“The projects running on Aurora represent some of the most ambitious and innovative science happening today,” said Katherine Riley, ALCF director of science. “From modeling extremely complex physical systems to processing huge amounts of data, Aurora will accelerate discoveries that deepen our understanding of the world around us.”
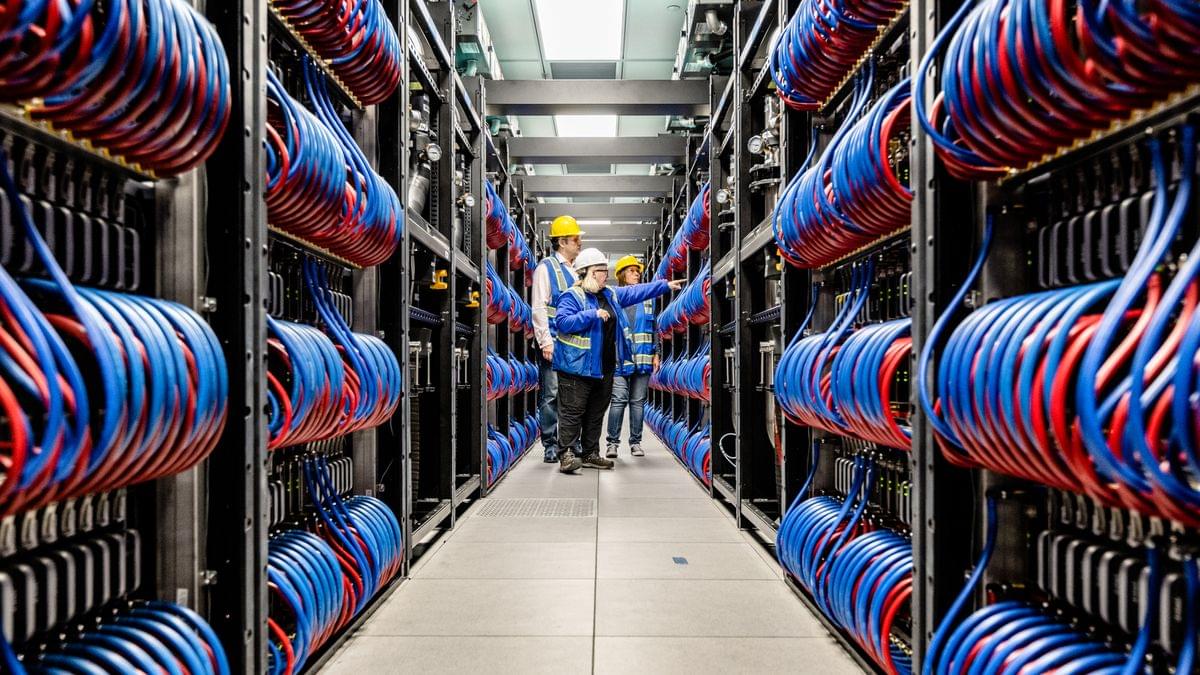
On the hardware side, Aurora clearly impresses. The supercomputer comprises 166 racks, each holding 64 blades, for a total of 10,624 blades. Each blade contains two Xeon Max processors with 64 GB of HBM2E memory onboard and six Intel Data Center Max ‘Ponte Vecchio’ GPUs, all cooled by a specialized liquid-cooling system.
In total, Aurora has 21,248 CPUs with over 1.1 million high-performance x86 cores, 19.9 PB of DDR5 memory, and 1.36 PB of HBM2E memory attached to the CPUs. It also features 63,744 GPUs optimized for AI and HPC equipped with 8.16 PB of HBM2E memory. Aurora uses 1,024 nodes with solid-state drives for storage, offering 220 PB of total capacity and 31 TB/s of bandwidth. The machine relies on HPE’s Shasta supercomputer architecture with Slingshot interconnects.