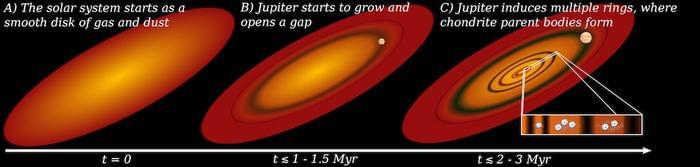
How did Jupiter’s formation shape the solar system, and specifically Earth’s orbit? This is what a recent study published in Science Advances h | Space
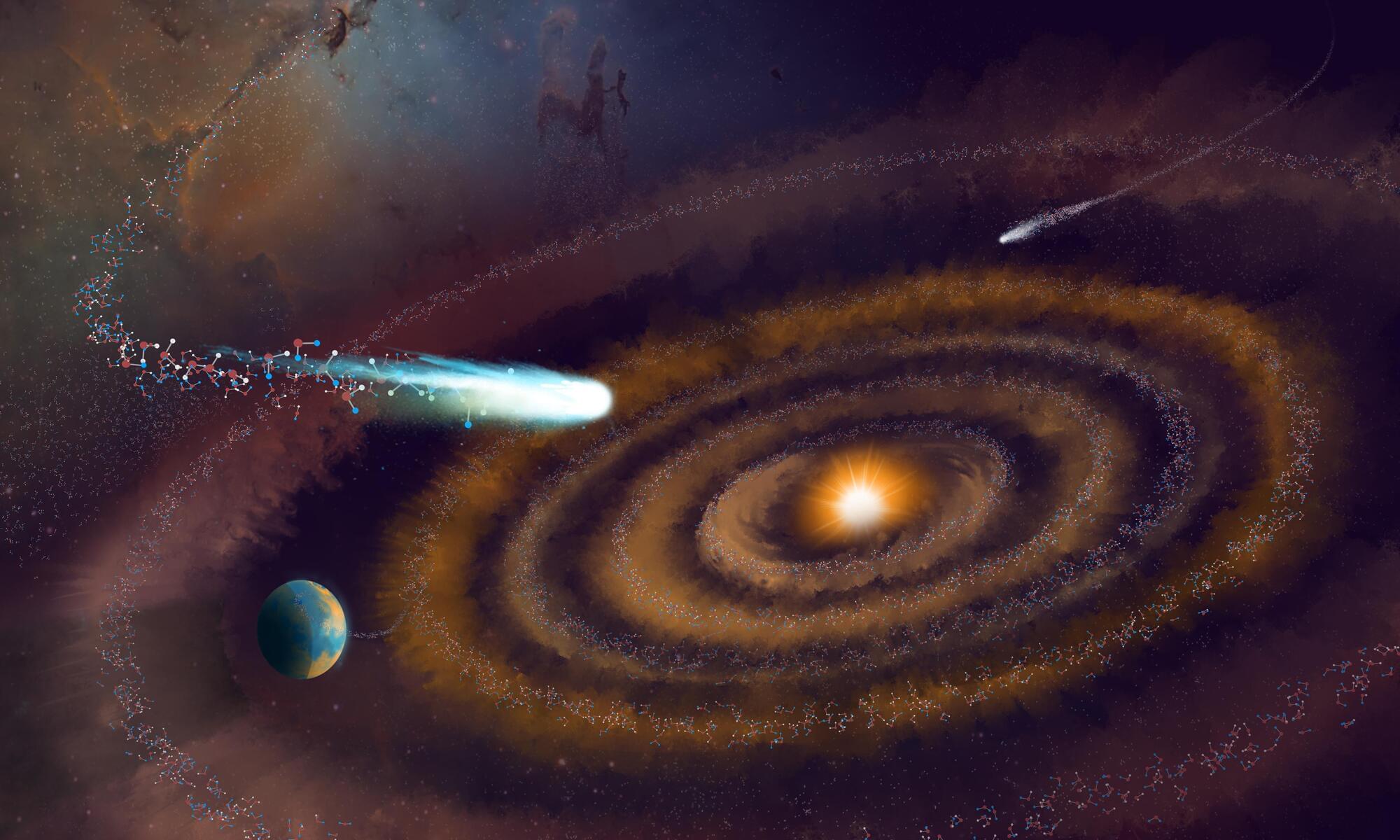


The discovery of ancient water in a planet-forming disk reveals that some of the water found in comets—and maybe even Earth—is older than the disk’s star itself, offering breakthrough insights into the history of water in our solar system.
Astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) have made a first-ever detection of doubly deuterated water (D₂O, or “heavy water”) in a planet-forming disk around V883 Ori, a young star. This means that the water in this disk, and by extension the water in comets that form here, predates the birth of the star itself, having journeyed through space from ancient molecular clouds long before this solar system formed.
The research is published in the journal Nature Astronomy.

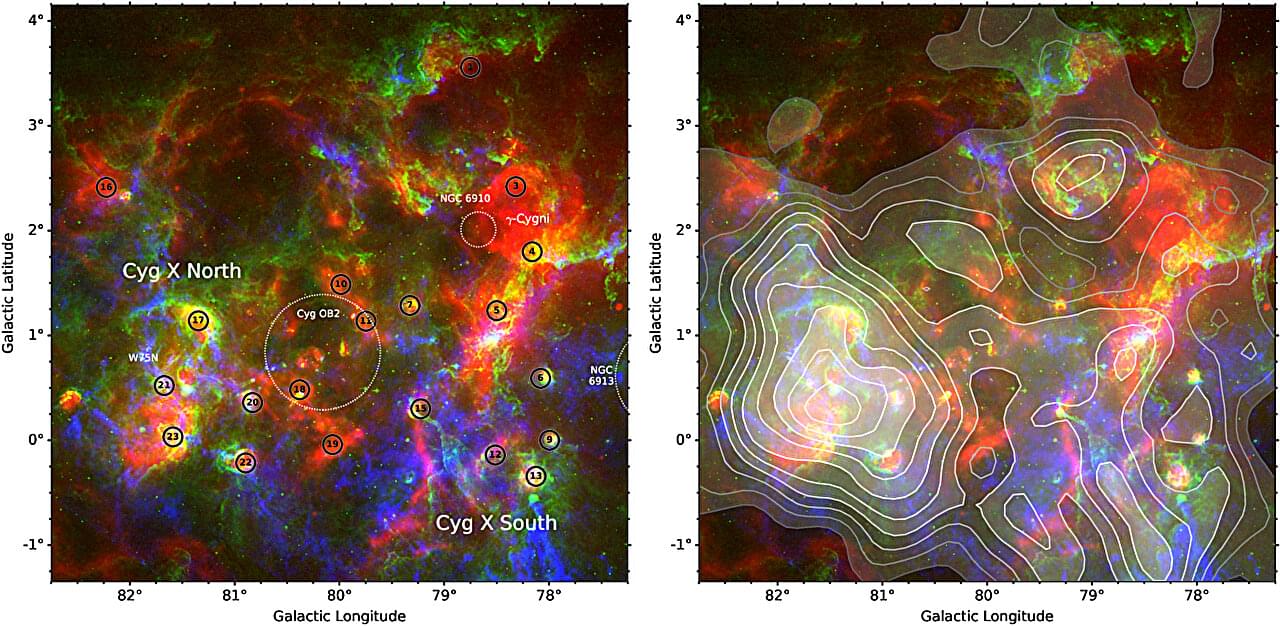
An international team of astronomers has created the first-ever large-scale maps of a mysterious form of matter, known as CO-dark molecular gas, in one of our Milky Way’s most active star-forming neighborhoods, Cygnus X. Their findings, using the Green Bank Telescope (GBT), are providing crucial new clues about how stars formed in the Milky Way.
While the technology of nuclear batteries has been available since the 1950s, today’s drive to electrify and decarbonize increases the impetus to find emission-free power sources and reliable energy storage. As a result, innovations are bringing renewed focus to nuclear energy in batteries.
Nuclear batteries — those using the natural decay of radioactive material to create an electric current — have been used in space applications or remote operations such as arctic lighthouses, where changing a battery is difficult or even impossible. The Mars Science Laboratory rover, for example, uses radioisotopic power systems (RPS), which convert heat from radioactive decay into electricity via a thermoelectric generator. Betavolt’s innovation, 3, is a betavoltaic battery that uses beta particles rather than heat as its energy source. (Probably a repost from March 11 2024)
There are additional challenges that hinder the wider usage of these and all types of nuclear batteries, particularly material supply and discomfort with the use of radioactive materials. Yet, the physical and materials science behind this technology could unlock important advances for CO2-free energy and provide power for applications where currently available energy storage technologies are insufficient.
How do betavoltaic batteries work?
