Scientists in Switzerland used solar energy to heat an object to over 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit that could potentially replace fossil fuels.



Tesla Gigafactory Berlin has probably become the most fun factory among the company’s facilities worldwide. While Giga Berlin plays a huge part in ramping Tesla’s output globally, the electric vehicle maker also seems determined to ensure that the facility’s employees are well supported. This means that if employees need to destress, they would not need to go too far.
With this in mind, it appears that Giga Berlin has launched an in-house “rave cave” of sorts. The facility’s teaser was posted by Tesla’s official Tesla Manufacturing account, which, strangely enough, shared its post with a hamster emoji. Amidst scenes of employees entering the apparent “rave cave” from a futuristic narrow tunnel, images of a cyber-hamster mascot could also be seen.


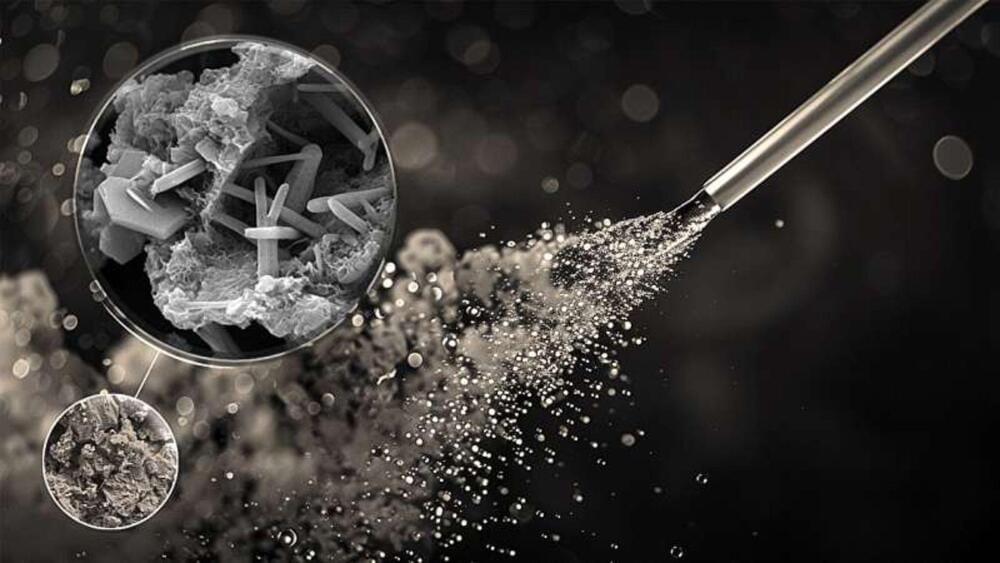
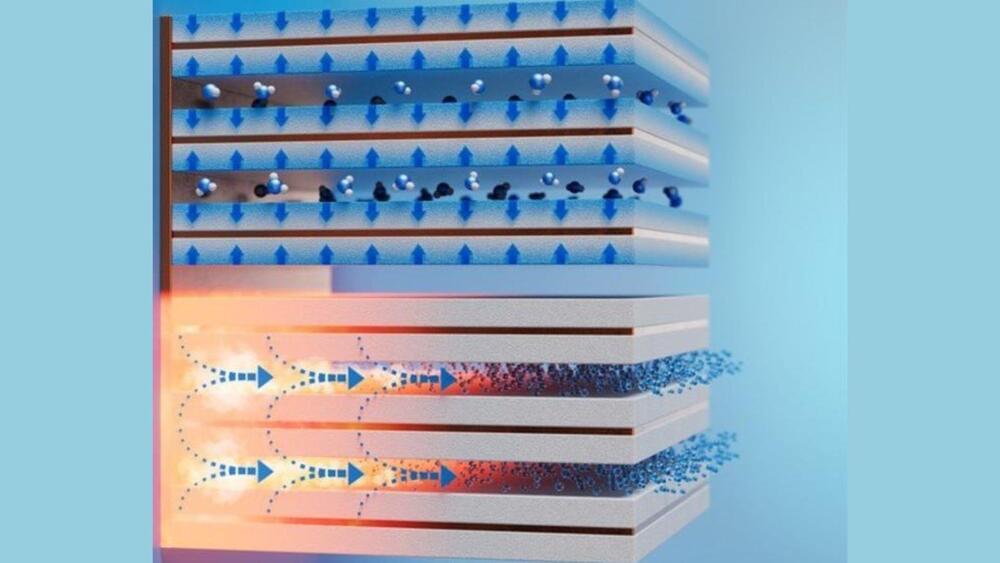
A material with a high electron mobility is like a highway without traffic. Any electrons that flow into the material experience a commuter’s dream, breezing through without any obstacles or congestion to slow or scatter them off their path.
