Collisions of neutron stars are key to our understanding of the Universe.



😳!!!
The Moon isn’t necessarily there if you don’t look at it. So says quantum mechanics, which states that what exists depends on what you measure. Proving reality is like that usually involves the comparison of arcane probabilities, but physicists in China have made the point in a clearer way. They performed a matching game in which two players leverage quantum effects to win every time—which they can’t if measurements merely reveal reality as it already exists.
“To my knowledge this is the simplest [scenario] in which this happens,” says Adan Cabello, a theoretical physicist at the University of Seville who spelled out the game in 2001. Such quantum pseudotelepathy depends on correlations among particles that only exist in the quantum realm, says Anne Broadbent, a quantum information scientist at the University of Ottawa. “We’re observing something that has no classical equivalent.”
A quantum particle can exist in two mutually exclusive conditions at once. For example, a photon can be polarized so that the electric field in it wriggles vertically, horizontally, or both ways at the same time—at least until it’s measured. The two-way state then collapses randomly to either vertical or horizontal. Crucially, no matter how the two-way state collapses, an observer can’t assume the measurement merely reveals how the photon was already polarized. The polarization emerges only with the measurement.
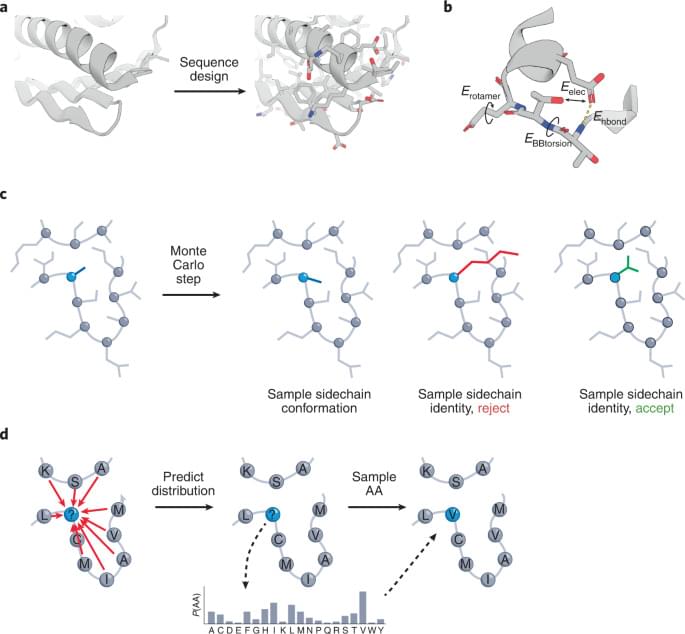
The design of protein sequences that can precisely fold into pre-specified 3D structures is a challenging task. A recently proposed deep-learning algorithm improves such designs when compared with traditional, physics-based protein design approaches.
ABACUS-R is trained on the task of predicting the AA at a given residue, using information about that residue’s backbone structure, and the backbone and AA of neighboring residues in space. To do this, ABACUS-R uses the Transformer neural network architecture6, which offers flexibility in representing and integrating information between different residues. Although these aspects are similar to a previous network2, ABACUS-R adds auxiliary training tasks, such as predicting secondary structures, solvent exposure and sidechain torsion angles. These outputs aren’t needed during design but help with training and increase sequence recovery by about 6%. To design a protein sequence, ABACUS-R uses an iterative ‘denoising’ process (Fig.
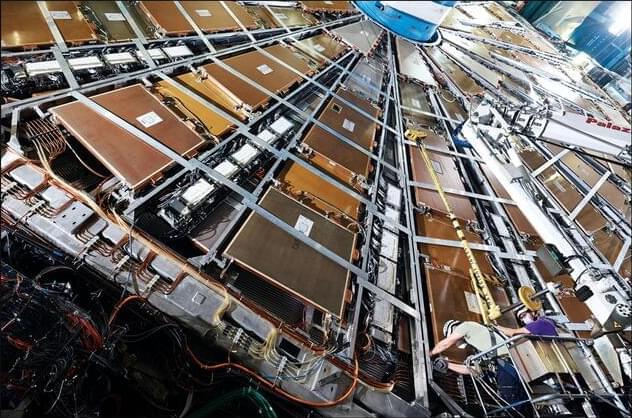



Unless Europe’s Large Hadron Collider coughs up a surprise, the field of particle physics may wheeze to its end.
CELESTA, the first CERN-driven satellite, successfully entered orbit during the maiden flight of Europe’s Vega-C launch vehicle. Launched by the European Space Agency from the French Guiana Space Centre (CSG) at 13.13 UTC on 13 July 2022, the satellite deployed smoothly and transmitted its first signals in the afternoon. Weighing one kilogram and measuring 10 centimetres on each of its sides, CELESTA (CERN latchup and radmon experiment student satellite) is a 1U CubeSat designed to study the effects of cosmic radiation on electronics. The satellite carries a Space RadMon, a miniature version of a well-proven radiation monitoring device deployed in CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC). CELESTA has been sent into an Earth orbit of almost 6,000 kilometres.