Betavoltaic batteries contain radioactive emitters and semiconductor absorbers. As the emitter material naturally decays, it releases beta particles, or high-speed electrons, which strike the absorber material in the battery, separating electrons from atomic nuclei in the semiconductor absorber. Separation of the resulting electron-hole pairs generates an electric current in the absorber, resulting in electrical power that can be delivered by the battery.
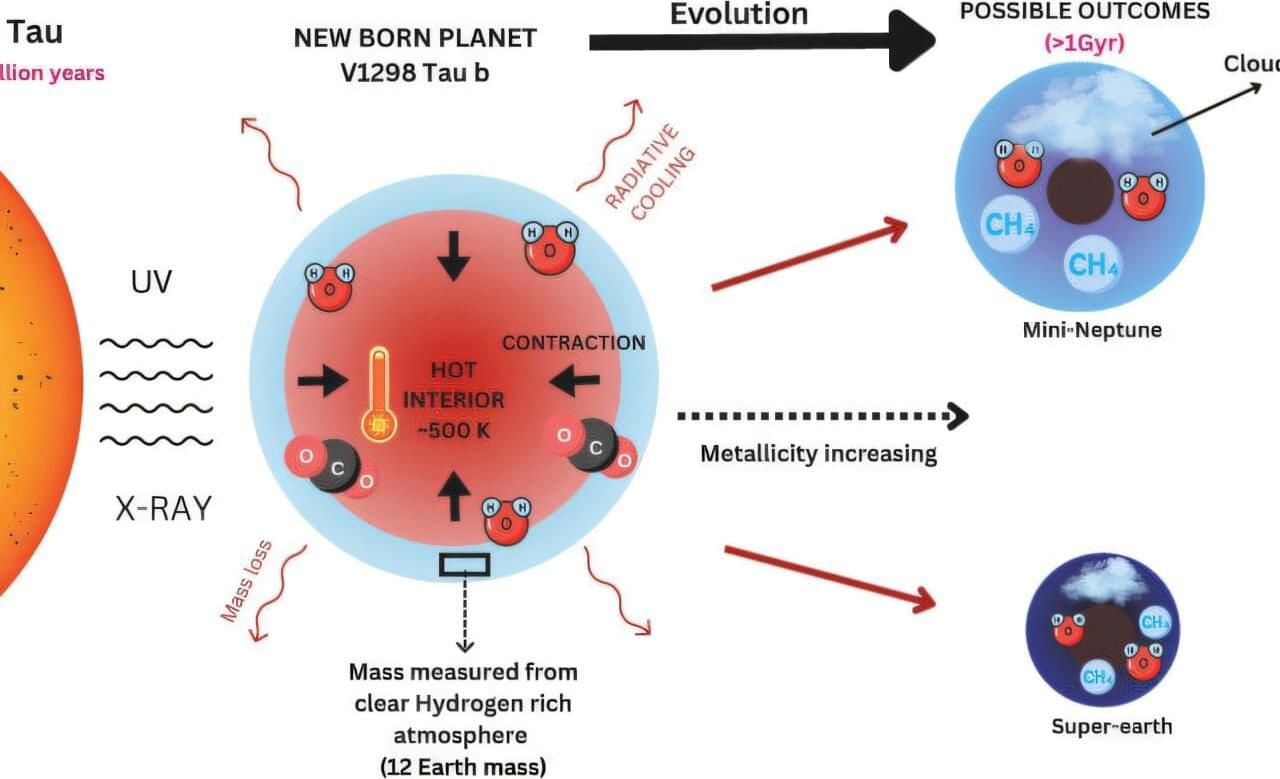
Astronomers have characterized the atmosphere of a young (20 Myr old) transiting exoplanet and found it to be unusually clear and puffy. By analyzing the planet’s atmospheric features, they were able to precisely measure the planet’s mass surpassing traditional dynamical techniques like radial velocity, which poorly perform with such active young stars. They found that V1298 Tau b is a proto-sub-Neptune, still hot and inflated from its recent formation.
The team, led by Saugata Barat (MIT, MA, US) and his Ph.D. supervisor Jean-Michel Désert (UvA, Netherlands) used the James Webb Space Telescope to study the very young planet, and their results are accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal and currently available on the preprint server arXiv.
V1298 Tau b is just 10 to 30 million years old and has an unusually clear and puffy atmosphere. The astronomers detected strong absorption signals from molecules like water vapor, methane, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and even hints of complex photochemical processes, such as tentative detections of sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and carbonyl sulfide (OCS).
