The minimum distance between Mars and Earth is about 34 million miles, according to NASA.

One of the most basic assumptions of fundamental physics is that the different properties of mass—weight, inertia and gravitation—always remain the same in relation to each other. Without this equivalence, Einstein’s theory of relativity would be contradicted and our current physics textbooks would have to be rewritten. Although all measurements to date confirm the equivalence principle, quantum theory postulates that there should be a violation.
This inconsistency between Einstein’s gravitational theory and modern quantum theory is the reason why ever more precise tests of the equivalence principle are particularly important. A team from the Center of Applied Space Technology and Microgravity (ZARM) at University of Bremen, in collaboration with the Institute of Geodesy (IfE) at Leibniz University Hannover, has now succeeded in proving with 100 times greater accuracy that passive gravitational mass and active gravitational mass are always equivalent—regardless of the particular composition of the respective masses.
The research was conducted within the framework of the Cluster of Excellence “QuantumFrontiers.” Today, the team published their findings as a highlights article in Physical Review Letters.
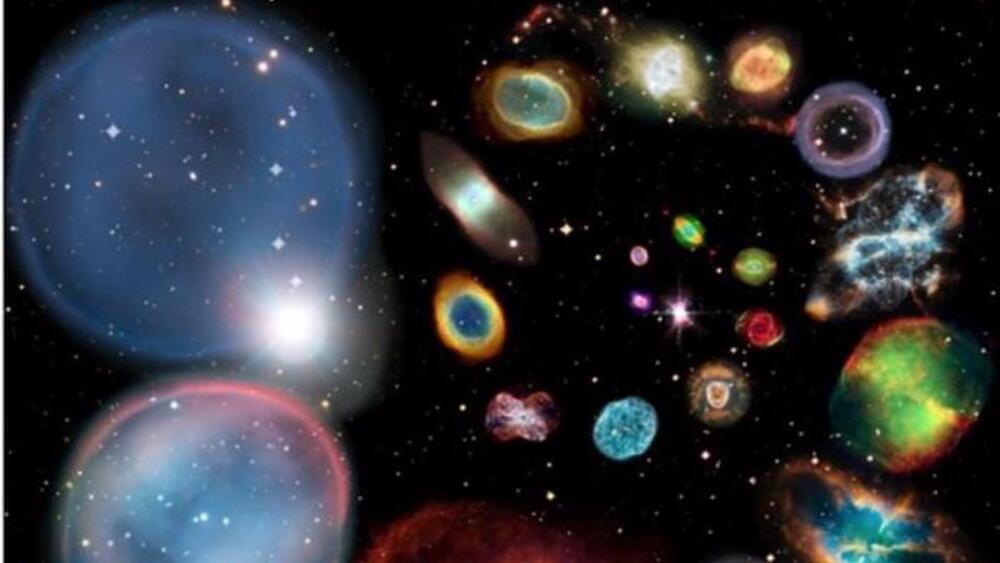

