisco, CNN
(CNN) — What would be the ultimate solution to the energy problems of an advanced civilization? Renowned British American physicist Freeman Dyson theorized it would be a shell made up of mirrors or solar panels that completely surrounds a star — harnessing all the energy it produces.
“One should expect that, within a few thousand years of its entering the stage of industrial development, any intelligent species should be found occupying an artificial biosphere which completely surrounds its parent star,” wrote Dyson in a 1960 paper in which he first explained the concept.
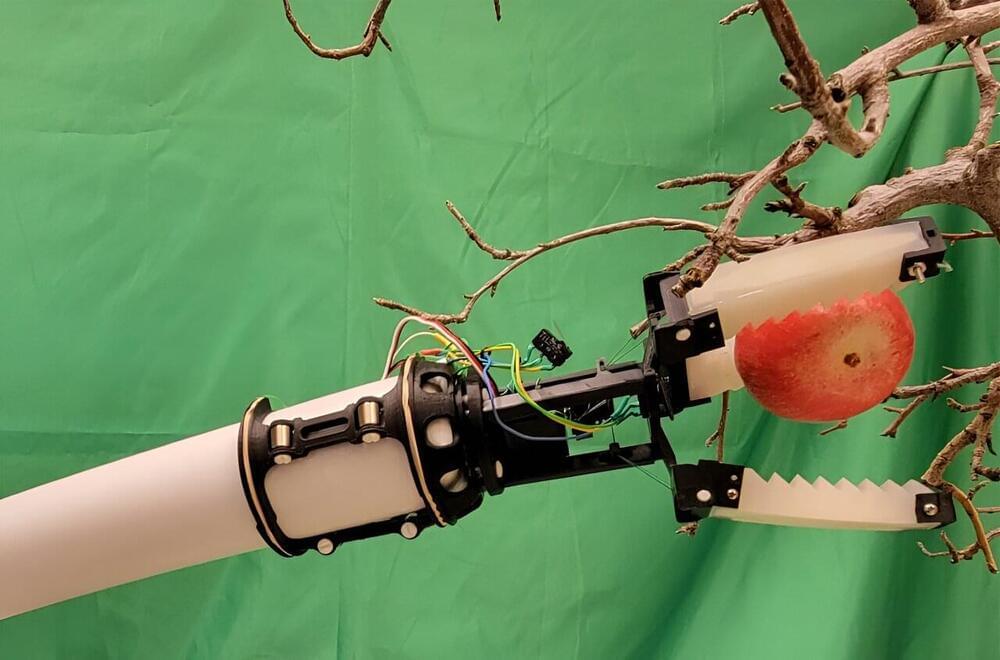
Washington state leads the nation in apple production, and in 2022, the industry contributed more than two billion dollars to the U.S. gross domestic product. Throughout Washington, farms employ anywhere from a dozen to hundreds of workers each year for orchard operations, including for pollination, pruning, flower thinning and fruit harvesting. With an aging population and a decrease in migrant farm workers, however, farmers have struggled to meet their needs for workers during harvest season.
In recent years, researchers have started developing robotic apple harvesting systems, but the ones that have been developed are expensive and complex to use in orchards.
Ninatanta, who grew up in Yakima, Washington, picked fruit alongside his parents during his childhood. When he began his work with Luo on a robotic apple gripper, he had his parents videotape their work, so he could model his gripper on their handiwork.

As some entities identify new (or at least overlooked) sources to meet the growing demand for rare earth materials, others are looking toward new tools. UK deep-tech company Materials Nexus announced on Tuesday that it has designed a new rare-earth-free permanent magnet with the help of its AI platform. It says the AI-driven discovery and development process was 200 times faster than the resource-intensive manual route, bringing new hope to an electrifying world with a growing appetite for powerful magnets.
With the world moving away from internal combustion engines and gradually embracing electric mobility, the demand for compact, high-power motors is rapidly rising. By far the most popular option in the automotive industry right now is the permanent magnet motor, which powers upward of 80% of modern electric vehicles.
Materials Nexus estimates that demand for permanent magnets will grow tenfold by 2030, in the EV industry alone. And it’s not just electric cars and trucks, either. Permanent magnet motors are in demand for many applications, including robotics, drones, wind turbines and HVAC equipment.
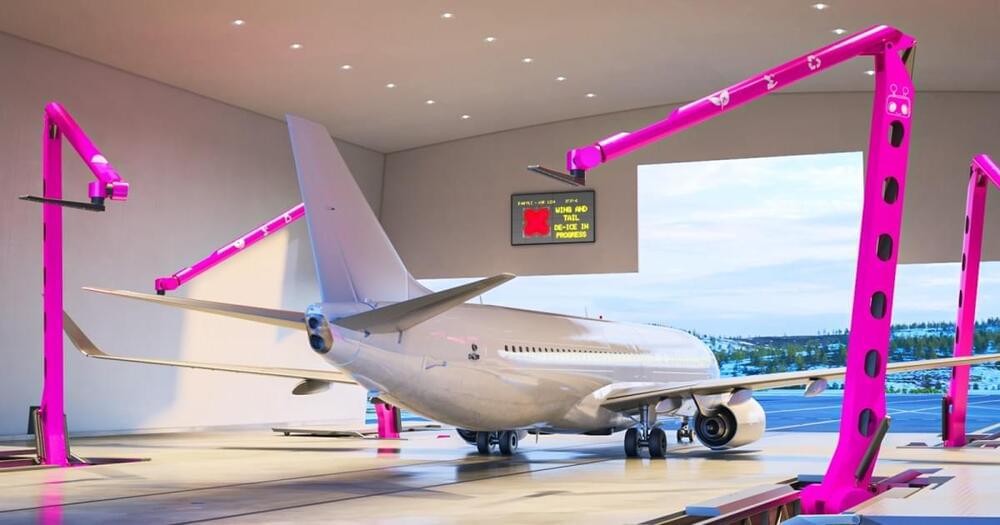


A Norwegian startup is building massive AI robots to help airlines reduce their carbon emissions, save water, and inspect their planes in a fraction of the time it usually takes.
The challenge: The aviation industry is responsible for about 2.5% of global carbon emissions, and while sustainable jet fuels or electric propulsion systems could one day slash that figure, airlines can reduce their emissions right now — simply by cleaning their planes more often.
Washing an airplane’s exterior reduces air resistance, which means it can decrease the amount of jet fuel a plane needs to burn by up to 2% — while that’s not a huge difference, it can add up when you consider there are about 28,000 commercial jets in the global fleet.