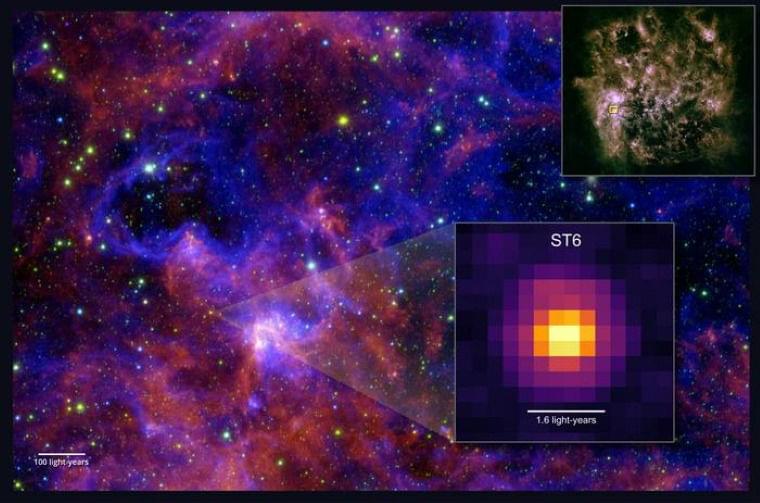
In a breakthrough first, University of Maryland scientists using the James Webb Space Telescope have announced the detection of large, complex, organic molecules beyond the Milky Way.
Often called “seeds of life” because these molecules make up the lifeforms found on Earth, the discovery was made within frozen ice particles around a young protostar, ST6, forming in a distant galaxy.
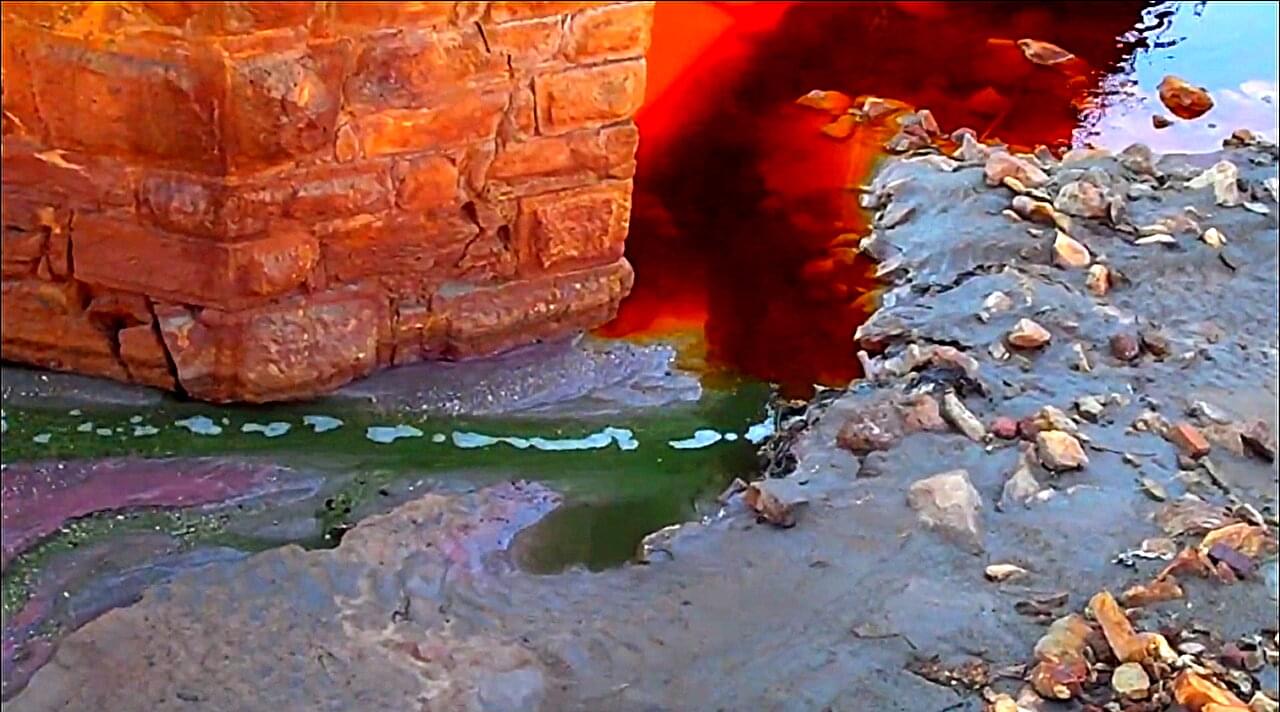

Because oxygen-bearing sulfate minerals trap and preserve signals from Earth’s atmosphere, scientists closely study how they form. Sulfates are stable over billions of years, so their oxygen isotopes are seen as a time capsule, reflecting atmospheric conditions while they were evolving on early Earth—and possibly on its planetary neighbor Mars.