Planetary nebulae are created by the gas “ghost” clouds expelled by the dying stars, finds study.
Back in 2013, Bryan Rees of the University of Manchester discovered the unusual alignment of stars at the galactic center of the Milky Way galaxy.
Rees discovered elongated planetary nebulae in the Milky Way’s center that appear to lay parallel to the plane of the galactic bulge — hinting at undiscovered underlying phenomena.
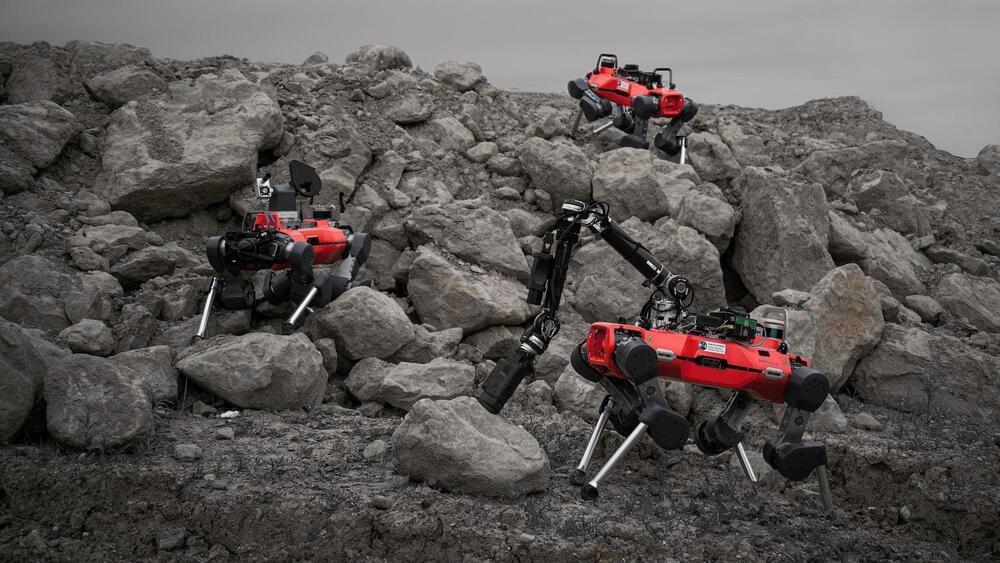

A team of robots would still be able to complete a mission if one or two of the machines malfunction.
Swiss researchers led by ETH Zurich are exploring the possibility of sending an interconnected team of walking and flying exploration robots to the Moon, a press statement reveals.
In recent tests, the researchers equipped three ANYmal robots with scientific instruments to test whether they would be suitable for lunar exploitation.

BENGALURU, July 13 (Reuters) — Tesla (TSLA.O) is discussing an investment proposal with the Indian government to set up a factory with an annual capacity to produce about half a million electric vehicles, the Times of India reported on Thursday, citing government sources.
The company, led by billionaire Elon Musk, is also looking at using India as an export base to ship cars to countries in the Indo-Pacific region, the report said.
The starting price for the vehicles will be 2 million rupees ($24,400.66), the report added, which is more than double of India’s cheapest EV, MG Comet, and half a million costlier than Tata Nexon EV, the top-selling electric car in the country.
The Webb Space Telescope is marking one year of cosmic photographs with one of its best yet: the dramatic close-up of dozens of stars at the moment of birth.
NASA unveiled the latest snapshot Wednesday, revealing 50 baby stars in a cloud complex 390 light-years away. A light-year is nearly 6 trillion miles (9.7 trillion kilometers).
The region is relatively small and quiet yet full of illuminated gases, jets of hydrogen and even dense cocoons of dust with the delicate beginnings of even more stars.

The scientific community has discovered a new planet. It is located 245 light-years away from Earth and has been named TOI-733b. Its size is slightly less than twice the radius of Earth. It has a unique feature: its atmosphere. For now, experts have presented two possibilities. The first is that it may have lost its atmosphere layer. The second is that it could be a “highly irradiated oceanic world.”
This is stated in a study published by the specialized astronomy journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. In the study, it is detailed that this new planet has a density of 3.98 grams per cubic centimeter. To give an idea, it is slightly lower than Earth’s density, which is 5.51 grams per cubic centimeter, but higher than that of our neighbor Mars.
Another point mentioned in the Astronomy & Astrophysics article is that this planet orbits a star slightly smaller than the Sun and completes its orbit in a total of 4.9 days. It is this proximity to the star that serves as an explanation for the first of the two scenarios that scientists have proposed regarding its atmosphere.
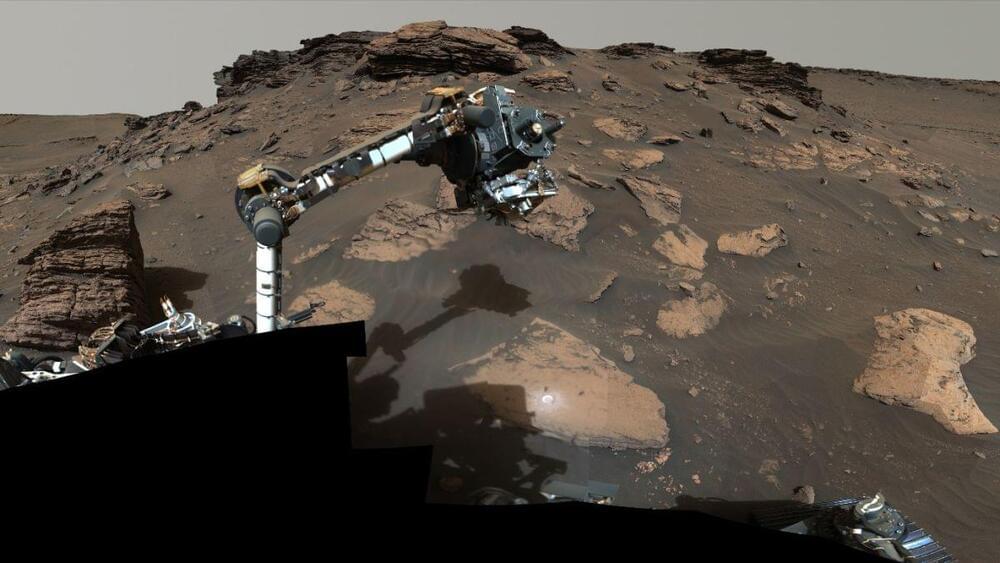

