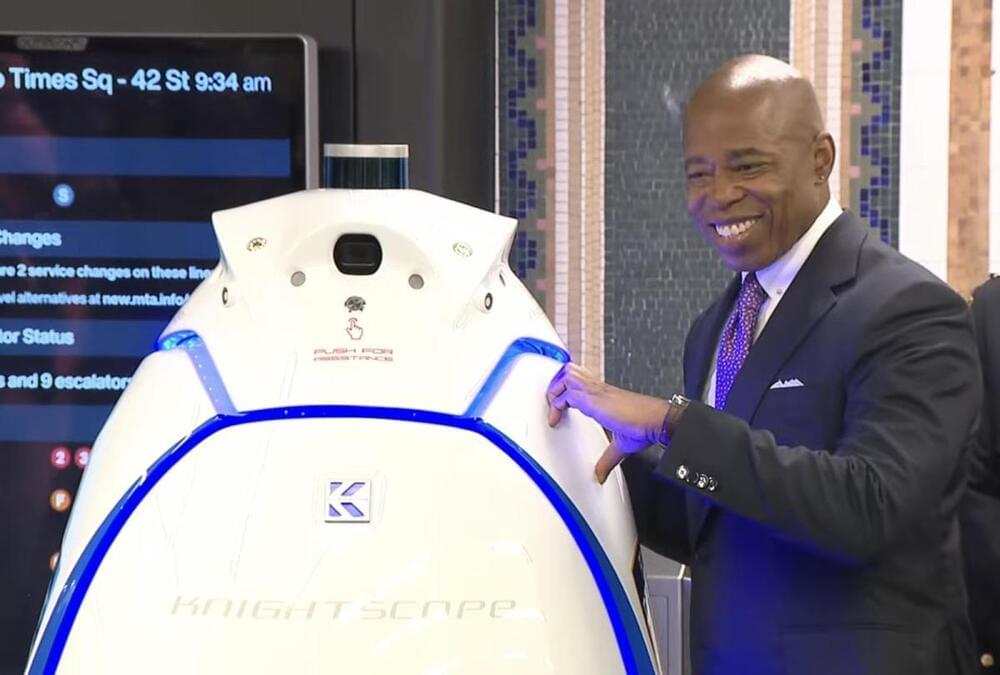
The New York Police Department (NYPD) is implementing a new security measure at the Times Square subway station. It’s deploying a security robot to patrol the premises, which authorities say is meant to “keep you safe.” We’re not talking about a RoboCop-like machine or any human-like biped robot — the K5, which was made by California-based company Knightscope, looks like a massive version of R2-D2. Albert Fox Cahn, the executive director of privacy rights group Surveillance Technology Oversight Project, has a less flattering description for it, though, and told The New York Times that it’s like a “trash can on wheels.”
K5 weighs 420 pounds and is equipped with four cameras that can record video but not audio. As you can guess from the image above, the machine also doesn’t come with arms — it didn’t quite ignore Mayor Eric Adams’ attempt at making a heart. The robot will patrol the station from midnight until 6 AM throughout its trial run that’s running over the next two months. But K5 won’t be doing full patrols for a while, since it’s spending its first two weeks mapping out the station and roaming only the main areas and not the platforms.
It’s not quite clear if NYPD’s machine will be livestreaming its camera footage, and if law enforcement will be keeping an eye on what it captures. Adams said during the event introducing the robot that it will “record video that can be reviewed in case of an emergency or a crime.” It apparently won’t be using facial recognition, though Cahn is concerned that the technology could eventually be incorporated into the machine. Obviously, K5 doesn’t have the capability to respond to actual emergencies in the station and can’t physically or verbally apprehend suspects. The only real-time help it can provide people is to connect them to a live person to report an incident or to ask questions, provided they’re able to press a button on the robot.