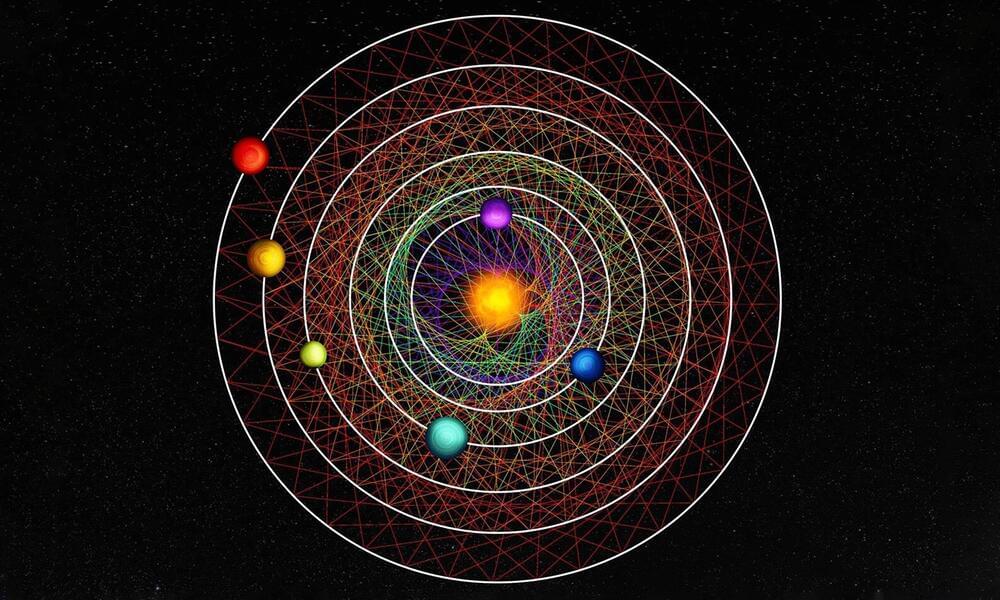
Emily Simpson has loved space since she was a 10-year-old kid celebrating her birthday at a planetarium. Now a recent Florida Tech graduate, she leaves with not only a dual degree in planetary science and astronomy and astrophysics but with published research, too. She mapped our solar system’s “alternate fate” had it housed an extra planet between Mars and Jupiter instead of the existing asteroid belt.
Simpson’s paper, “How might a planet between Mars and Jupiter influence the inner solar system? Effects on orbital motion, obliquity, and eccentricity,” was published in Icarus, a journal devoted to the publication of research around solar system studies. It was co-authored by her advisor, assistant professor of planetary science Howard Chen.
They developed a 3D model that simulates how the solar system’s orbital architecture may have evolved differently with the formation of a planet that is at least twice the size of Earth’s mass—a super-Earth—instead of an asteroid belt.