July 15 (Reuters) — NASA and Russia’s space agency Roscosmos have signed a long-sought agreement to integrate flights to the International Space Station, allowing Russian cosmonauts to fly on U.S.-made spacecraft in exchange for American astronauts being able to ride on Russia’s Soyuz, the agencies said Friday.
“The agreement is in the interests of Russia and the United States and will promote the development of cooperation within the framework of the ISS program,” Roscosmos said in a statement, adding it will facilitate the “exploration of outer space for peaceful purposes.”
NASA and Roscosmos, the two-decade-old space station’s core partners, have sought for years to renew routine integrated crewed flights as part of the agencies’ long-standing civil alliance, now one of the last links of cooperation between the United States and Russia as tensions flare over the war in Ukraine.
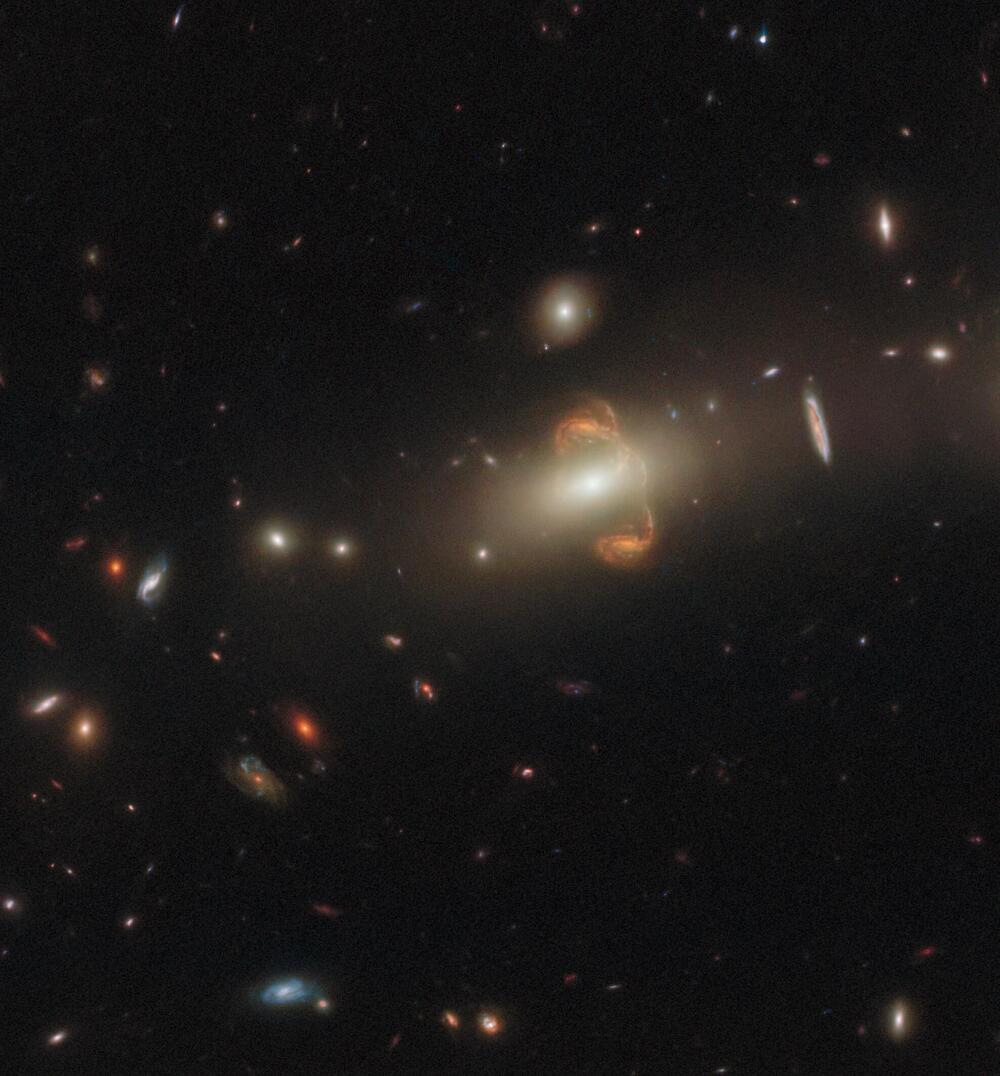


This intriguing observation from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope shows a gravitationally lensed galaxy with the long-winded identification SGAS J143845+145407. Gravitational lensing has resulted in a mirror image of the galaxy near the center of this image, creating a captivating centerpiece. A third distorted image of the galaxy appears as a bridge between them.
Gravitational lensing occurs when the mass of an enormous celestial body – such as a galaxy cluster – curves spacetime and causes the path of light from distant objects to visibly bend around it, as if by a lens. Appropriately, the body causing the light to curve is called a gravitational lens, and the distorted background object is referred to as being “lensed.” Gravitational lensing can result in multiple images of the original galaxy, as seen in this image, or in the background object appearing as a distorted arc or even a ring. Another important consequence of this lensing distortion is magnification, allowing astronomers to observe objects that would otherwise be too far away or be too faint to see.