NASA’s Perseverance rover has found a diverse menagerie of organic molecules in a Martian crater, a new study reports.
Organic compounds are molecules composed of carbon, and often include other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur. Previously, scientists had detected several types of organic molecules of Martian origin — in meteorites blasted off Mars by cosmic impacts that landed on Earth, and in Gale Crater on the Red Planet, which NASA’s Curiosity rover has been exploring since 2012.
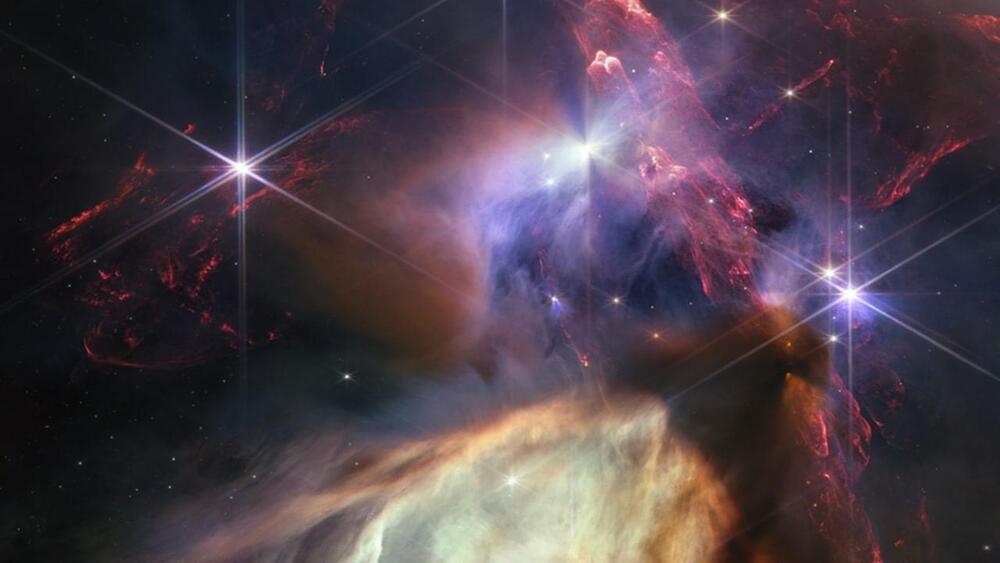


To celebrate the completion of the James Webb Space Telescope’s first year of science operations, NASA has released a close-up image of the birth of sun-like stars.
The image, captured on Webb’s telescope is a small star-forming region in the Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex – the nearest star-forming region to Earth.
The region’s proximity at 390 light-years allows for a highly detailed close-up, with no foreground stars in the intervening space.