Astronauts on the space station may seem distant, but they’re only 248 miles from Earth: a little more than the drive from New York City to Washington DC. Everything they need can be delivered in relatively short order. Astronauts visiting Mars won’t have such easy access. The red planet’s average distance from Earth is 140 million miles.
We can plan supply missions, but taking everything along for the ride would be expensive and impractical. Like Mark Watney in The Martian, explorers will have to live off the land too.
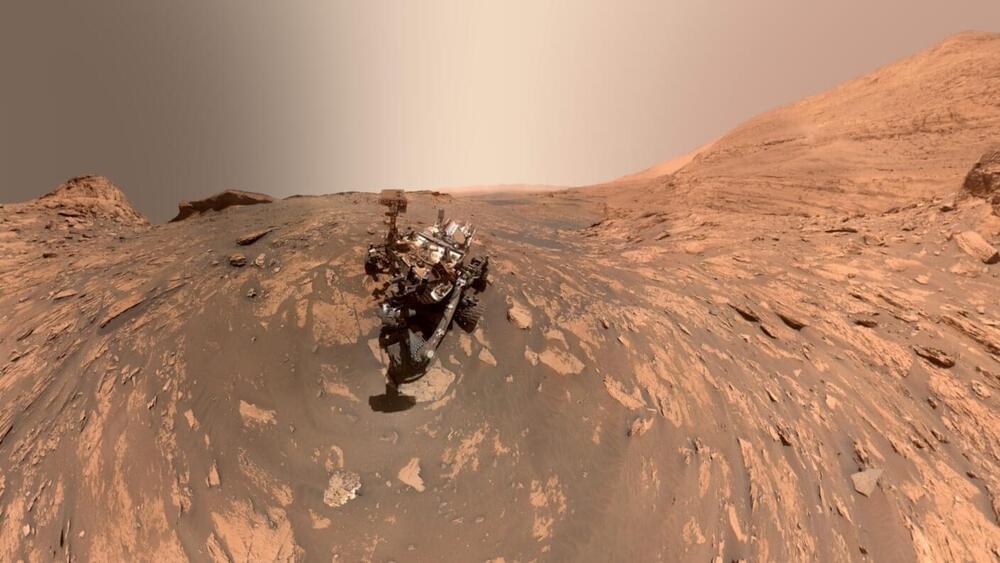
There’ve been plenty of proposals for how astronauts might produce the essentials, but until recently no technology had been field tested. Now, thanks to a machine called MOXIE, built by MIT and stowed away on NASA’s Perseverance rover, we can definitively say humans will be able to make oxygen on Mars.