The higher a material’s electron mobility, the more efficient its electrical conductivity, and the less energy is lost or wasted as electrons zip through. Advanced materials that exhibit high electron mobility will be essential for more efficient and sustainable electronic devices that can do more work with less power.
Now, physicists at MIT, the Army Research Lab, and elsewhere have achieved a record-setting level of electron mobility in a thin film of ternary tetradymite—a class of mineral that is naturally found in deep hydrothermal deposits of gold and quartz.
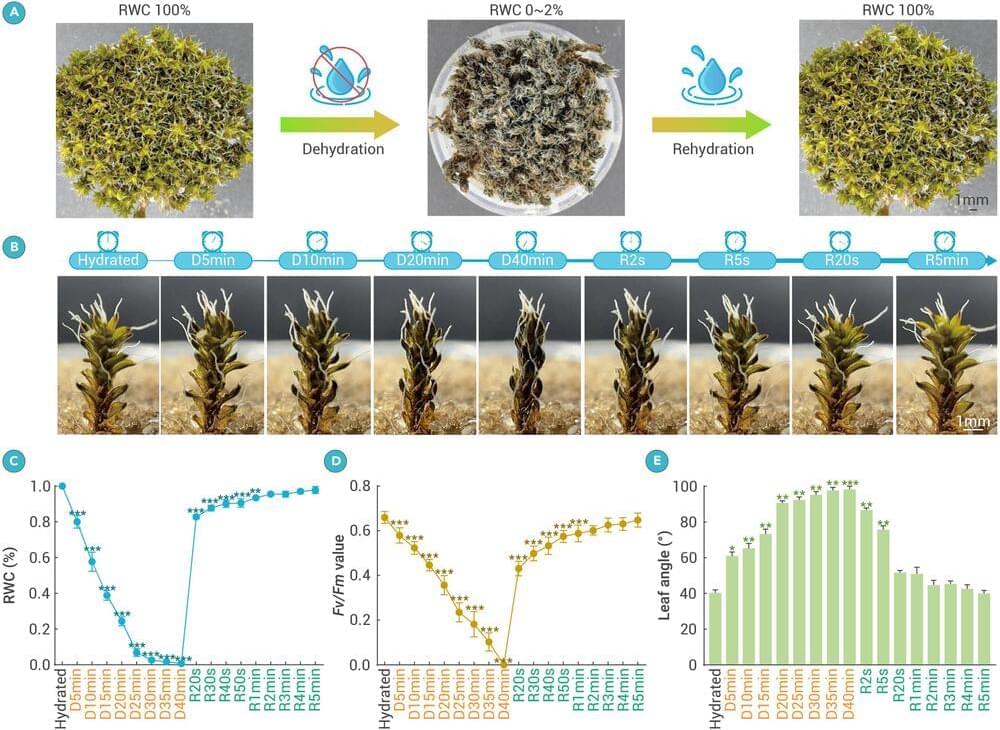
The desert moss Syntrichia caninervis is a promising candidate for Mars colonization thanks to its extreme ability to tolerate harsh conditions lethal to most life forms. The moss is well known for its ability to tolerate drought conditions, but researchers report in the journal The Innovation that it can also survive freezing temperatures as low as −196°C, high levels of gamma radiation, and simulated Martian conditions involving these three stressors combined. In all cases, prior dehydration seemed to help the plants cope.
“Our study shows that the environmental resilience of S. caninervis is superior to that of some of highly stress-tolerant microorganisms and tardigrades,” write the researchers, who include ecologists Daoyuan Zhang and Yuanming Zhang and botanist Tingyun Kuang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
“S. caninervis is a promising candidate pioneer plant for colonizing extraterrestrial environments, laying the foundation for building biologically sustainable human habitats beyond Earth.”
In this episode of the 5th Industrial Revolution VODcast we sit down with Dr. Jordan Okie of Arizona State University School of Earth and Space Exploration to discuss a key relevancy to the next industrial revolution, sustainability, through the lens of Dr. Okie’s area of expertise: Ecology and Biology. Our key takeaways: We are in a race against time and extinction. We will need to find a way to evolve through technology to survive, be it here on Earth or in our exploration of Space.