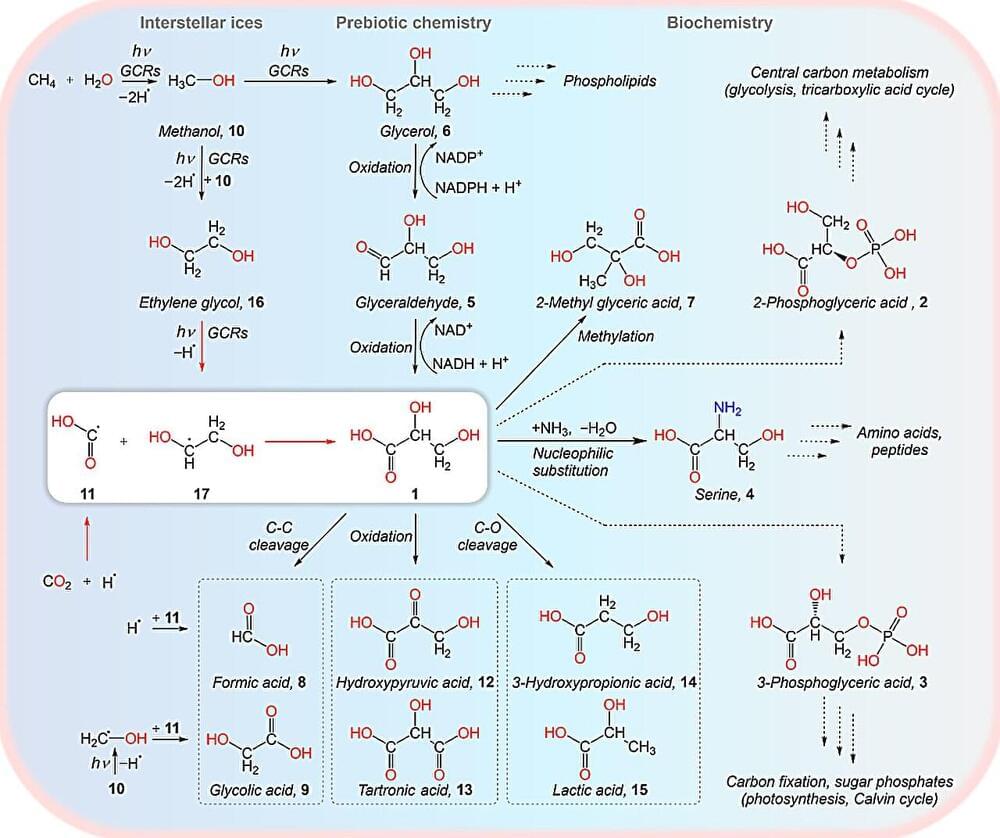
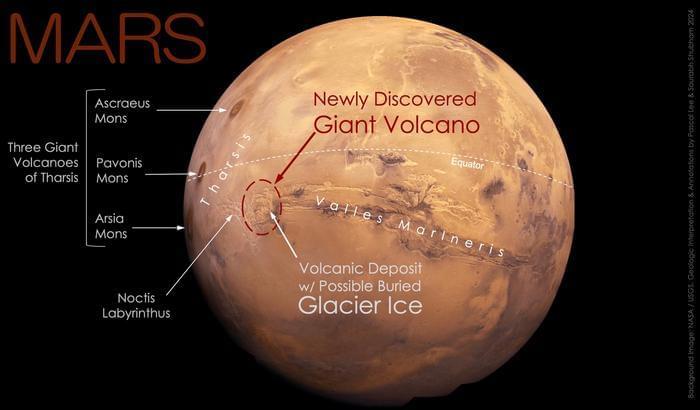
Sourabh Shubham: “This area of Mars is known to have a wide variety of hydrated minerals spanning a long stretch of Martian history. A volcanic setting for these minerals had long been suspected. So, it may not be too surprising to find a volcano here. In some sense, this large volcano is a long-sought ‘smoking gun’.”
The planet Mars is known for its vast array of inactive shield volcanoes, and a new volcano could be added to the family with a recent study presented at the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, as a team of researchers announced the discovery of a massive volcano on Mars that is buried underneath the surface and could even possess a base comprised of glacier ice. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand past volcanism and glaciation on the Red Planet that could provide clues to Mars’ geologic history.
For the study, the researchers used images from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera and data from the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM), which are both onboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), along with data from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) that was onboard the Mars Global Surveyor to analyze “Noctis Mons” (official name pending), which is located southeast of Mars’ Tharsis volcanic region and in the western region of Valles Marineris, known as the largest and deepest canyon in the solar system.