A new study led by a University of Utah geochemist examines how sulfate forms when pyrite, commonly known as “fool’s gold,” is oxidized in environments teeming with microbes versus those without them. The researchers focused on Spain’s Rio Tinto, a contaminated river passing through a region where iron and copper were mined for thousands of years.
The paper titled, “Triple-oxygen isotopic evidence of prolonged direct bioleaching of pyrite with O2,” appears in Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
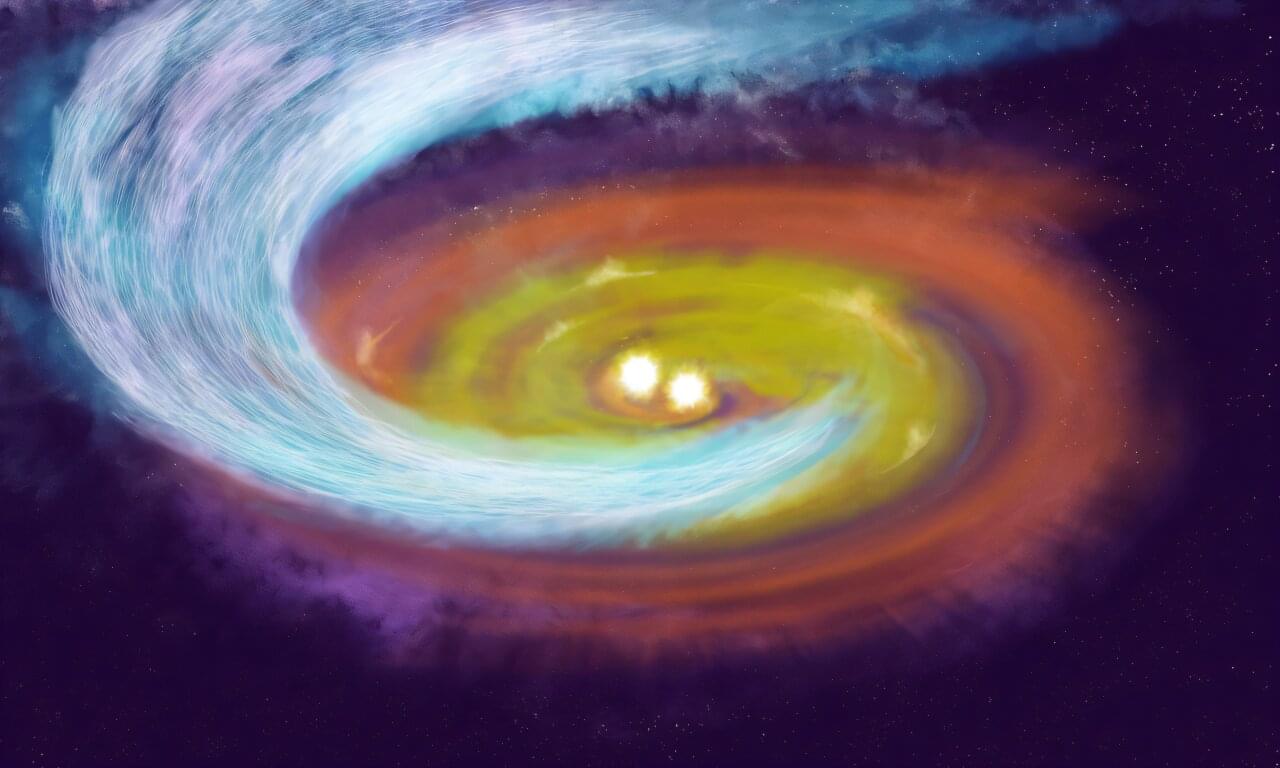

A team of astronomers led by Paulo Cortes, a scientist with the U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory and the Joint ALMA Observatory, have made a groundbreaking discovery about how young star systems grow.
Using the powerful Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), their team observed— for the first time ever— a narrow, spiral-shaped streamer of gas guided by magnetic fields, channeling matter from the surrounding cloud of a star-forming region in Perseus, directly onto a newborn binary star system.
The work is published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
